Climate Change Research ›› 2021, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 525-536.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.193
• Impacts of Climate Change • Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of climate change on the volume capture ratio of annual rainfall’s partition
CHEN Yan( ), HUI Pin-Hong, ZHOU Xue-Dong, YANG Jie
), HUI Pin-Hong, ZHOU Xue-Dong, YANG Jie
- Jiangsu Provincial Climate Center, Nanjing 210008, China
-
Received:2020-08-31Revised:2020-11-02Online:2021-09-30Published:2021-09-28
Cite this article
CHEN Yan, HUI Pin-Hong, ZHOU Xue-Dong, YANG Jie. Influence of climate change on the volume capture ratio of annual rainfall’s partition[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(5): 525-536.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.193

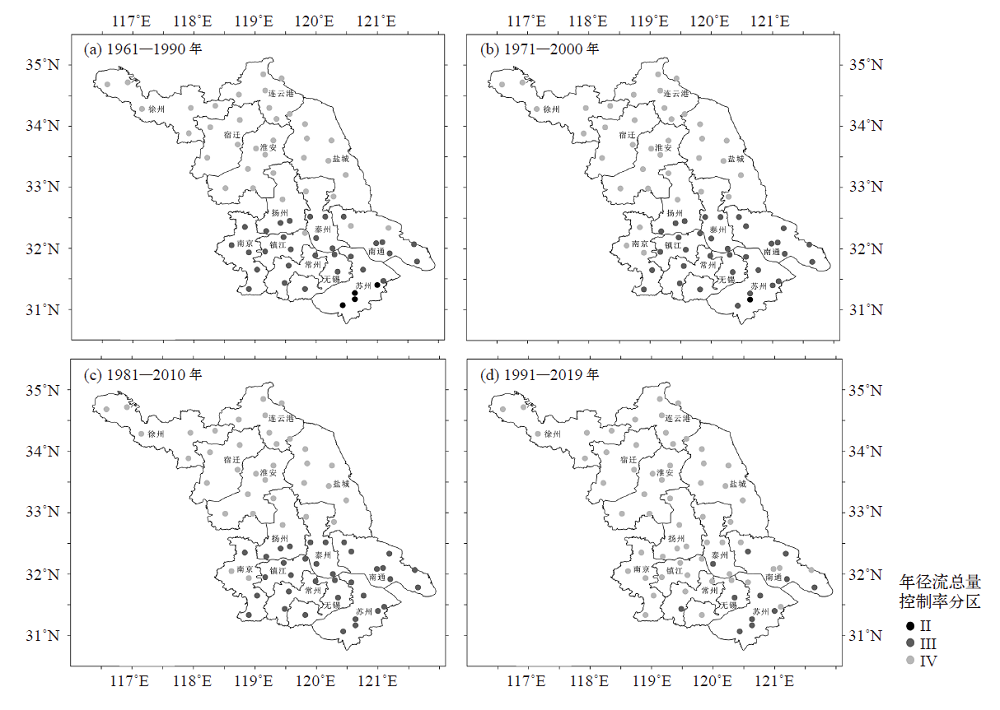
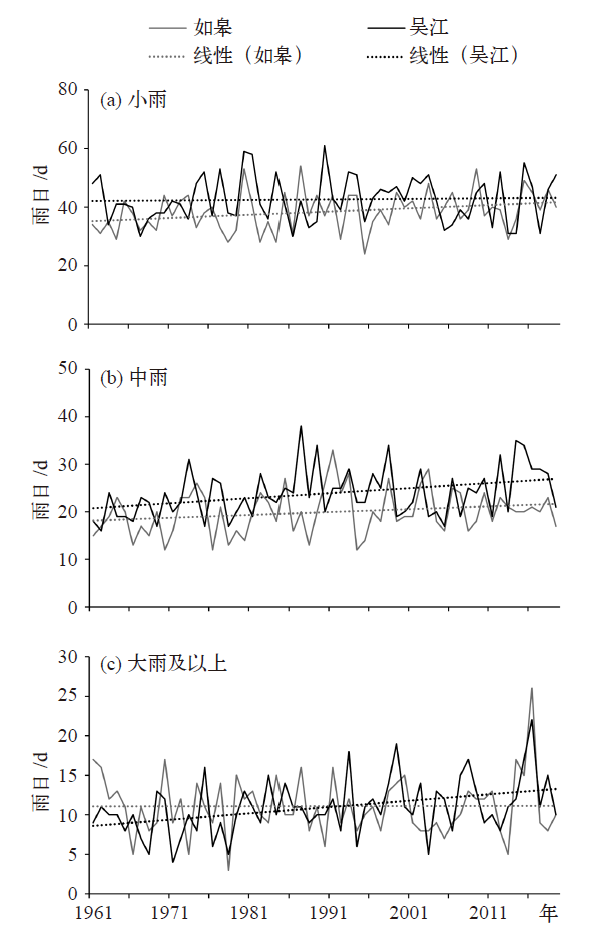
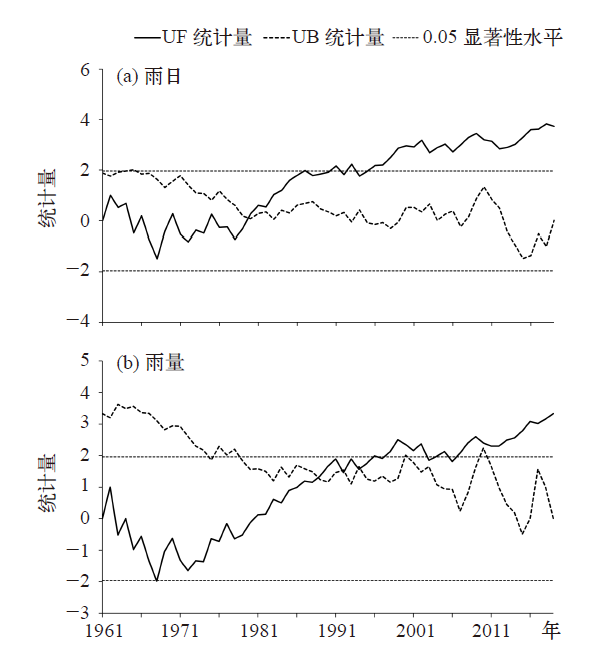
Fig. 2 The spatial distribution of effective precipitation in 1961-2019 (a) average annual precipitation, (c) average annual precipitation days, (e) average annual precipitation intensity, and their trends (b, d, f)
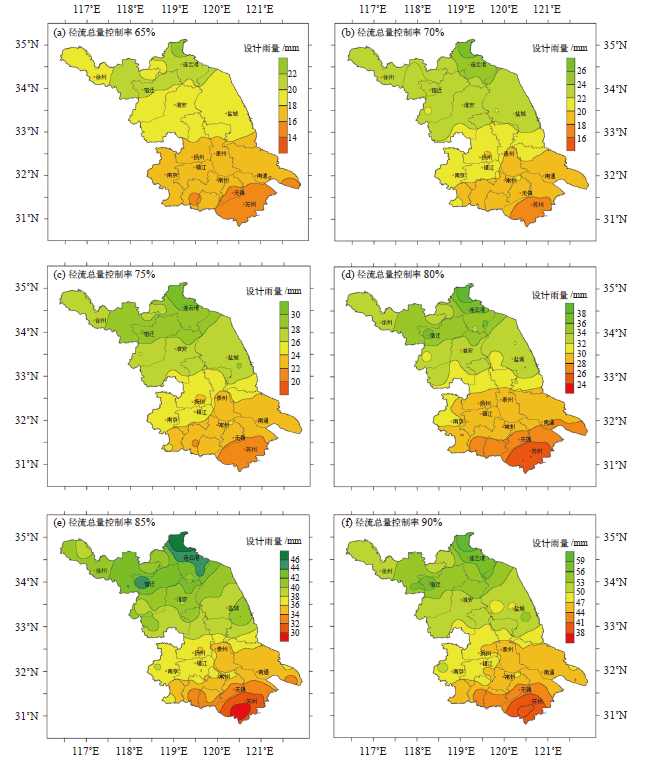
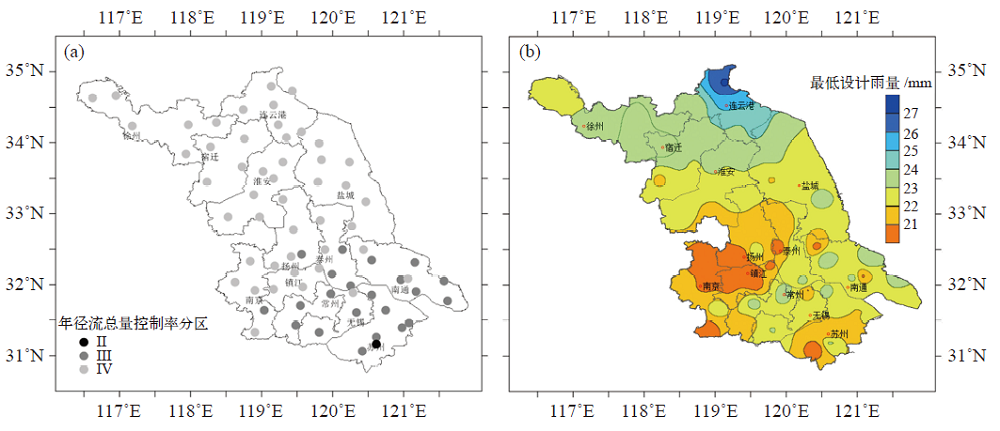
Fig. 3 Spatial distribution of design rainfall depth of different volume capture ratio of annual rainfall during 1961-2019 (a) 65%, (b) 70%, (c) 75%, (d) 80%, (e) 85%, and (f) 90%
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014 |
| [2] |
Karl T R, Knight R W, Plummer N. Trends in high-frequency climate variability in the twentieth century[J]. Nature, 1995, 377:217-220
doi: 10.1038/377217a0 URL |
| [3] |
Osborn T J, Hulme M, Jones P D, et al. Observed trends in the daily intensity of United Kingdom precipitation[J]. International Journal Climatology, 2000, 20:347-364
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0088 URL |
| [4] |
Groisman P, Karl T, Easterling D, et al. Changes in the probability of extreme precipitation: important indicators of climate change[J]. Climatic Change, 1999, 42:243-283
doi: 10.1023/A:1005432803188 URL |
| [5] |
Kitoh A, Hosaka M, Adachi Y. Future projections of precipitation characteristics in East Asia simulated by the MRI CGCM2[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2005, 22(4):467-478
doi: 10.1007/BF02918481 URL |
| [6] | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 海绵城市建设技术指南: 低影响开发雨水系统构建(试行)[EB/OL]. 2014 [2020-01-20]. http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/201411/t20141102_219465.html. |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban and Rural Construction of the People’s Republic of China. Sponge city construction technical guide: low impact development rainwater system construction (Trial)[EB/OL]. 2014 [2020-01-20]. http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/201411/t20141102_219465.html(in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 任心欣, 汤伟真. 海绵城市年径流总量控制率等指标应用初探[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(13):105-109. |
