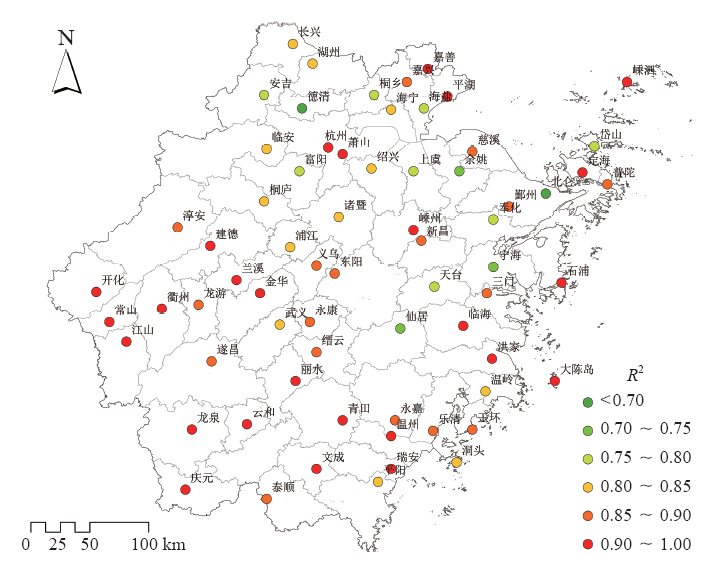
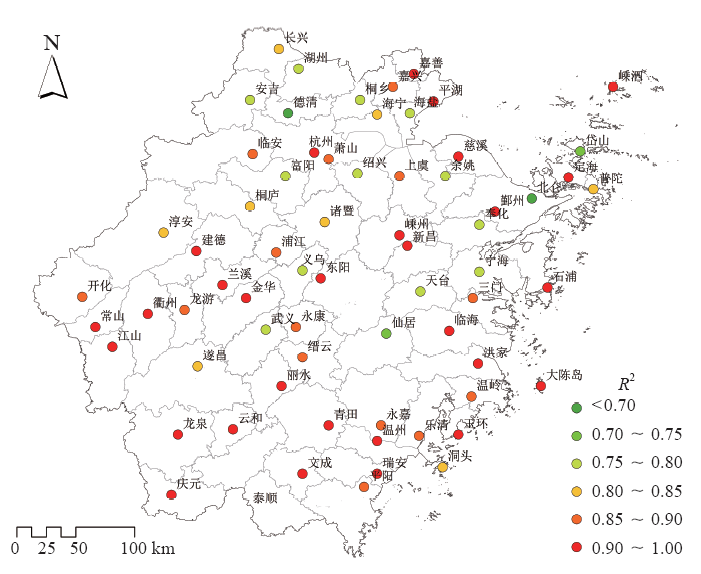
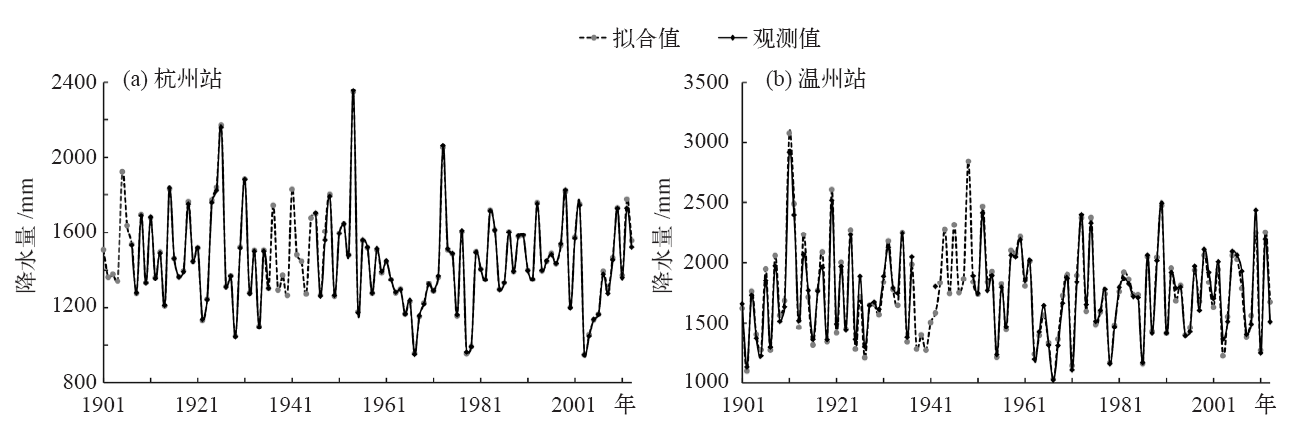
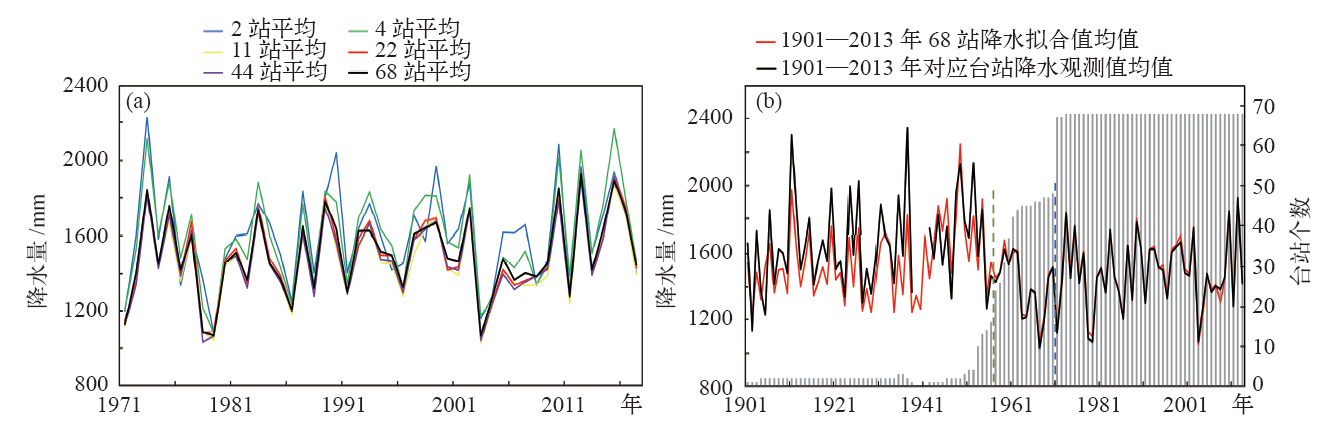
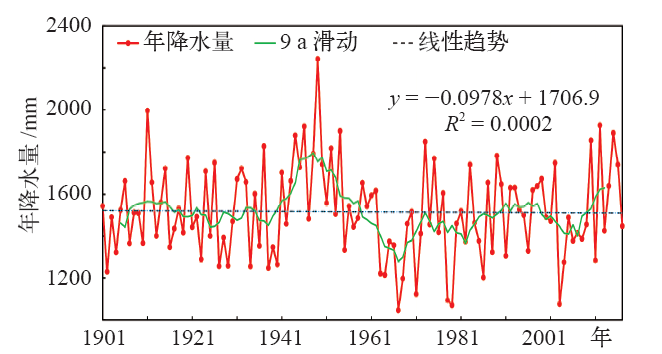
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013 | | [2] | 秦大河, 陈振林, 罗勇 , 等. 气候变化科学的最新认知[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007,3(2):63-73 | | [3] | 杨溯, 徐文慧, 许艳 , 等. 全球地面降水月值历史数据集研制[J]. 气象学报, 2016,74(2):259-270 | | [4] | 丁一汇, 任国玉, 赵宗慈 , 等. 中国气候变化的检测及预估[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2007,1(1):1-10 | | [5] | Tank A M G K, Wijngaard J B, K?nnen G P , et al. Daily surface air temperature and precipitation dataset 1901-1999 for European Climate Assessment (ECA)[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2002,22(12):1441-1453 | | [6] | 李庆祥, 彭嘉栋, 沈艳 . 1900—2009年中国均一化逐月降水数据集研制[J]. 地理学报, 2012,67(3):301-311 | | [7] | 秦大河, 丁一汇, 苏纪兰 , 等. 中国气候与环境演变(上卷): 气候与环境的演变[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 83 | | [8] | 屠其璞 . 近百年来我国降水量的变化[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 1987,10(2):177-187 | | [9] | 李庆祥 . 气候资料均一性研究导论[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2011: 86-102 | | [10] | 施能, 陈绿文, 封国林 , 等. 1920—2000年全球陆地降水气候特征与变化[J]. 