Climate Change Research ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (4): 492-502.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.237
• Greenhouse Gas Emissions • Previous Articles Next Articles
Economical analysis of vessels’ shore power usage
TAO Xue-Zong( ), WANG Qian-Yi, LI Han-Qing
), WANG Qian-Yi, LI Han-Qing
- College of Transport and Communications, Shanghai Maritime University, Shanghai 201306, China
-
Received:2021-10-09Revised:2021-12-15Online:2022-07-30Published:2022-02-09
Cite this article
TAO Xue-Zong, WANG Qian-Yi, LI Han-Qing. Economical analysis of vessels’ shore power usage[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(4): 492-502.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.237
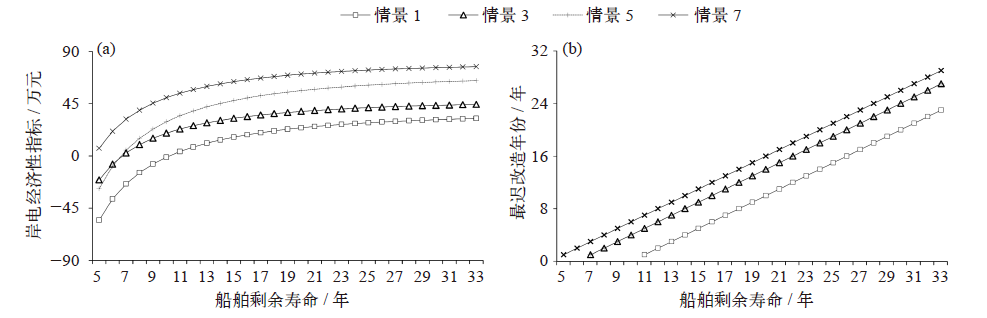
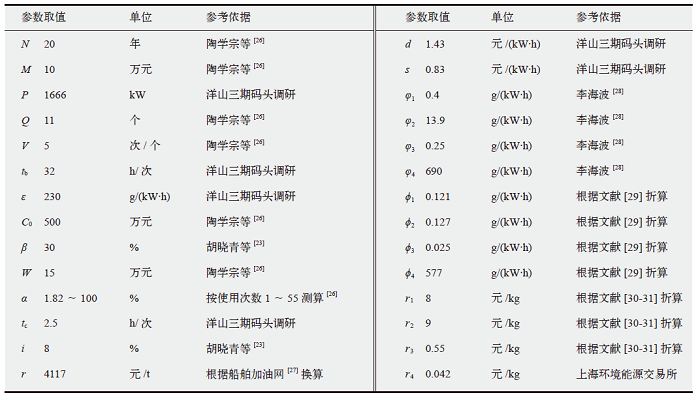
Fig. 2 The impact of vessel’s residual life on the economical indicator of shore power (a) and the latest installation of shore power system on ship (b)
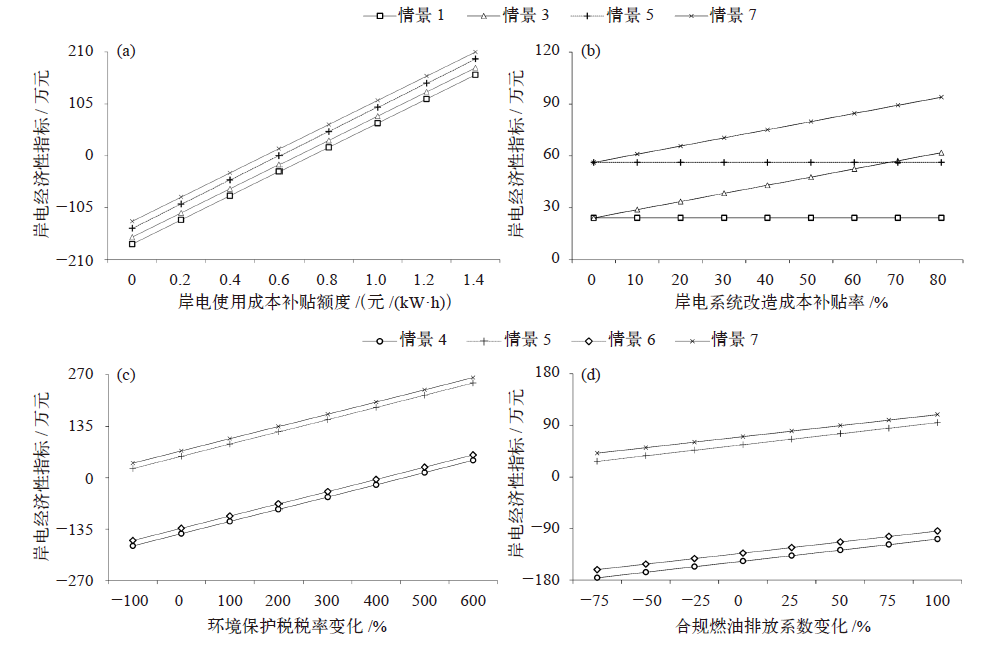
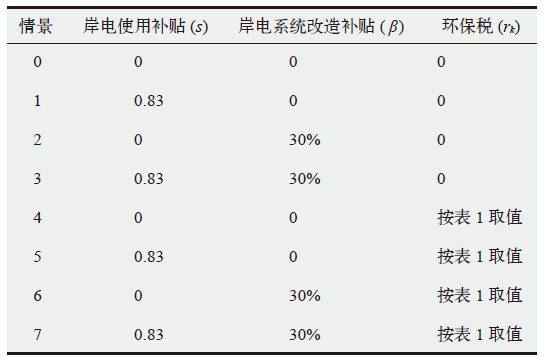
Fig. 3 The impact of policy factors on the economical indicator of shore power. (a) Subsidy of using cost, (b) subsidy rate of installing cost, (c) rate of environmental protection tax, and (d) emission factors of compliant fuel

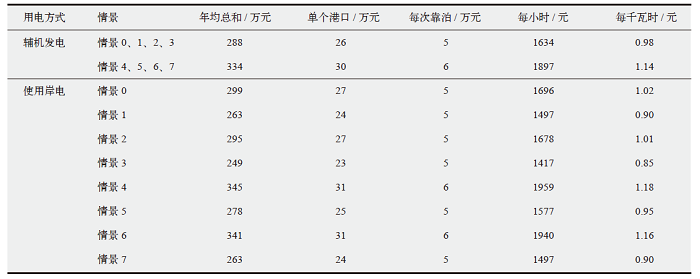
Fig. 4 The impact of non-policy factors on the economical indicator of shore power. (a) Installing cost of shore power, (b) utilization rate of shore power, (c) fuel consumption rate, and (d) fuel price
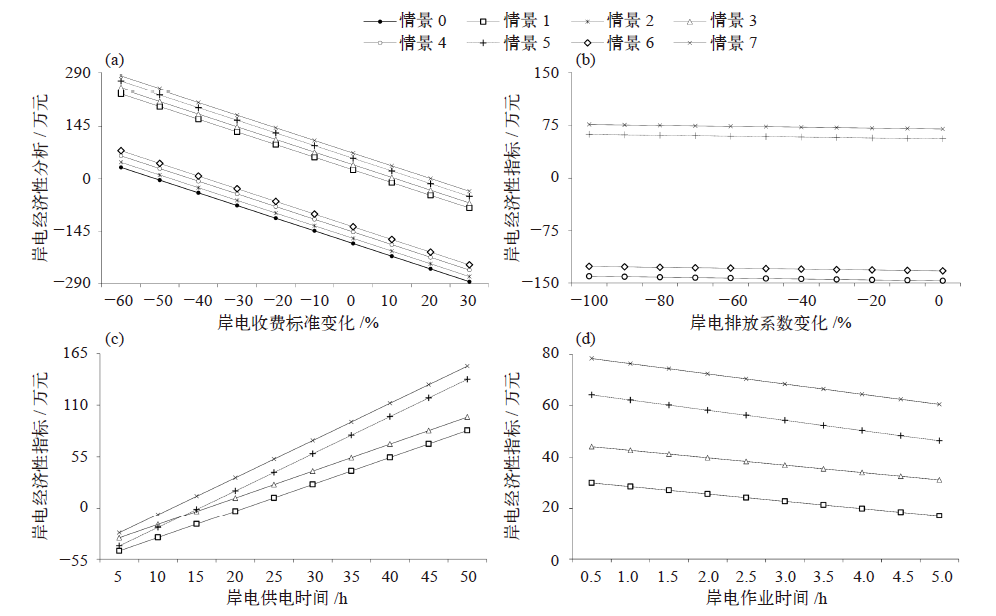
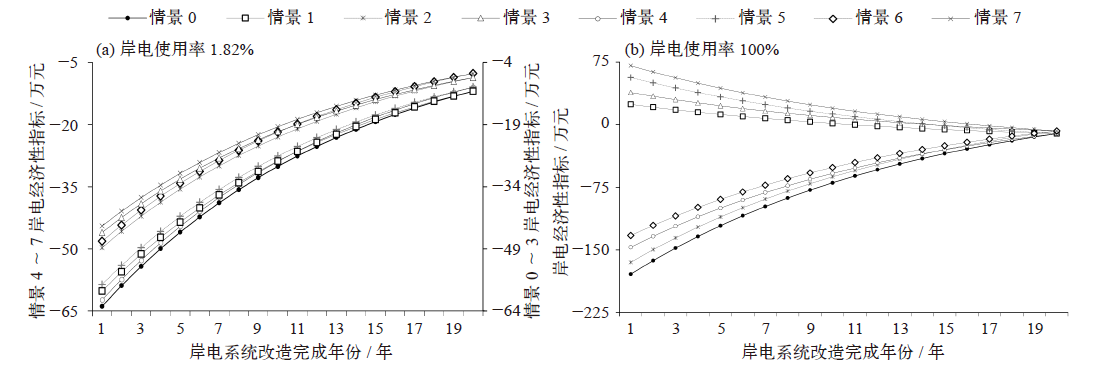
Fig. 5 The impact of non-policy factors of port on the economical indicator of shore power. (a) Toll standard, (b) emission factors, (c) supply time, and (d) operation time of shore power
| [1] | 国家统计局. 2020中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020. |
| National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2020 China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 伏晴艳, 沈寅, 张健. 上海港船舶大气污染物排放清单研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2012, 12 (5): 57-64. |
| Fu Q Y, Shen Y, Zhang J. On the ship pollutant emission inventory in Shanghai port[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2012, 12 (5): 57-64 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 交通运输部. 船舶与港口污染防治专项行动实施方案(2015—2020年) [EB/OL]. 2015—2021 [2021-10-01]. http://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2016/content_5038094.htm. |
| Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Implementation plan of special action on pollution prevention and control of ships and ports (2015-2022)[EB/OL]. 2015-2021 [2021-10-01]. http://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2016/content_5038094.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 彭传圣. 靠港集装箱船岸电技术的应用[J]. 集装箱化, 2011, 22 (8):21-24. |
| Peng C S. Application of shore power technology for berthing container ship[J]. Containerization, 2011, 22 (8): 21-24 (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 李海波, 李睿瑜, 贾远明. 靠港船舶使用岸电技术及应用[M]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学出版社, 2019. |
| Li H B, Li R Y, Jia Y M. Technology and application of shore power by berthing vessels[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology Press, 2019 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 刘纯, 唐苇苇, 姚建新. 国内外码头岸电系统技术应用及发展综述[J]. 水运工程, 2020 (5): 173-176, 234. |
| Liu C, Tang W W, Yao J X. View of technological application and development of terminal cold ironing system in China and abroad[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2020 (5): 173-176, 234 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 交通运输部水运局. 我国港口岸电建设及使用情况[EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-07-26]. http://www.port.org.cn/info/2020/205399.htm. |
| Water Transport Bureau of The Ministry of Transport of The People’s Republic of China. Construction and usage of shore power in China[EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-07-26]. http://www.port.org.cn/info/2020/205399.htm. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 魏鋆依. 岸电使用为何遇冷?[N]. 中国水运报, 2020-09-18 (2). |
| Wei Y Y. Why the shore power suffers the cold shoulder?[N]. China Water Transport, 2020-09-18 (2) (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 彭传圣. 国外应用靠港船舶使用岸电技术的经验分析[J]. 港口经济, 2012 (11): 11-14. |
| Peng C S. Experience analysis of overseas application of shore power technology for ships calling at port[J]. Port Economy, 2012 (11): 11-14 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 上海市交通委员会. 上海市港口岸电建设方案[EB/OL]. 2019 [2021-07-26]. http://jtw.sh.gov.cn/cmsres/16/16eefe6f70fa4ed5a34bea75231edeb6/ab4e8fd678f34069e0d1f0dade0491f0.pdf. |
| Shanghai Municipal Transportation Commission. The development scheme of shore power in Shanghai[EB/OL]. 2019 [2021-07-26]. http://jtw.sh.gov.cn/cmsres/16/16eefe6f70fa4ed5a34bea75231edeb6/ab4e8fd678f34069e0d1f0dade0491f0.pdf (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 深圳市交通运输委员会, 深圳市人居环境委员会. 深圳市绿色低碳港口建设补贴资金管理暂行办法实施细则[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-07-26]. http://www.sz.gov.cn/zfgb/zcjd/content/post_4980524.html. |
