气候变化研究进展 ›› 2021, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 525-536.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.193
气候变化对城市年径流总量控制率分区的影响
- 江苏省气候中心,南京 210008
-
收稿日期:2020-08-31修回日期:2020-11-02出版日期:2021-09-30发布日期:2021-09-28 -
作者简介:陈燕,女,正研级高级工程师,chenyan_willow@163.com -
基金资助:国家重点基础研究发展计划“多源数据的不确定性对全球变化认知的影响”(2016YFA0600303);中国气象局气候变化专项“江苏降水
Influence of climate change on the volume capture ratio of annual rainfall’s partition
CHEN Yan( ), HUI Pin-Hong, ZHOU Xue-Dong, YANG Jie
), HUI Pin-Hong, ZHOU Xue-Dong, YANG Jie
- Jiangsu Provincial Climate Center, Nanjing 210008, China
-
Received:2020-08-31Revised:2020-11-02Online:2021-09-30Published:2021-09-28
摘要:
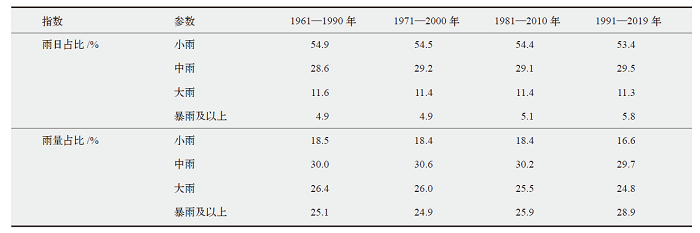
城市地区强降水发生频次和强度的增加容易诱发内涝现象,年径流总量控制率作为海绵城市的重要设计参数,更是直接受到降水变化的影响。以江苏省为例,利用全省70个国家级气象观测站1961—2019年最新的日降水量资料评估了气候变化对城市年径流总量控制率分区的影响。研究发现,有效降水的年代际变化十分明显,1991—2019年降水日数、降水量、降水强度均比其他时间段上更多、更强;太湖流域的设计雨量较小,连云港地区的设计雨量较大,南北差异随着控制率的提高而扩大,当控制率为85%时,全省设计雨量平均值为38.1 mm,最大值是最小值的1.7倍;气候变化对年径流总量控制率分区影响明显,江苏的苏南、江淮南部大部分地区的分区变大,导致全省IV区所占面积明显增加。不同等级降水的变化趋势是影响年径流控制率分区的关键因素,大雨以上的雨日、雨量在有效降水中占比增加,则分区变大。
引用本文
陈燕, 惠品宏, 周学东, 杨杰. 气候变化对城市年径流总量控制率分区的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 525-536.
CHEN Yan, HUI Pin-Hong, ZHOU Xue-Dong, YANG Jie. Influence of climate change on the volume capture ratio of annual rainfall’s partition[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(5): 525-536.

图2 1961—2019年有效降水分布特征(a)年平均降水量,(c)年平均降水日数,(e)年平均降水强度及其变化趋势(b,d,f)
Fig. 2 The spatial distribution of effective precipitation in 1961-2019 (a) average annual precipitation, (c) average annual precipitation days, (e) average annual precipitation intensity, and their trends (b, d, f)
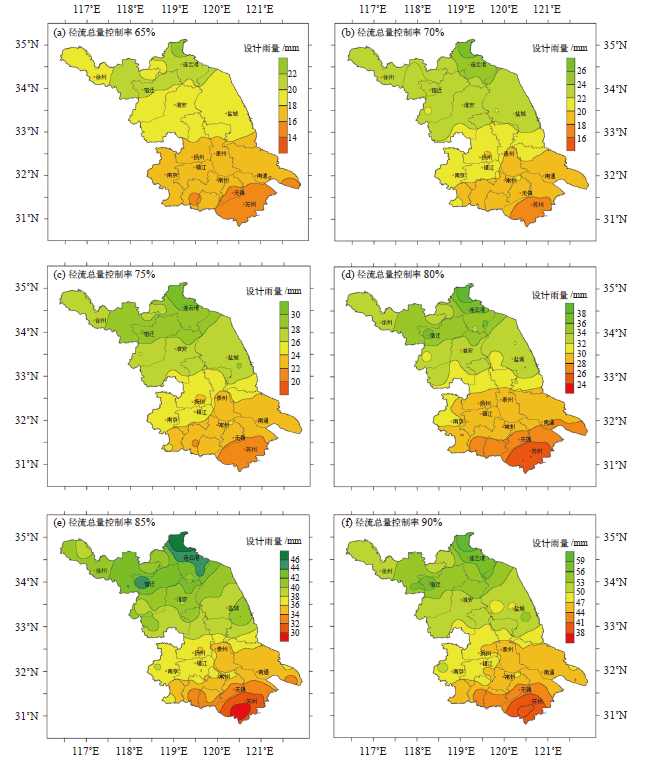
图3 1961—2019年不同年径流总量控制率的设计雨量分布特征(a) 65%,(b) 70%,(c) 75%,(d) 80%,(e) 85%,(f) 90%
Fig. 3 Spatial distribution of design rainfall depth of different volume capture ratio of annual rainfall during 1961-2019 (a) 65%, (b) 70%, (c) 75%, (d) 80%, (e) 85%, and (f) 90%
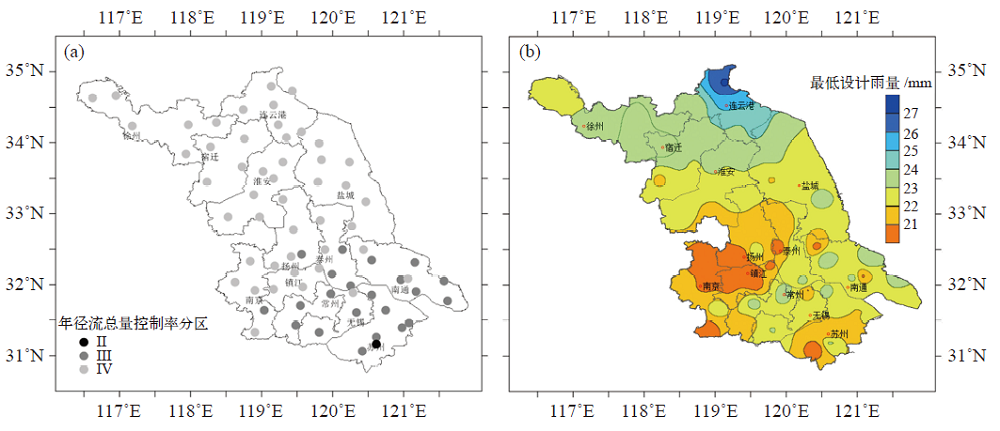
图5 1961—2019年径流总量控制率分区(a)和最低设计雨量(b)
Fig. 5 Spatial distribution of the volume capture ratio of annual rainfall’s partition (a) and the minimum design rainfall depth (b) in 1961-2019
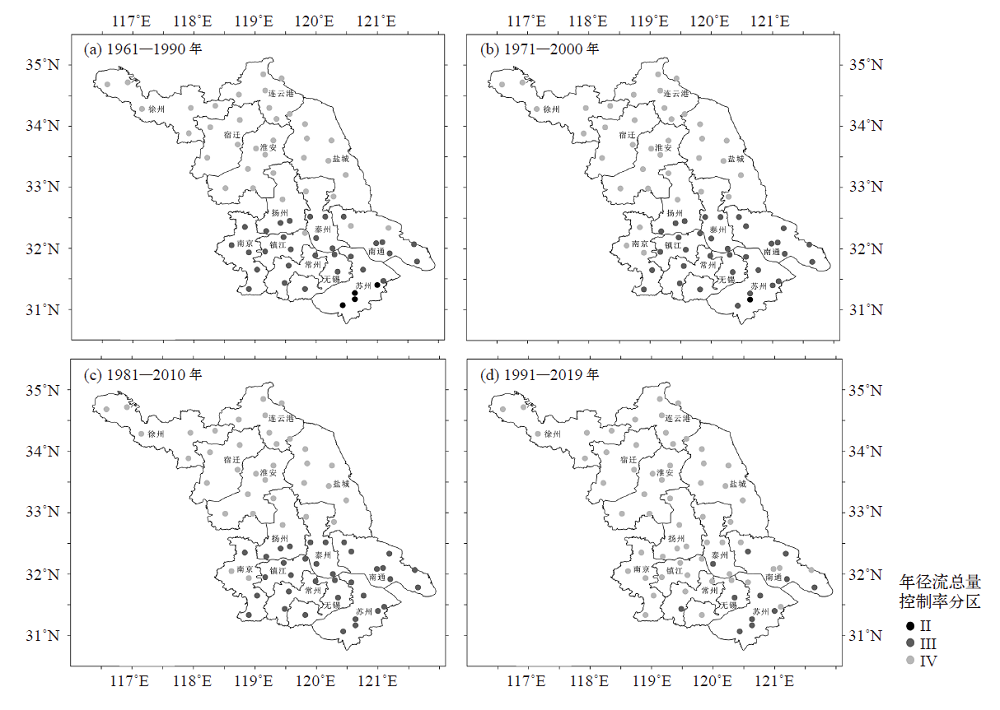
图6 年径流总量控制率分区(a) 1961—1990年,(b) 1971—2000年,(c) 1981—2010年和(d) 1991—2019年
Fig. 6 Spatial distribution of the volume capture ratio of annual rainfall’s partition (a) 1961-1990, (b) 1971-2000, (c) 1981-2010,and (d) 1991-2019
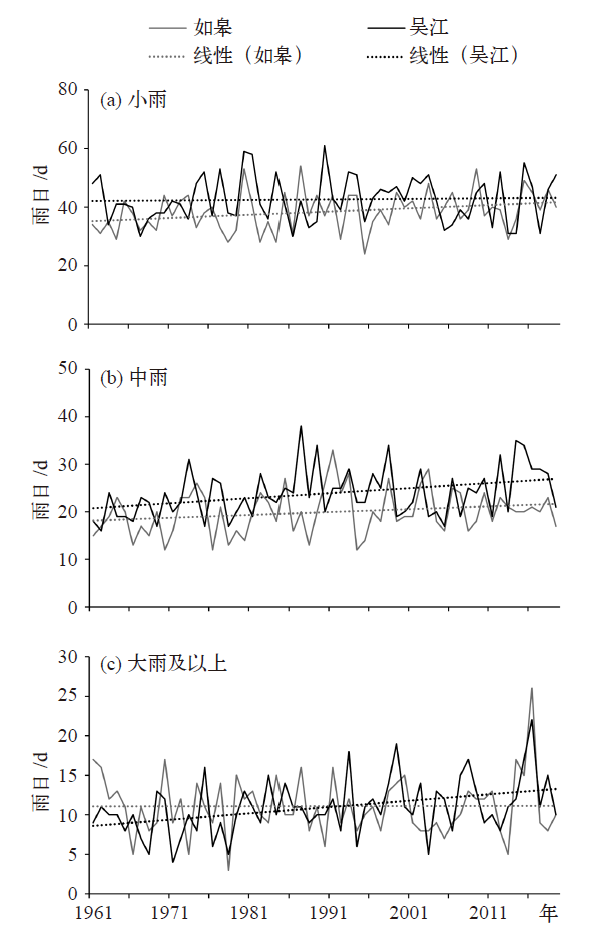
图7 1961—2019年如皋和吴江不同等级降水日数变化(a)小雨,(b)中雨,(c)大雨及以上
