Climate Change Research ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (4): 468-481.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.261
• Changes in Climate System • Previous Articles Next Articles
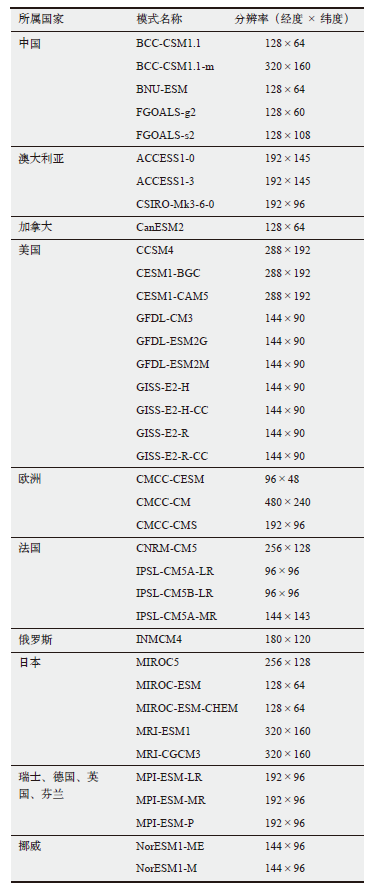
Comparison between CMIP6 and CMIP5 models in simulating historical spatiotemporal variations in radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface
WAN Zi-Wen1,2, WANG Wei1,2( ), LYU Heng1,2, QIU Pei-Yu3, LI Yu-Zhu1,2, LU Yang4
), LYU Heng1,2, QIU Pei-Yu3, LI Yu-Zhu1,2, LU Yang4
- 1 Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters (CIC-FEMD), Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology (NUIST), Nanjing 210044, China
2 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Agricultural Meteorology, NUIST, Nanjing 210044, China
3 Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing 100081, China
4 Meteorological Bureau of Shunde District, Foshan 528399, China
-
Received:2021-11-10Revised:2022-01-07Online:2022-07-30Published:2022-06-01 -
Contact:WANG Wei E-mail:wangw@nuist.edu.cn
Cite this article
WAN Zi-Wen, WANG Wei, LYU Heng, QIU Pei-Yu, LI Yu-Zhu, LU Yang. Comparison between CMIP6 and CMIP5 models in simulating historical spatiotemporal variations in radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(4): 468-481.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.261

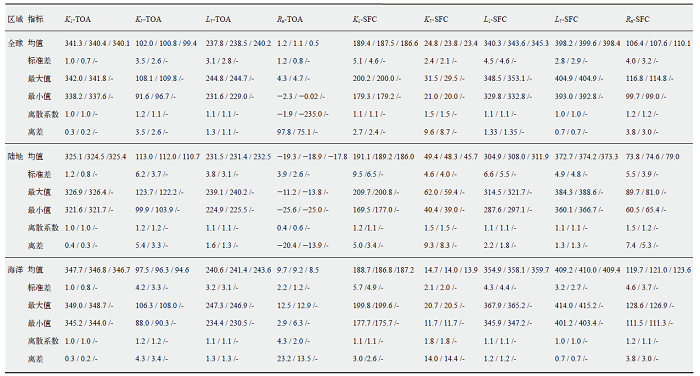
Fig. 1 Interannual variations in radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface for CMIP5 from 1850 to 2005, CMIP6 from 1850 to 2014 and CERES from 2001 to 2018. (Blue and red shading areas represent the one standard derivation among Earth System Models in CMIP5 and CMIP6, respectively)

Fig. 2 Geographical distribution of radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface from CERES and zonal means from CERES, CMIP5 and CMIP6 for the period 2001-2005

Fig. 3 Geographical distribution and zonal mean of CMIP5, CMIP6 radiation budgets deviation relative to CERES observation at the top of atmosphere and the surface for the period 2001-2005

Fig. 4 Geographical distribution of regions with large inter-model variability in radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface from CMIP5 models and CMIP6 models for the period 2001-2005
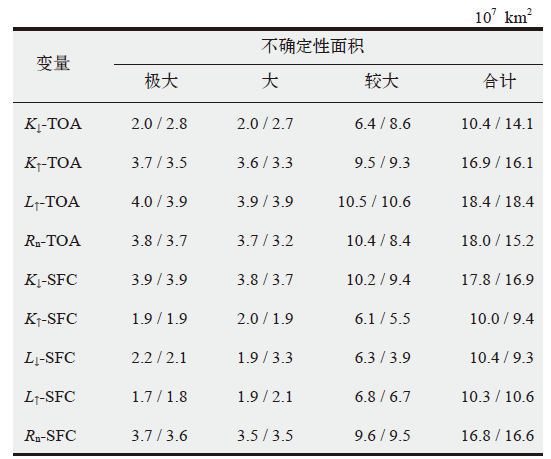 |
Table 4 Area of regions with large inter-model variability for radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface from CMIP5 models and CMIP6 models
 |
| [1] |
Stephens G L, Li J, Wild M, et al. An update on Earth’s energy balance in light of the latest global observations[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5 (10): 691-696. DOI: 10.1038/ngeo1580
doi: 10.1038/ngeo1580 URL |
| [2] |
Wild M. The global energy balance as represented in CMIP6 climate models[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2020, 55 (16): 553-577. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-020-05282-7
doi: 10.1007/s00382-020-05282-7 URL |
| [3] |
Wild M, Folini D, Hakuba M Z, et al. The energy balance over land and oceans: an assessment based on direct observations and CMIP5 climate models[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2015, 44 (11-12): 3393-3429. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-014-2430-z
doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2430-z URL |
| [4] |
Loeb N, Natividad M S, Su W Y, et al. CERES Top-of-Atmosphere Earth radiation budget climate data record: accounting for in-orbit changes in instrument calibration[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8 (182): 1-14. DOI: 10.3390/rs8030182
doi: 10.3390/rs8030182 URL |
| [5] |
Allen M R, Ingram J W. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle[J]. Nature: International Weekly Journal of Science, 2002, 419 (6903): 228-232. DOI: 10.1038/nature01092
doi: 10.1038/nature01092 |
| [6] |
DeAngelis A M, Qu X, Zelinka M D, et al. An observational radiative constraint on hydrologic cycle intensification[J]. Nature, 2015, 528 (7581): 249-253. DOI: 10.1038/nature15770
doi: 10.1038/nature15770 URL |