| Transport Commission of Shenzhen Municipality, Human Settlements and Environment Commission of Shenzhen Municipality. Detailed rules for implementing the interim management measures for subsidy funds for green low-carbon port construction in Shenzhen[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-07-26]. http://www.sz.gov.cn/zfgb/zcjd/content/post_4980524.html (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 包起帆, 黄细霞, 葛中雄, 等. 上海港口外高桥六期码头岸电试点项目方案论证[J]. 港口科技, 2009 (12): 6-11, 14. |
| Bao Q F, Huang X X, Ge Z X, et al. Plan proving of the onshore power supply trial project in Shanghai port Waigaoqiao terminal[J]. Port Science & Technology, 2009 (12): 6-11, 14 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 霍伟强, 付威, 徐广林, 等. 港口岸电技术及其推广分析[J]. 能源与节能, 2017 (2): 2-5. |
| Huo W Q, Fu W, Xu G L, et al. Shore power technology and analysis of its extension[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation, 2017 (2): 2-5 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 赖单宏, 陈文炜, 黄文焘, 等. 岸电技术经济性分析[J]. 港工技术, 2016, 53 (3): 57-62. |
| Lai D H, Chen W W, Huang W T, et al. Economic analysis of shore power techniques[J]. Port Engineering Technology, 2016, 53 (3): 57-62 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | Tseng P H, Pilcher N. A study of the potential of shore power for the port of Kaohsiung, Taiwan: to introduce or not to introduce?[J]. Research in Transportation Business & Management, 2015, 17: 83-91 |
| [16] | Ballini F, Bozzo R. Air pollution from ships in ports: the socio-economic benefit of cold-ironing technology[J]. Research in Transportation Business & Management, 2015, 17: 92-98 |
| [17] |
Innes A, Monios J. Identifying the unique challenges of installing cold ironing at small and medium ports: the case of Aberdeen[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2018, 62: 298-313
doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2018.02.004 URL |
| [18] |
Yu J, Voss S, Tang G. Strategy development for retrofitting ships for implementing shore side electricity[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2019, 74: 201-213
doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2019.08.004 URL |
| [19] | 宋向群, 周勇, 王文渊, 等. 内支线船舶岸电系统改造策略及经济影响因素研究[J]. 上海海事大学学报, 2015, 36 (4): 43-47. |
| Song X Q, Zhou Y, Wang W Y, et al. Research on retrofit strategy of shore power system for feeder ships and its economic influencing factors[J]. Journal of Shanghai Maritime University, 2015, 36 (4): 43-47 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] |
