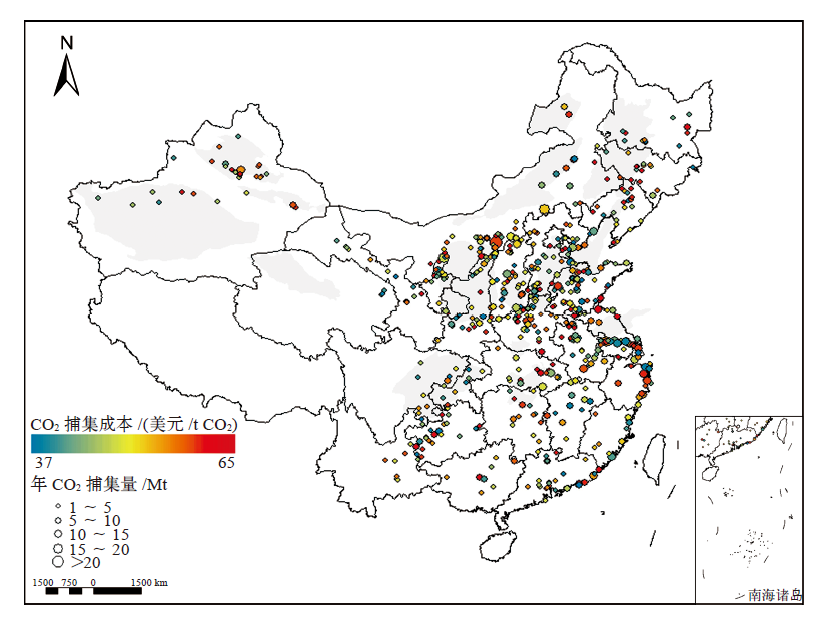
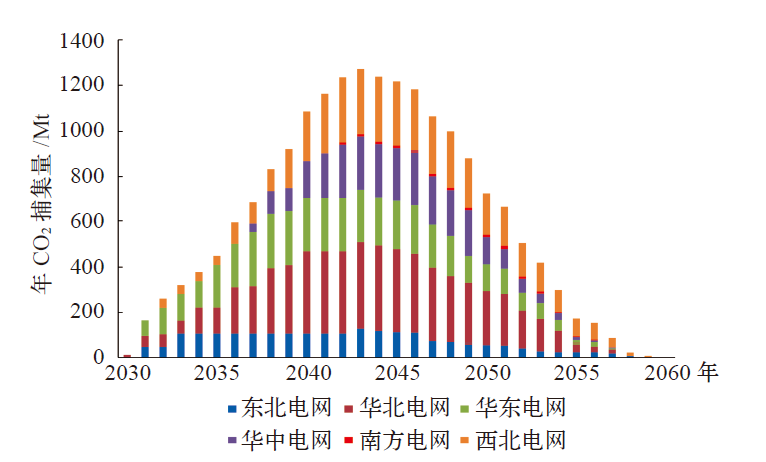
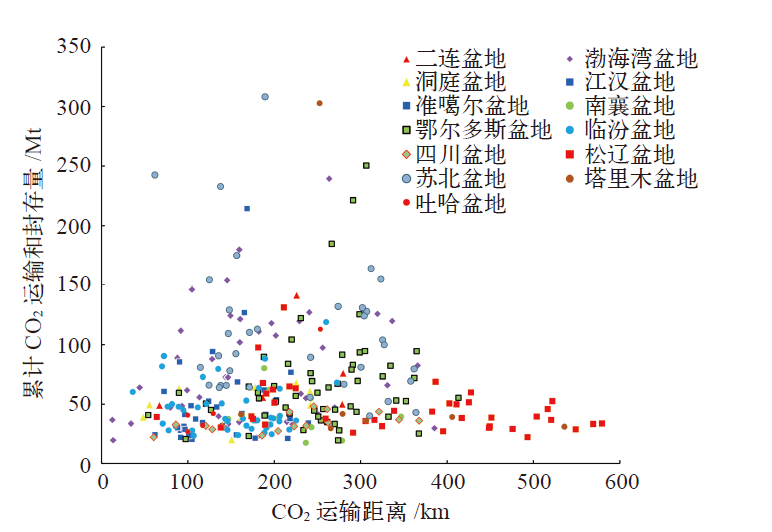
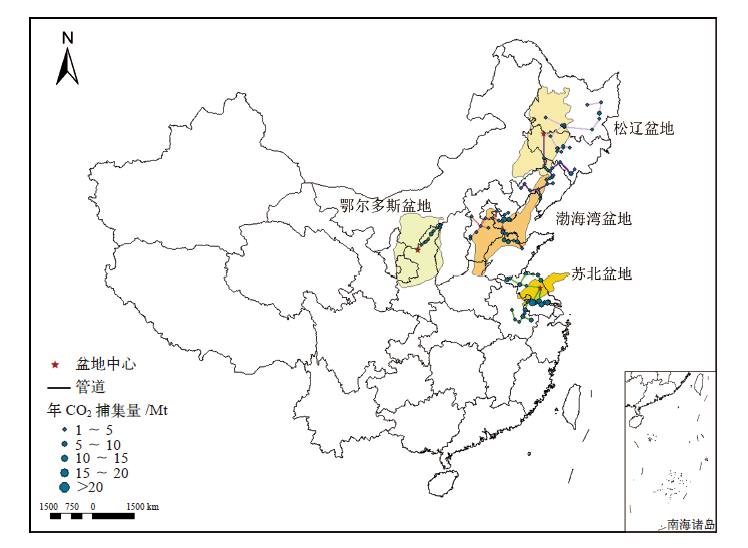
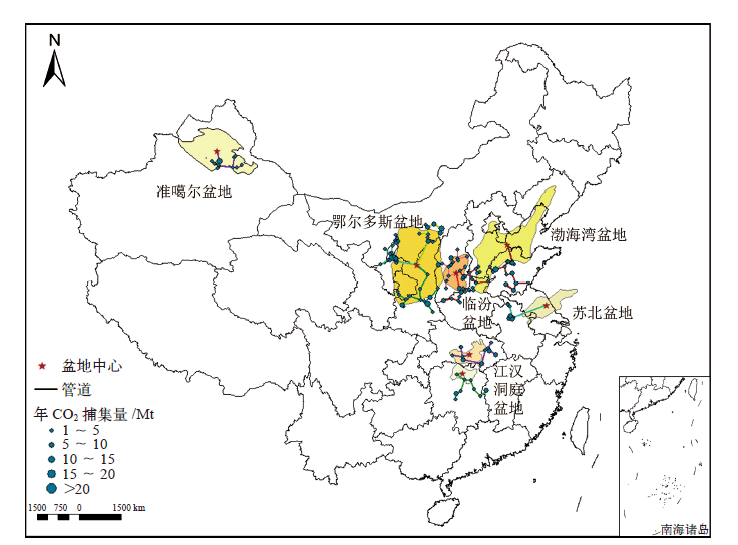
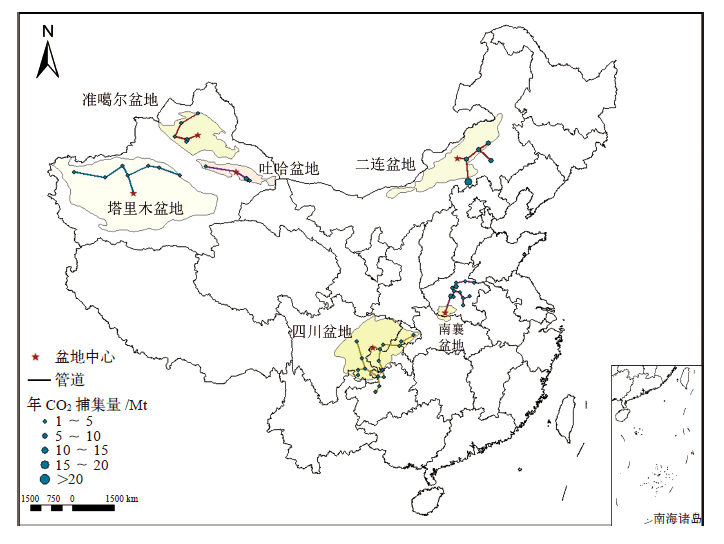
Climate Change Research ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (3): 261-271.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.258
Special Issue: “碳中和”目标下的关键节点——2035美丽中国低碳发展路径研究专栏
• Low carbon development path under the target of beautiful China 2035—a study of key milestone in carbon neutrality • Previous Articles Next Articles
The optimal layout of CCUS clusters in China’s coal-fired power plants towards carbon neutrality
- 1 School of Economics and Management, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing 100029, China
2 School of Environment, State Key Joint Laboratory of Environment Simulation and Pollution Control, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
3 Institute for Carbon Neutrality, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
4 Beijing Laboratory of Environmental Frontier Technologies, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2021-11-08Revised:2021-12-26Online:2022-05-30Published:2022-04-20 -
Contact:LU Xi E-mail:xilu@tsinghua.edu.cn
Cite this article
CHEN Wen-Hui, LU Xi. The optimal layout of CCUS clusters in China’s coal-fired power plants towards carbon neutrality[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(3): 261-271.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.258
| [1] |
Duan H, Zhou S, Jiang K, et al. Assessing China’s efforts to pursue the 1.5℃ warming limit[J]. Science, 2021, 372: 378-385
doi: 10.1126/science.aba8767 URL |
| [2] | 李政, 陈思源, 董文娟, 等. 碳约束条件下电力行业低碳转型路径研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41 (12): 3987-4001. |
| Li Z, Chen S Y, Dong W J, et al. Low carbon transition pathway of power sector under carbon emission constraints[J]. Proceedings of The CSEE, 2021, 41 (12): 3987-4001 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 中国电力企业联合会. 中国电力行业年度发展报告2021[R]. 北京: 中国电力行业协会, 2021. |
| China Electricity Conucle. China electric power industry annual development report 2021[R]. Beijing: China Electricity Council, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | IEA. Energy technology perspectives 2020: special report on clean energy innovation[R/OL]. 2020 [2021-11-08]. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/energy/energy-technology-perspectives-2020_ab43a9a5-en. |
| [5] |
Cui R Y, Hultman N, Cui D, et al. A plant-by-plant strategy for high-ambition coal power phaseout in China[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12: 1468