| [7] | Lee X. Fundamentals of boundary-layer meteorology[M]. Gewerbestrasse: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 22-24 |
| [8] |
Wang W, Chakraborty T C, Xiao W, et al. Ocean surface energy balance allows a constraint on the sensitivity of precipitation to global warming[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12 (2115): 1-9. DOI: 10.1038/S41467-021-22406-7
doi: 10.1038/S41467-021-22406-7 URL |
| [9] |
Wild M. Short-wave and long-wave surface radiation budgets in GCMs: a review based on the IPCC-AR4/CMIP3 models[J]. Dynamic Meteorology and Oceanography, 2008, 60 (5): 932-945. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0870.2008.00342.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0870.2008.00342 |
| [10] |
周天军, 陈梓明, 邹立维, 等. 中国地球气候系统模式的发展及其模拟和预估[J]. 气象学报, 2020, 78 (3): 332-350. DOI: 10.11676/qxxb2020.029.
doi: 10.11676/qxxb2020.029 |
|
Zhou T J, Chen Z M, Zou L W, et al. Development of climate and Earth System Models in China[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2020, 78 (3): 332-350. DOI: 10.11676/qxxb2020.029 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11676/qxxb2020.029 |
|
| [11] |
周天军, 邹立维, 陈晓龙. 第六次国际耦合模式比较计划(CMIP6) 评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15 (5): 445-456. DOI: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2019.193.
doi: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2019.193 |
|
Zhou T J, Zou L W, Chen X L. Commentary on the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6)[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15 (5): 445-456. DOI: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2019.193 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2019.193 |
|
| [12] |
赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 从检验CMIP5气候模式看CMIP6地球系统模式的发展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14 (6): 643-648. DOI: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2018.036.
doi: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2018.036 |
|
Zhao Z C, Luo Y, Huang J B. The detection of the CMIP5 climate model to see the development of CMIP6 Earth System Models[J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14 (6): 643-648. DOI: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2018.036 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2018.036 |
|
| [13] |
Wild M, Folini D, Schaer C, et al. The global energy balance from a surface perspective[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2013, 40 (11-12): 3107-3134. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-012-1569-8
doi: 10.1007/s00382-012-1569-8 URL |
| [14] |
Taylor K E, Stouffer R J, Meehl G A. An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design[J]. Bulletin of The American Meteorological Society, 2012, 93 (4): 485-498. DOI: 10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00094.1
doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00094.1 URL |
| [15] |
Veronika E, Sandrine B, Meehl G A, et al. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2016, 9 (5): 1937-1958. DOI: 10.5194/gmd-9-1937-2016
doi: 10.5194/gmd-9-1937-2016 URL |
| [16] |
Thornhill G, Collins W, Olivié D, et al. Climate-driven chemistry and aerosol feedbacks in CMIP6 Earth System Models[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2021, 21 (2): 1105-1126. DOI: 10.5194/acp-21-1105-2021
doi: 10.5194/acp-21-1105-2021 |
| [17] |
Wild M. Validation of general circulation model radiative fluxes using surface observations[J]. Journal of Climate, 1995, 8 (5): 1309-1324. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(1995)0082.0.CO;2
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1995)0082.0.CO;2 URL |
| [18] |
Wild M, Long C N, Ohmura A. Evaluation of clear-sky solar fluxes in GCMs participating in AMIP and IPCC-AR4 from a surface perspective[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2006, 111 (D1): 1-15. DOI: 10.1029/2005JD006118
doi: 10.1029/2005JD006118 |
| [19] |
赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 评估43个CMIP5模式模拟全球能量平衡能力[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2015 (3): 227-230. DOI: 10.3969/.issn.1673-1719.2015.03.010.
