Climate Change Research ›› 2019, Vol. 15 ›› Issue (1): 23-32.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2018.104
• Changes in Climate System • Previous Articles Next Articles
Extreme flood in the Lancang River Basin under climate change
Shu-Xia WANG,Li-Ping ZHANG,Yi LI,Dun-Xian SHE
- State Key Laboratory of Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
-
Received:2018-07-17Revised:2018-09-14Online:2019-01-30Published:2019-01-30 -
Contact:Li-Ping ZHANG
Cite this article
Shu-Xia WANG,Li-Ping ZHANG,Yi LI,Dun-Xian SHE. Extreme flood in the Lancang River Basin under climate change[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(1): 23-32.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2018.104
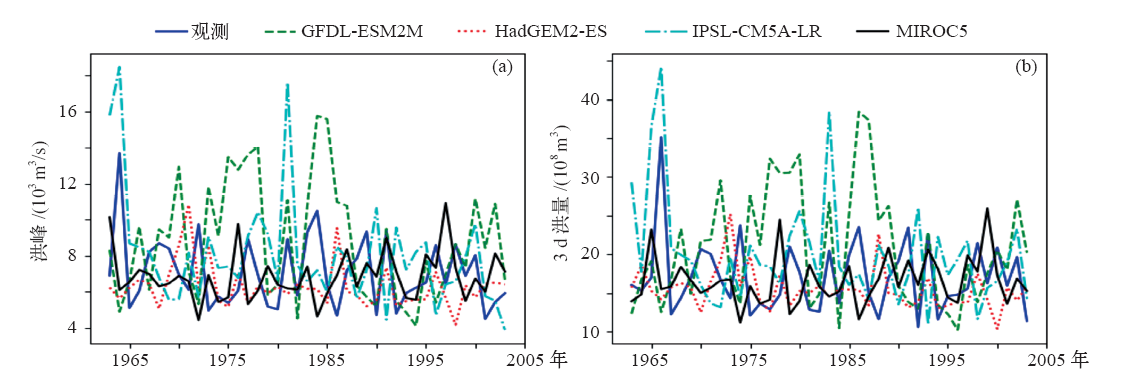
Fig. 2 Time series of annual maximum flood peak and flood volumes based on observations and model output data coupling VIC model in the past during 1961-2005

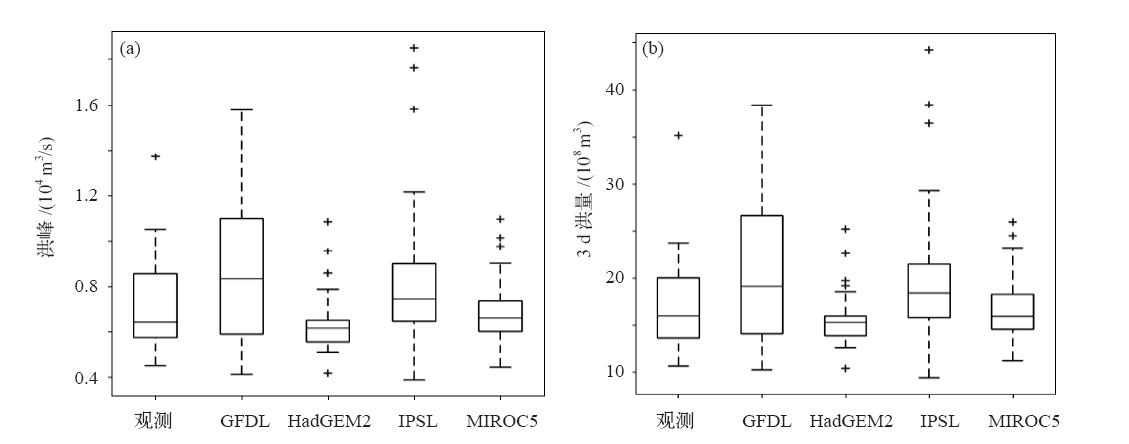
Fig. 4 P-III frequency distribution of annual maximum flood peak and flood volumes based on observations and climate model output data coupling VIC model simulation in the past

Fig. 5 The range of annual maximum flood peak and flood volumes based on observations in the past and model simulations in the future under RCP2.6 scenario
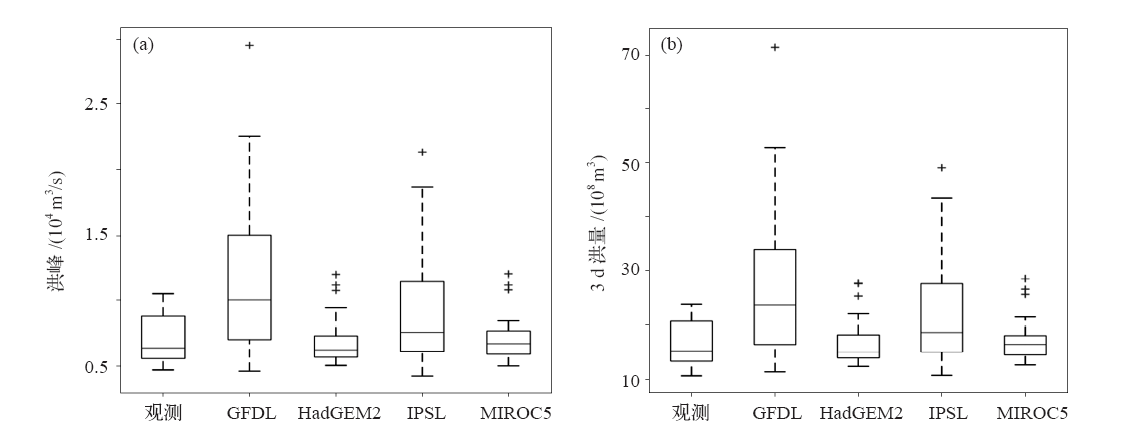
Fig. 6 The range of annual maximum flood peak and flood volumes based on observations in the past and model simulations in the future under RCP6.0 scenario
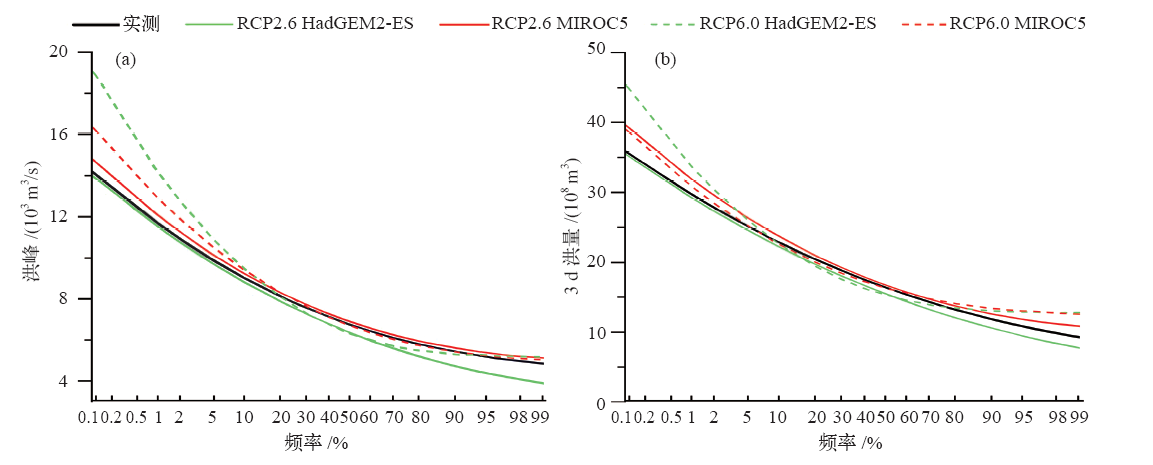
Fig. 7 P-III frequency distribution of annual maximum flood peak and flood volumes based on observations in the past and model simulations in the future
|
