中国气候变化检测归因研究进展
Progress in climate change detection and attribution studies in China
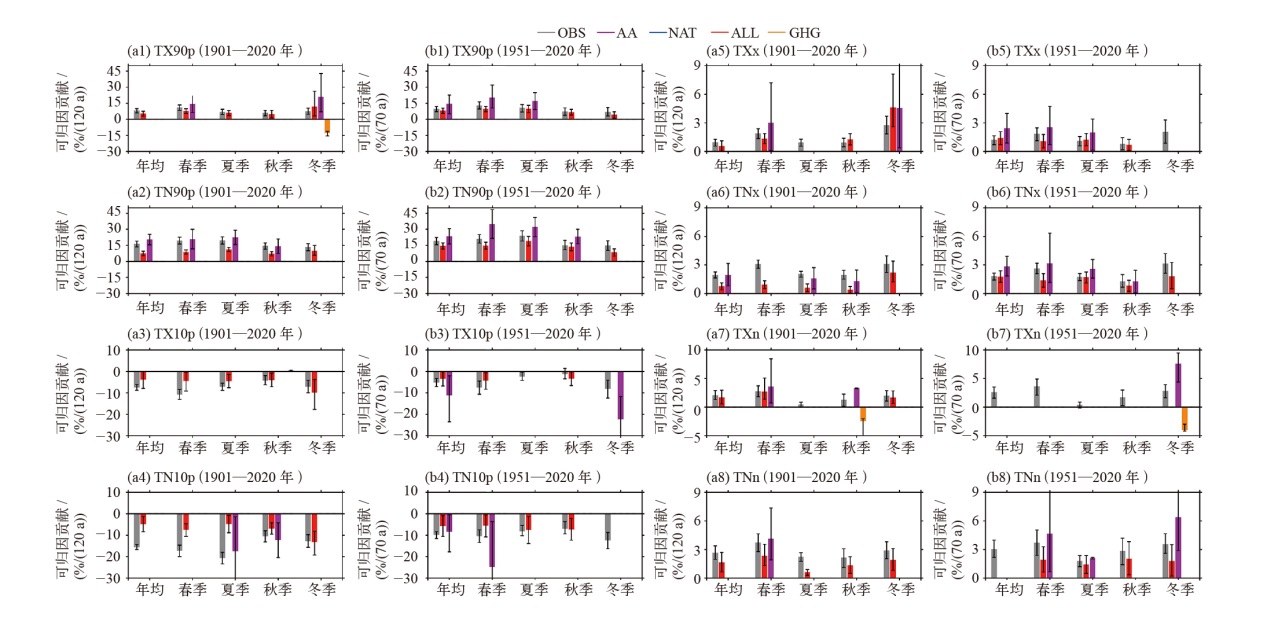
注:图中显示为观测到的极端温度变化趋势的最优估计(OBS)以及不同因子贡献的最优估计值,包括全强迫(ALL)、温室气体(GHG)、人为气溶胶(AA)和自然强迫(NAT),误差栏表示5%~95%的置信区间。
中国气候变化检测归因研究进展 |
| 孙颖, 王东阡, 张学斌 |
|
Progress in climate change detection and attribution studies in China |
| SUN Ying, WANG Dong-Qian, ZHANG Xue-Bin |
| 图3 基于中国东部(105°E以东)百年逐日观测和CMIP6模式资料的极端气温指标变化检测归因[ 注:图中显示为观测到的极端温度变化趋势的最优估计(OBS)以及不同因子贡献的最优估计值,包括全强迫(ALL)、温室气体(GHG)、人为气溶胶(AA)和自然强迫(NAT),误差栏表示5%~95%的置信区间。 |
| Fig. 3 Detection and attribution of changes in extreme temperature indices based on centennial observations and CMIP6 model data in eastern China. (The figure shows attributable trends to ALL, GHG, AA, and NAT signals compared with the observed trends (OBS) for annual and seasonal indices during 1901-2020 (a) and 1951-2020 (b))[ |

|