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21786-0 URL |
| [6] | 张贤. 碳中和目标下中国碳捕集利用与封存技术应用前景[J]. 可持续发展经济导刊, 2020 (12): 3. |
| Zhang X. The application prospect of CCUS in China under the target of carbon neutrality[J]. China WTO Tribune, 2020 (12): 3 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 蔡博峰, 李琦, 张贤, 等. 中国二氧化碳捕集利用与封存(CCUS) 年度报告(2021): 中国CCUS 路径研究[R]. 北京: 生态环境部环境规划院, 中国科学院武汉岩土力学研究所, 中国21世纪议程管理中心, 2021. |
| Cai B F, Li Q, Zhang X, et al. China carbon dioxide capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) annual report (2021): study on the CCUS pathway in China[R]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Environmental Planning, Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, The Administrative Center for China’s Agenda 21, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] |
Yang L, Lv H D, Jiang D L, et al. Whether CCS technologies will exacerbate the water crisis in China: a full life-cycle analysis[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 134: 110374. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.110374
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.110374 |
| [9] | 黄晶. 中国碳捕集利用与封存技术评估报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021. |
| Huang J. Assessment report on carbon capture utilization and storage technology in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 李阳. 碳中和与碳捕集利用封存技术进展[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2021. |
| Li Y. Progress in carbon neutrality and storage technology for carbon capture and utilization[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] |
Fan J L, Shen S, Wei S J, et al. Near-term CO2 storage potential for coal-fired power plants in China: a county-level source-sink matching assessment[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 279. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115878
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115878 |
| [12] |
Fan J L, Xu M, Wei S, et al. Carbon reduction potential of China’s coal-fired power plants based on a CCUS source-sink matching model[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021: 168. DOI: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105320
doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105320 |
| [13] |
Wang P T, Wei Y M, Yang B, et al. Carbon capture and storage in China’s power sector: optimal planning under the 2℃ constraint[J]. Applied Energy, 2020: 263. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114694
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114694 |
| [14] |