| Ren X X, Tang W Z. Application of capture ratio of total annual runoff volume in spongy city[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2015, 31(13):105-109 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 周广胜, 何奇瑾. 城市内涝防治需充分预估气候变化的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(16):4961-4964. |
| Zhou G S, He Q J. Impact of climate change should be fully predicted in urban waterlogging control[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(16):4961-4964 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 夏军, 石卫, 雒新萍, 等. 气候变化下水资源脆弱性的适应性管理新认识[J]. 水科学进展, 2015, 26(2):279-286. |
| Xia J, Shi W, Luo X P, et al. Revisions on water resources vulnerability and adaption measures under climate change[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2015, 26(2):279-286 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 张建云, 王银堂, 胡庆芳, 等. 海绵城市建设有关问题讨论[J]. 水科学进展, 2016, 27(6):793-799. |
| Zhang J Y, Wang Y T, Hu Q F, et al. Discussion and views on some issues of the sponge city construction in China[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2016, 27(6):793-799 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 杨金虎, 江志红, 王鹏祥, 等. 中国年极端降水事件的时空分布特征[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2008, 13(1):75-83. |
| Yang J H, Jiang Z H, Wang P X, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristic of extreme precipitation event in China[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2008, 13(1):75-83 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 何书樵, 郑有飞, 尹继福. 近50年长江中下游地区降水特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(7):1187-1192. |
| He S Q, Zheng Y F, Yin J F. Analysis on precipitation characteristics over middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River in the last 50 years[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 22(7):1187-1192 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 贺冰蕊, 翟盘茂. 中国1961—2016年夏季持续和非持续性极端降水的变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5):437-444. |
| He B R, Zhai P M. Characteristics of the persistent and non-persistent extreme precipitation in China from 1961 to 2016[J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(5):437-444 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 梅伟, 杨修群. 我国长江中下游地区降水变化趋势分析[J]. 南京大学学报: 自然科学, 2005, 41(6):577-589. |
| Mei W, Yang X Q. Trends of precipitation variations in the mid-lower Yangtze River valley of China[J]. Journal of Nanjing University: Natural Sciences, 2005, 41(6):577-589 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 叶殿秀, 王遵娅, 高荣, 等. 1961—2016年我国区域性暴雨过程的客观识别及其气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(6):575-583. |