doi: 10.3969/.issn.1673-1719.2015.03.010 |
|
Zhao Z C, Luo Y, Huang J B. Assessment of global energy balance as simulated by 43 CMIP5 climate models[J]. Climate Change Reasearch, 2015 (3): 227-230. DOI: 10.3969/.issn.1673-1719.2015.03.010 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3969/.issn.1673-1719.2015.03.010 |
|
| [20] |
Wild M, Hakuba M Z, Folini D, et al. The cloud-free global energy balance and inferred cloud radiative effects: an assessment based on direct observations and climate models[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018, 52 (7-8): 4787-4812. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-018-4413-y
doi: 10.1007/s00382-018-4413-y URL |
| [21] |
Wild M, Folini D, Henschel F, et al. Projections of long-term changes in solar radiation based on CMIP5 climate models and their influence on energy yields of photovoltaic systems[J]. Solar Energy, 2015, 116 (6): 12-24. DOI: 10.1016/j.solener.2015.03.039
doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2015.03.039 URL |
| [22] |
Wild M, Ohmura A, Gilgen H, et al. Evaluation of downward longwave radiation in General Circulation Models[J]. Journal of Climate, 2001, 14 (15): 3227-3239. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(2001)0142.0.CO;2
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2001)0142.0.CO;2 URL |
| [23] |
Loeb N G, Doelling D R, Wang H, et al. Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Energy Balanced and Filled (EBAF) top-of-atmosphere (TOA) edition-4.0 data product[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017 (1): 895-918. DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0208.1
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0208.1 |
| [24] |
Trenberth K E, Fasullo J T, Kiehl J. Earth’s global energy budget[J]. Bulletin of The American Meteorological Society, 2009, 90 (3): 311-323. DOI: 10.1175/2008BAMS2634.1
doi: 10.1175/2008BAMS2634.1 URL |
| [25] |
Loeb N G, Wielicki B A, Doelling D R, et al. Toward optimal closure of the Earth’s Top-of-Atmosphere radiation budget[J]. Journal of Climate, 2009, 22 (3): 748-766. DOI: 10.1175/2008JCLI2637.1
doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2637.1 URL |
| [26] |
Von Schuckmann K, Palmer M D, Trenberth K E, et al. An imperative to monitor Earth’s energy imbalance[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2016, 6: 138-144. DOI: 10.1038/nclimate2876
doi: 10.1038/nclimate2876 URL |
| [27] |
Kato S, Rose F G, Rutan D A, et al. Surface irradiances of edition 4.0 Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Energy Balanced and Filled (EBAF) data product[J]. Journal of Climate, 2018, 31 (11): 4501-4527. DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0523.1
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0523.1 URL |
| [28] |
Li J, Sun Z, Liu Y, et al. Top-of-Atmosphere radiation budget and cloud radiative effects over the Tibetan Plateau and adjacent monsoon regions from CMIP6 simulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2021, 126 (9): 1-26. DOI: 10.1002/essoar.10505197.1
doi: 10.1002/essoar.10505197.1 |
| [29] |
Zhang X T, Liang S L, Wild M, et al. Analysis of surface incident shortwave radiation from four satellite products[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015 (165): 186-202. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.05.015
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.05.015 |
| [30] |
Gui S, Liang S, Li L. Evaluation of satellite-estimated surface longwave radiation using ground-based observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2010, 115 (D18): 1-16. DOI: 10.1029/2009JD013635
doi: 10.1029/2009JD013635 |
| [31] |
黄禄丰, 朱再春, 黄萌田, 等. 基于CMIP6模式优化集合平均预估21世纪全球陆地生态系统总初级生产力变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (5): 514-524. DOI: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.221.
doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.221 |
|
Huang L F, Zhu Z C, Huang M T, et al. Projection of gross primary productivity change of global terrestrial ecosystem in the 21st century based on optimal ensemble averaging of CMIP6 models[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17 (5): 514-524. DOI: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.221 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.221 |
|
| [32] |
Fläschner D, Mauritsen T, Stevens B. Understanding the intermodel spread in global-mean hydrological sensitivity[J]. Journal of Climate, 2016, 29 (2): 801-817. DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0351.1
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0351.1 URL |
| [33] |
Jung M, Reichstein M, Margolis H A, et al. Global patterns of land-atmosphere fluxes of carbon dioxide, latent heat, and sensible heat derived from eddy covariance, satellite, and meteorological observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2011, 116 (G3): 1-16. DOI: 10.1029/2010JG001566
doi: 10.1029/2010JG001566 |
| [34] |
Zhou C, Zelinka M D, Dessler A E, et al. The relationship between interannual and long-term cloud feedbacks[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42 (23): 10463-10469. DOI: 10.1002/2015GL066698
doi: 10.1002/2015GL066698 |
| [35] |
Zhou L J, Zhang M H, Bao Q, et al. On the incident solar radiation in CMIP5 models[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42 (6): 1930-1935. DOI: 10.1002/2015GL063239
doi: 10.1002/2015GL063239 URL |
| [36] |
Dolinar E K, Dong X, Xi B, et al. Evaluation of CMIP5 simulated clouds and TOA radiation budgets using NASA satellite observations[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2015, 44 (7-8): 2229-2247
doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2158-9 URL |
| [37] |
Schwarz M, Folini D, Yang S, et al. Changes in atmospheric shortwave absorption as important driver of dimming and brightening[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2020, 13: 110-115. DOI: 10.1038/s41561-019-0528-y
doi: 10.1038/s41561-019-0528-y URL |
| [1] | HUANG Lu-Feng, ZHU Zai-Chun, HUANG Meng-Tian, ZHAO Qian, MA Wei-Rui, ZENG Hui. Projection of gross primary productivity change of global terrestrial ecosystem in the 21st century based on optimal ensemble averaging of CMIP6 models [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(5): 514-524. |
| [2] | Duo-Ying JI,Qian ZHANG,Zhi-Cheng LUO,Yang-Xin CHEN. Short commentary on CMIP6 Carbon Dioxide Removal Model Intercomparison Project (CDRMIP) [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(5): 457-464. |
| [3] | Zhen-Ya SONG,Ying BAO,Fang-Li QIAO. Introduction of FIO-ESM v2.0 and its participation plan in CMIP6 experiments [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(5): 558-565. |
| [4] | Jian CAO,Li-Bin MA,Juan LI,WANG Bin,Bo WANG. Introduction of NUIST-ESM model and its CMIP6 activities [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(5): 566-570. |
| [5] | Xiao-Ge XIN,Tong-Wen WU,Jie ZHANG,Fang ZHANG,Wei-Ping LI,Yan-Wu ZHANG,Yi-Xiong LU,Yong-Jie FANG,Wei-Hua JIE,Li ZHANG,Min DONG,Xue-Li SHI,Jiang-Long LI,Min CHU,Qian-Xia LIU,Jing-Hui YAN. Introduction of BCC models and its participation in CMIP6 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(5): 533-539. |
| [6] | Yan-Luan LIN,Xiao-Meng HUANG,Yi-Shuang LIANG,Yi QIN,Shi-Ming XU,Wen-Yu HUANG,Fang-Hua XU,Li LIU,Yong WANG,Yi-Ran PENG,Lan-Ning WANG,Wei XUE,Hao-Huan FU,Guang-Jun ZHANG,Bin WANG,Rui-Zhe LI,Cheng ZHANG,Hui LU,Kun YANG,Yong LUO,Yu-Qi BAI,Zhen-Ya SONG,Min-Qi WANG,Wen-Jie ZHAO,Feng ZHANG,Jing-Heng XU,Xi ZHAO,Chun-Song LU,Yi-Qi LUO,Yi-Zhao CHEN,Yong HU,Qiang TANG,De-Xun CHEN,Guang-Wen YANG,Peng GONG. The Community Integrated Earth System Model (CIESM) from Tsinghua University and its plan for CMIP6 experiments [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(5): 545-550. |
| [7] | Xin-Yao RONG,Jian LI,Hao-Ming CHEN,Yu-Fei XIN,Jing-Zhi SU,Li-Juan HUA,Zheng-Qiu ZHANG. Introduction of CAMS-CSM model and its participation in CMIP6 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(5): 540-544. |
| [8] | Shi-Li YANG,Wen-Jie DONG,Jie-Ming CHOU,Chang-Xin LIU. Research progress for the bidirectional coupling of the Earth system model and integrated assessment model [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(4): 335-342. |
| [9] | Qi-Meng WU,Li-Guang WU,Jian CAO. Analysis of climate characteristics of tropical cyclone activities simulated by the NUIST Earth system model [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(2): 107-118. |
| [10] | Zhao Zongci Luo Yong. A Review on Evaluation Methods of Climate Modeling [J]. Climate Change Research, 2013, 9(1): 1-8. |
| [11] | . Atlantic Thermohaline Circulation and Abrupt Climate Changes [J]. Climate Change Research, 2007, 03(01): 1-007. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||