中国气候变化检测归因研究进展
Progress in climate change detection and attribution studies in China
中国气候变化检测归因研究进展 |
| 孙颖, 王东阡, 张学斌 |
|
Progress in climate change detection and attribution studies in China |
| SUN Ying, WANG Dong-Qian, ZHANG Xue-Bin |
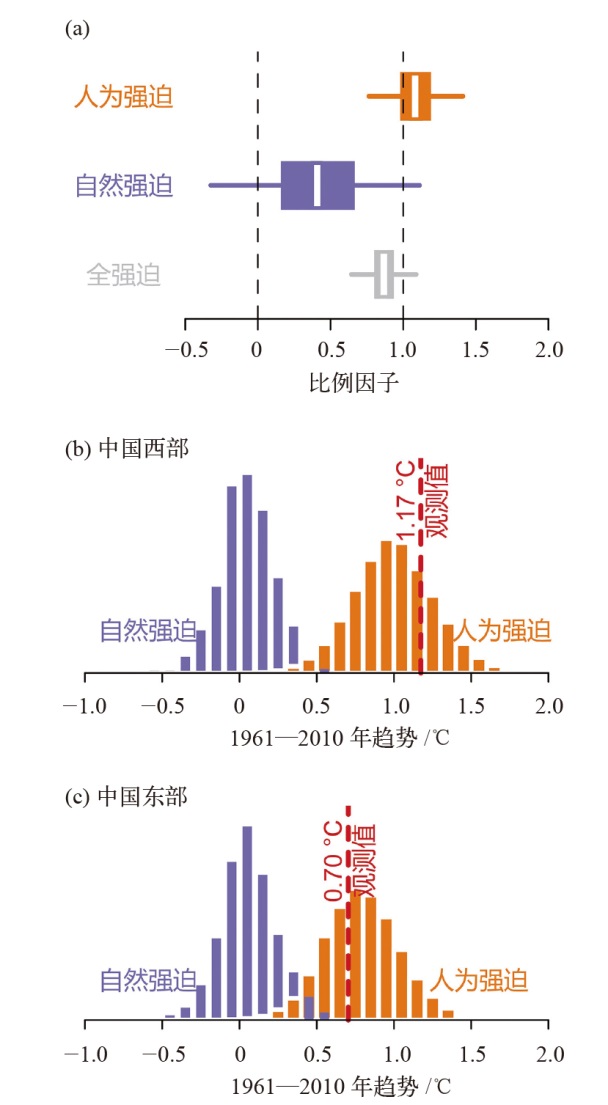
| 图5 中国夏季平均湿球温度全强迫(ALL)单信号和人为强迫(ANT)、自然强迫(NAT)双信号比例因子最佳估计及其25%~75%(箱型图)和5%~95%(横线)置信区间范围(a),中国西部地区(b)和东部地区(c)在人为辐射强迫(ANT,橙色)和自然强迫(NAT,蓝色)下1961—2010年夏季平均湿球温度概率密度分布[ |
| Fig. 5 Climatic conditions that are increasingly conducive to summer heat stress as measured by summer mean wet bulb globe temperature (WGBT) in China have human-induced origins: estimates of scaling factors for one-signal (ALL) and two-signal (ANT and NAT) ?ngerprint analyses (a). The white lines mark the scaling-factor best estimates. The width of the boxplot represents the 25%-75% un-certainty ranges of the scaling-factor estimates, and the whiskers extend to the 5%-95% uncertainties ranges. Also shown are trend histograms of the observation-constrained 1961-2010 summer mean WBGT in a climate with anthropogenic-only forcings (orange) and with natural-only forcings (blue) for western (b) and eastern (c) China. The observed trends are marked by vertical red lines[ |

|