| Ye D X, Wang Z Y, Gao R, et al. Objective identification and climatic characters of the regional rainstorm event in China from 1961 to 2016[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(6):575-583 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 张峻, 张艺玄. 长江中下游地区近60 a降水变化规律研究[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2019, 38(3):259-266. |
| Zhang J, Zhang Y X. Study on the variation of precipitation in the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River in recent 60 years[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2019, 38(3):259-266 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 潘欣, 尹义星, 王小军. 1960—2010年长江流域极端降水的时空演变及未来趋势[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2017, 3:436-444. |
| Pan X, Yin Y X, Wang X J. Spatio-temporal characteristics and future trend of extreme precipitation in the Yangtze River basin during 1960 to 2010[J]. Resources and Environment in The Yangtze Basin, 2017, 3:436-444 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 李俊奇, 林翔. 极端降雨事件对雨水年径流总量控制率和24 h降雨场次控制率的影响规律探析[J]. 给水排水, 2018, 44(1):21-26. |
| Li J Q, Lin X. The influence of extreme rainfall events on the total annual runoff control rate of rainwater and the 24 h rainfall control rate[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2018, 44(1):21-26 (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 张质明, 胡蓓蓓, 李俊奇, 等. 中国日降雨空间变化对雨水径流源头总量控制的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 2018, 29(4):465-472. |
| Zhang Z M, Hu B B, Li J Q, et al. Influence of spatial variation in daily rainfall on volume capture of rainfall by source control facilities in China[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(4):465-472 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 庞璇, 张永勇, 潘兴瑶, 等. 城市雨洪模拟与年径流总量控制目标评估: 以北京市未来科技城为例[J]. 资源科学, 2019, 41(4):803-813. |
| Pang X, Zhang Y Y, Pan X Y, et al. Urban storm water simulation and assessment of the control rate of total annual runoff: a case of the future science and technology park in Beijing[J]. Resources Science, 2019, 41(4):803-813 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 成丹, 陈正洪. 湖北宜昌市区暴雨雨型的演变特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2017, 35(2):225-231. |
| Cheng D, Chen Z H. Evolution characteristics of rainstorm hyetograph in Yichang of Hubei province[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2017, 35(2):225-231 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 顾正强, 龚强, 晁华, 等. 辽宁省海绵城市建设中年径流总量控制率分区及其分布差异研究[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2019, 35(1):59-65. |
| Gu Z Q, Gong Q, Chao H, et al. Analysis of the regional division of volume capture ratio of annual rainfall runoff and its spatial variation in sponge city construction in Liaoning province[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2019, 35(1):59-65 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 王文亮, 李俊奇, 车伍, 等. 海绵城市建设指南解读之城市径流总量控制指标[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(8):18-23. |