高原气象, 2004,23(4):435-443 | | [11] | 黄雪松, 况雪源, 覃峥嵘 , 等. 广西近百年气温和降水序列的多时间尺度分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007,3(6):362-367 | | [12] | 顾骏强, 施能, 薛根元 . 近40年浙江省降水量、雨日的气候变化[J]. 应用气象学报, 2002,13(3):322-329 | | [13] | 刘德地, 李梅, 楼章华 , 等. 近50年来浙江省降雨特性变化分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2009,24(11):1973-1983 | | [14] | 吕俊梅, 琚建华, 江剑民 . 近一百年中国东部区域降水的年代际跃变[J]. 大气科学, 2009,33(3):524-536 | | [15] | 王绍武, 龚道溢, 叶瑾林 , 等. 1880年以来中国东部四季降水量序列及其变率[J]. 地理学报, 2000,55(3):281-293 | | [16] | 王守荣, 苗长明 . 浙江气候资源环境及其变化[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2008: 46 | | [17] | 姜贵祥, 孙旭光 . 格点降水资料在中国东部夏季降水变率研究中的适用性[J]. 气象科学, 2016,36(4):448-456 | | [18] | 王芬, 曹杰, 李腹广 , 等. 多套格点降水资料在云南及周边地区的对比[J]. 应用气象学报, 2013,24(4):472-483 | | [19] | Groisman P Y, Koknaeva V V, Belokrylova T A , et al. Overcoming biases of precipitation measurement: a history of the USSR experience[J]. Bulletin of American Meteorological Society, 1991,72(11):1725-1733 | | [20] | 刘佳, 马振峰, 范广洲 , 等. 多种均一性检验方法比较研究[J]. 气象, 2012,38(9):1121-1128 | | [21] | 曹丽娟, 严中伟 . 