Fig. 7 Variations of precipitation days in different grades of Rugao and Wujiang during 1961-2019 (a) rainy, (b) medium rain, (c) heavy rain or above
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014 |
| [2] |
Karl T R, Knight R W, Plummer N. Trends in high-frequency climate variability in the twentieth century[J]. Nature, 1995, 377:217-220
doi: 10.1038/377217a0 URL |
| [3] |
Osborn T J, Hulme M, Jones P D, et al. Observed trends in the daily intensity of United Kingdom precipitation[J]. International Journal Climatology, 2000, 20:347-364
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0088 URL |
| [4] |
Groisman P, Karl T, Easterling D, et al. Changes in the probability of extreme precipitation: important indicators of climate change[J]. Climatic Change, 1999, 42:243-283
doi: 10.1023/A:1005432803188 URL |
| [5] |
Kitoh A, Hosaka M, Adachi Y. Future projections of precipitation characteristics in East Asia simulated by the MRI CGCM2[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2005, 22(4):467-478
doi: 10.1007/BF02918481 URL |
| [6] | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 海绵城市建设技术指南: 低影响开发雨水系统构建(试行)[EB/OL]. 2014 [2020-01-20]. http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/201411/t20141102_219465.html. |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban and Rural Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Sponge city construction technical guide: low impact development rainwater system construction (Trial)[EB/OL]. 2014 [2020-01-20]. http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/201411/t20141102_219465.html(in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 任心欣, 汤伟真. 海绵城市年径流总量控制率等指标应用初探[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(13):105-109. |
| Ren X X, Tang W Z. Application of capture ratio of total annual runoff volume in spongy city[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2015, 31(13):105-109 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 周广胜, 何奇瑾. 城市内涝防治需充分预估气候变化的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(16):4961-4964. |
| Zhou G S, He Q J. Impact of climate change should be fully predicted in urban waterlogging control[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(16):4961-4964 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 夏军, 石卫, 雒新萍, 等. 气候变化下水资源脆弱性的适应性管理新认识[J]. 水科学进展, 2015, 26(2):279-286. |
| Xia J, Shi W, Luo X P, et al. Revisions on water resources vulnerability and adaption measures under climate change[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2015, 26(2):279-286 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 张建云, 王银堂, 胡庆芳, 等. 海绵城市建设有关问题讨论[J]. 水科学进展, 2016, 27(6):793-799. |