| Wang W L, Li J Q, Che W, et al. Explanation of sponge city development technical guide: planning index for urban total runoff volume capture[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2015, 31(8):18-23 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] |
Mann H B. Nonparametric tests against trend[J]. Econometrica, 1945, 13(3):245-259
doi: 10.2307/1907187 URL |
| [25] | Kendall M G. Rank correlation methods[J]. British Journal of Psychology, 1955, 25(1):86-91 |
| [26] | 杜尧, 陈启慧, 和鹏飞, 等. 南京地区暴雨变化特性分析[J]. 水资源保护, 2019, 35(6):89-94. |
| Du Y, Chen Q H, He P F, et al. Analysis of rainstorm variation characteristics in Nanjing region[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2019, 35(6):89-94 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 姚建群. 连续小波变换在上海近100年降水分析中的应用[J]. 气象, 2001, 27(2):20-24. |
| Yao J Q. An application of continuous wavelet transforms to precipitation analysis in Shanghai during one hundred years[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2001, 27(2):20-24 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 姜晓艳, 刘树华, 马明敏, 等. 东北地区近百年降水时间序列变化规律的小波分析[J]. 地理研究, 2009, 28(2):354-362. |
| Jiang X Y, Liu S H, Ma M M, et al. A wavelet analysis of the precipitation time series in Northeast China during the last 100 years[J]. Geographical Research, 2009, 28(2):354-362 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 朱继前, 韩美, 徐泽华, 等. 淮河流域不同量级降雨时空分布特征及其影响影响因素[J]. 水土保持研究, 2019, 26(4):87-95. |
| Zhu J Q, Han M, Xu Z H, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution characteristics and factors of different magnitude rainfall in Huaihe River basin[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 26(4):87-95 (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 李俊奇, 王文亮, 车伍, 等. 海绵城市建设指南解读之降雨径流总量控制目标区域划分[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(8):6-12. |
| Li J Q, Wang W L, Che W, et al. Explanation of sponge city development technical guide: regional division for total rainfall runoff volume capture target[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2015, 31(8):6-12 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | FANG Jia-Yi, YIN Jie, SHI Xian-Wu, FANG Jian, DU Shi-Qiang, LIU Min. A review of compound flood hazard research in coastal areas [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(3): 317-328. |
| [2] | . Advances in Extremes Statistics and Their Application to Climate Change Study [J]. Climate Change Research, 2011, 7(4): 248-252. |
| [3] | GUO Jun. Spatio-temporal Variations of Extremely Heavy Precipitation in the Circum-Bohai Sea Region During 1961-2007 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2010, 6(05): 319-324. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||