地面气候资料均一性研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2011,7(2):129-135 | | [22] | Wang X L . Penalized maximal F-test for detecting undocumented mean shifts without trend change[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2008,25(3):368-384 | | [23] | Wang X L, Wen Q H, Wu Y . Penalized maximal test for detecting undocumented mean change in climate date series[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2007,46(6):916-931 | | [24] | Wang X L, Chen H, Wu Y , et al. New techniques for detection and adjustment of shifts in daily precipitation data series[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2010,49(12):2416-2436 | | [25] | 张高杰, 何金海, 周自江 , 等. RHtest方法对我国降水资料的均一性检验试验[J]. 气象科技, 2012,40(6):914-921 | | [26] | 赵琳琳 . 基于PW-MK及小波分析的辽阳降水特征研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2017,36(9):97-101 | | [27] | 魏凤英 . 现代气候统计诊断预测技术[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1999: 63-66 | | [28] | 郭芬芬, 肖晶晶, 张蕾 , 等. 1961—2013年中国农业界限温度的时空变化特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2016,35(2):489-498 | | [29] | 丁一汇, 任国玉, 石广玉 , 等. 气候变化国家评估报告(I):中国气候变化的历史和未来趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2006,2(1):3-9 | | [30] | 沈锦花, 胡波 . 浙江省近534年旱涝发生规律及突变分析[J]. 气象, 2005,31(10):76-78 |
|