| Zhang J Y, Wang Y T, Hu Q F, et al. Discussion and views on some issues of the sponge city construction in China[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2016, 27(6):793-799 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 杨金虎, 江志红, 王鹏祥, 等. 中国年极端降水事件的时空分布特征[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2008, 13(1):75-83. |
| Yang J H, Jiang Z H, Wang P X, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristic of extreme precipitation event in China[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2008, 13(1):75-83 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 何书樵, 郑有飞, 尹继福. 近50年长江中下游地区降水特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(7):1187-1192. |
| He S Q, Zheng Y F, Yin J F. Analysis on precipitation characteristics over middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River in the last 50 years[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 22(7):1187-1192 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 贺冰蕊, 翟盘茂. 中国1961—2016年夏季持续和非持续性极端降水的变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5):437-444. |
| He B R, Zhai P M. Characteristics of the persistent and non-persistent extreme precipitation in China from 1961 to 2016[J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(5):437-444 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 梅伟, 杨修群. 我国长江中下游地区降水变化趋势分析[J]. 南京大学学报: 自然科学, 2005, 41(6):577-589. |
| Mei W, Yang X Q. Trends of precipitation variations in the mid-lower Yangtze River valley of China[J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Sciences, 2005, 41(6):577-589 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 叶殿秀, 王遵娅, 高荣, 等. 1961—2016年我国区域性暴雨过程的客观识别及其气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(6):575-583. |
| Ye D X, Wang Z Y, Gao R, et al. Objective identification and climatic characters of the regional rainstorm event in China from 1961 to 2016[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(6):575-583 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 张峻, 张艺玄. 长江中下游地区近60 a降水变化规律研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2019, 38(3):259-266. |
| Zhang J, Zhang Y X. Study on the variation of precipitation in the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River in recent 60 years[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2019, 38(3):259-266 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 潘欣, 尹义星, 王小军. 1960—2010年长江流域极端降水的时空演变及未来趋势[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2017, 3:436-444. |