Vaishnav P, Fischbeck P, Morgan M, et al. Shore power for vessels calling at U.S. ports: benefits and costs[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50 (3): 1102-1110
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b04860 URL |
| [21] | 冯华, 林朝华, 张旭, 等. 基于沿海港口的岸电运营系统经济性分析[J]. 港工技术, 2018, 55 (2): 69-73. |
| Feng H, Lin Z H, Zhang X, et al. Economic analysis of shore power operation system of coastal port[J]. Port Engineering Technology, 2018, 55 (2): 69-73 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 李勇, 张旭, 林朝华, 等. 基于政府补贴政策下的岸电技术经济性分析[J]. 港工技术, 2018, 55 (3): 88-92. |
| Li Y, Zhang X, Lin Z H, et al. Economic analysis of shore power techniques based on government subsidy policy[J]. Port Engineering Technology, 2018, 55 (3): 88-92 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 胡晓青, 王蓓蓓, 黄俊辉, 等. 岸电建设运营各方成本效益最优化分析及江湖海岸电特性比较[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2018, 38 (9): 169-178. |
| Hu X Q, Wang B B, Huang J H, et al. Cost-benefit optimization analysis of participants in shore-side power construction and operation and characteristic comparison among river, lake and ocean shore-side power[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2018, 38 (9): 169-178 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 郑欣, 张新民, 缪新招, 等. 考虑多方经济效益综合优化的岸电定价策略[J]. 港工技术, 2019, 56 (S1): 75-81. |
| Zheng X, Zhang X M, Miao X Z, et al. Shore power pricing strategy considering the comprehensive optimization of multiple economic benefits[J]. Port Engineering Technology, 2019, 56 (S1): 75-81 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | Yin M, Wang Y, Zhang Q. Policy implementation barriers and economic analysis of shore power promotion in China[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2020, 87: 102506 |
| [26] | 陶学宗, 尹传忠, 吴琴, 等. 港口船舶岸电补贴标准优化研究[R]. 上海: 上海海事大学, 2021. |
| Tao X Z, Yin C Z, Wu Q, et al. Optimizing the subsidy level of shore power usage by berthing vessels[R]. Shanghai: Shanghai Maritime University, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | Ship & Bunker. World bunker prices[EB/OL]. 2019 [2021-08-06]. https://shipandbunker.com/prices |
| [28] | 李海波. 靠港船舶使用岸电和低硫油效益分析[EB/OL]. 2019 [2021-08-06]. https://www.wti.ac.cn/wti/TAfbdwzlhb/2521.jhtml. |
| Li H B. Analysis of benefit from using shore power and low sulfur oil by berthing vessels[EB/OL]. 2019 [2021-08-06]. https://www.wti.ac.cn/wti/TAfbdwzlhb/2521.jhtml (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 中电联行业发展与环境资源部. 中国电力行业年度发展报告2020 [EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-08-06]. http://chinapower.com.cn/zx/zxbg/20200615/22414.html. |