| [1] | DING Kai-Xi,ZHANG Li-Ping,SHE Dun-Xian,ZHANG Qin,XIANG Jun-Wen. Variation of extreme precipitation in Lancang River basin under global warming of 1.5℃ and 2.0℃ [J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(4): 466-479. |
| [2] | LI Rou-Ke,HAN Zhen-Yu,XU Ying,SHI Ying,WU Jia. An ensemble projection of GDP and population exposure to high temperature events over Jing-Jin-Ji district based on high resolution combined dynamical and statistical downscaling datasets [J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(4): 491-504. |
| [3] | Qi-Mou ZHANG,Run WANG,Tong JIANG,Song-Sheng CHEN. Projection of extreme precipitation in the Hanjiang River basin under different RCP scenarios [J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(3): 276-286. |
| [4] | Ying SHI,Zhen-Yu HAN,Ying XU,Bo-Tao ZHOU,Jia WU. Future changes of climate extremes in Xiongan New Area and Jing-Jin-Ji district based on high resolution (6.25 km) combined statistical and dynamical downscaling datasets [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(2): 140-149. |
| [5] | Li-Quan WU,Qing-Quan LI,Yi-Hui DING,Li-Juan WANG,Xiao-Ge XIN,Min WEI. Preliminary assessment on the seasonal hindcast skill of the Arctic Oscillation with decadal experiment by BCC_CSM1.1 climate model [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(1): 1-11. |
| [6] | Qian-Yu ZHA,Chao GAO,Ru YANG,Yue LIU,Tian RUAN,Peng LI. Study on runoff under global warming of 1.5℃ and 2.0℃ in main stream of upper reaches of the Huaihe River [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(6): 583-592. |
| [7] | Zhen-Yu HAN,Yao TONG,Xue-Jie GAO,Ying XU. Correction based on quantile mapping for temperature simulated by the RegCM4 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(4): 331-340. |