| Pan X, Yin Y X, Wang X J. Spatio-temporal characteristics and future trend of extreme precipitation in the Yangtze River basin during 1960 to 2010[J]. Resources and Environment in The Yangtze Basin, 2017, 3:436-444 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 李俊奇, 林翔. 极端降雨事件对雨水年径流总量控制率和24 h降雨场次控制率的影响规律探析[J]. 给水排水, 2018, 44(1):21-26. |
| Li J Q, Lin X. The influence of extreme rainfall events on the total annual runoff control rate of rainwater and the 24 h rainfall control rate[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2018, 44(1):21-26 (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 张质明, 胡蓓蓓, 李俊奇, 等. 中国日降雨空间变化对雨水径流源头总量控制的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 2018, 29(4):465-472. |
| Zhang Z M, Hu B B, Li J Q, et al. Influence of spatial variation in daily rainfall on volume capture of rainfall by source control facilities in China[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(4):465-472 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 庞璇, 张永勇, 潘兴瑶, 等. 城市雨洪模拟与年径流总量控制目标评估: 以北京市未来科技城为例[J]. 资源科学, 2019, 41(4):803-813. |
| Pang X, Zhang Y Y, Pan X Y, et al. Urban storm water simulation and assessment of the control rate of total annual runoff: a case of the future science and technology park in Beijing[J]. Resources Science, 2019, 41(4):803-813 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 成丹, 陈正洪. 湖北宜昌市区暴雨雨型的演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(2):225-231. |
| Cheng D, Chen Z H. Evolution characteristics of rainstorm hyetograph in Yichang of Hubei province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(2):225-231 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 顾正强, 龚强, 晁华, 等. 辽宁省海绵城市建设中年径流总量控制率分区及其分布差异研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2019, 35(1):59-65. |
| Gu Z Q, Gong Q, Chao H, et al. Analysis of the regional division of volume capture ratio of annual rainfall runoff and its spatial variation in sponge city construction in Liaoning province[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(1):59-65 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 王文亮, 李俊奇, 车伍, 等. 海绵城市建设指南解读之城市径流总量控制指标[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(8):18-23. |
| Wang W L, Li J Q, Che W, et al. Explanation of sponge city development technical guide: planning index for urban total runoff volume capture[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2015, 31(8):18-23 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] |
Mann H B. Nonparametric tests against trend[J]. Econometrica, 1945, 13(3):245-259
doi: 10.2307/1907187 URL |
| [25] | Kendall M G. Rank correlation methods[J]. British Journal of Psychology, 1955, 25(1):86-91 |