| Industry Development and Environmental Resources Department, China Electricity Council. Annual development report of China’s power industry 2020 [EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-08-06]. http://chinapower.com.cn/zx/zxbg/20200615/22414.html (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 第十二届全国人民代表大会常务委员会. 中华人民共和国环保税法[EB/OL]. 2016 [2021-08-06]. http://www.chinatax.gov.cn/chinatax/n610/c12223113/content.html. |
| Standing Committee of The 12th National People’s Congress. Environmental protection tax law of the People’s Republic of China[EB/OL]. 2016 [2021-08-06]. http://www.chinatax.gov.cn/chinatax/n610/c12223113/content.html (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 上海市财政局, 上海市地方税务局, 上海市环境保护局. 关于本市应税大气污染物和水污染物环保税适用税额标准等有关问题的通知[EB/OL]. 2017 [2021-08-06]. http://service.shanghai.gov.cn/XingZhengWenDangKuJyh/XZGFDetails.aspx?docid=REPORT_NDOC_003679. |
| Shanghai Municipal Bureau of Finance, Shanghai Municipal Bureau of Local Taxation, Shanghai Municipal Bureau of Environmental Protection. Notice on applicable tax standards of environmental protection tax of air pollutant and water pollutant in Shanghai[EB/OL]. 2017 [2021-08-06]. http://service.shanghai.gov.cn/XingZhengWenDangKuJyh/XZGFDetails.aspx?docid=REPORT_NDOC_003679 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | Ying HUANG,Hong-Xu GUO,Cui-Ping LIAO,Dai-Qing ZHAO. Study on low-carbon development path of urban transportation sector based on LEAP model—take Guangzhou as an example [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(6): 670-683. |
| [2] | Jie-Ming CHOU, Ru-Feng DAI, Wen-Jie DONG, Jing-Han BAN, Chuan-Ye HU. Future CO2 emissions projection of China based on U.S. new climate policy [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(1): 95-105. |
| [3] | Yi Si, Tan Jinkai, Li Mengya, Liang Xinxin, Wang Jun. Projection of Sea Level Rise and Its Impacts on Coastal Wetlands Within the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Climate Change Research, 2017, 13(6): 598-605. |
| [4] | Su Shenshen, Zhao Jinyang, Hu Jianxin. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Power Sector in China from 1990 to 2050 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2015, 11(5): 353-362. |
| [5] | . Selection of CO2 Emission Scenarios in China During 2000-2050 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2010, 6(01): 53-59. |
| [6] | Zhuang Guiyang. Energy Subsidy Policies and Their Reform: Providing economic incentives for climate change mitigation [J]. Climate Change Research, 2007, 03(00): 92-96. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||