| [8] | Xu Ying, Zhou Botao, Wu Jie, Han Zhenyu, Zhang Yongxiang, Wu Jia. Asian Climate Change in Response to Four Global Warming Targets [J]. Climate Change Research, 2017, 13(4): 306-315. |
| [9] | Zhu Qingzhao, Wen Xinyu. Performance of Chinese Climate Models in Simulating Arctic Sea-Ice in CMIP5 Experiments [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(4): 276-285. |
| [10] | Xu Jingwei, Xu Min, Jiang Xi, ArmelleReca C. Remedio, Dmitry V. Sein, Nikolay Koldunov, Daniela Jacob. The Assessment of Surface Air Temperature and Precipitation Simulated by Regional Climate Model REMO over China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(4): 286-293. |
| [11] | Zhang Yanwu, Zhang Li, Xu Ying . Simulations and Projections of the Surface Air Temperature in China by CMIP5 Models [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(1): 10-19. |
| [12] | Huang Yue, Chen Xi, Liu Tie, Ma Yonggang. Flood Frequency Analysis for Kaidu Watershed in Tianshan Mountains [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(1): 37-44. |
| [13] | Lu Guihua, Zhang Yazhou, Xiao Heng, Liu Zhiyu, Hu Jianwei, Wu Zhiyong. Coincidence Probability of Urban Rainstorm in Bengbu and Flood in the Upper Reaches of Huaihe River Under Climate Change [J]. Climate Change Research, 2015, 11(1): 31-37. |
| [14] | Yang Wei, Zhang Liping, Shan Lijie, Chen Xinchi, Yang Yanrong. Spatiotemporal Distribution Features of Extreme Hydrological Events in the Hanjiang River Basin [J]. Climate Change Research, 2015, 11(1): 15-21. |
| [15] | Chen Xiaochen, Xu Ying, Xu Chonghai, Yao Yao. Assessment of Precipitation Simulations in China by CMIP5 Multi-models [J]. Climate Change Research, 2014, 10(3): 217-225. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||