| [26] | 杜尧, 陈启慧, 和鹏飞, 等. 南京地区暴雨变化特性分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2019, 35(6):89-94. |
| Du Y, Chen Q H, He P F, et al. Analysis of rainstorm variation characteristics in Nanjing region[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2019, 35(6):89-94 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 姚建群. 连续小波变换在上海近100年降水分析中的应用[J]. 气象, 2001, 27(2):20-24. |
| Yao J Q. An application of continuous wavelet transforms to precipitation analysis in Shanghai during one hundred years[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2001, 27(2):20-24 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 姜晓艳, 刘树华, 马明敏, 等. 东北地区近百年降水时间序列变化规律的小波分析[J]. 地理研究, 2009, 28(2):354-362. |
| Jiang X Y, Liu S H, Ma M M, et al. A wavelet analysis of the precipitation time series in Northeast China during the last 100 years[J]. Geographical Research, 2009, 28(2):354-362 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 朱继前, 韩美, 徐泽华, 等. 淮河流域不同量级降雨时空分布特征及其影响影响因素[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(4):87-95. |
| Zhu J Q, Han M, Xu Z H, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution characteristics and factors of different magnitude rainfall in Huaihe River basin[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(4):87-95 (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 李俊奇, 王文亮, 车伍, 等. 海绵城市建设指南解读之降雨径流总量控制目标区域划分[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(8):6-12. |
| Li J Q, Wang W L, Che W, et al. Explanation of sponge city development technical guide: regional division for total rainfall runoff volume capture target[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2015, 31(8):6-12 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 吴燕汶, 晏红明, 史正涛, 舒康宁. 昆明强降水对城市化和热环境变化的响应研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 723-737. |
| [2] | 方佳毅, 殷杰, 石先武, 方建, 杜士强, 刘敏. 沿海地区复合洪水危险性研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(3): 317-328. |
| [3] | 丁裕国 李佳耘 江志红 余锦华. 极值统计理论的进展及其在气候变化研究中的应用[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2011, 7(4): 248-252. |
| [4] | 郭军;李明财;段丽瑶. 环渤海地区1961-2007年极端强降水时空变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(05): 319-324. |
| [5] | 李威;翟盘茂. 中国极端强降水日数与ENSO的关系[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2009, 5(06): 336-342. |
| [6] | 余卫东 柳俊高 常军 王纪军. 1957-2005年河南省降水和温度极端事件变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(002): 78-083. |
| [7] | 苏布达;姜彤;任国玉;陈正洪. 长江流域极端降水时空分布和趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2006, 02(01): 9-14. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||