Wang F, Wang P, Wang Q, et al. Optimization of CCUS source-sink matching for large coal-fired units: a case of North China[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2018, 170: 042045
doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/170/4/042045 URL |
| [15] | Xu M, Zhang X, Shen S, et al. Assessment of potential, cost, and environmental benefits of CCS-EWR technology for coal-fired power plants in Yellow River basin of China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 292: 112717 |
| [16] |
Sun L, Chen W. Development and application of a multi-stage CCUS source-sink matching model[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 185: 1424-1432
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.01.009 URL |
| [17] | 汪芳, 秦积舜, 周体尧. 基于油藏CO2驱油潜力的CCUS源汇匹配方法[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37 (2): 51-56. |
| Wang F, Qin J S, Zhou T Y. CCUS source-sink matching method based on the potential of CO2 flooding[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37 (2): 51-56 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Zhu Q, Wang C, Fan Z, et al. Optimal matching between CO2 sources in Jiangsu province and sinks in Subei-Southern South Yellow Sea basin, China[J]. Greenhouse Gases: Science and Technology, 2019, 9: 95-105
doi: 10.1002/ghg.1835 URL |
| [19] | 魏宁, 刘胜男, 李小春. 中国煤化工行业开展CO2强化深部咸水开采技术的潜力评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (1): 70-78. |
| Wei N, Liu S N, Li X C. Evaluation on potential of CO2 enhanced water recovery deployment in China’s coal chemical industry[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17 (1): 70-78 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 科学技术部社会发展科技司, 中国21世纪议程管理中心. 中国碳捕集利用与封存技术发展路线图(2019版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019. |
| The Administrative Center for China’s Agenda 21, Department of Social Development Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology. Technology roadmap study of carbon capture, utilization and storage technologies in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | The Global Coal Plant Tracker. Global coal plant tracker[EB/OL]. 2021[2022-01-12]. https://globalenergymonitor.org/projects/global-coal-plant-tracker/ |
| [22] | Global Power Plant Database. Global power plant database v1.3.0[EB/OL]. 2018 [2022-01-06]. https://datasets.wri.org/dataset/globalpowerplantdatabase |
| [23] | 中国电力企业联合会. 关于公示2018年度全国火电300 MW、600 MW、1000 MW级机组能效水平对标结果的通知[EB/OL]. 2018 [2020-07-12]. |
| China Electricity Council. Notification of energy efficiency benchmarking results for 300 MW, 600 MW and 1000 MW class units of thermal power plants in 2018[EB/OL]. 2018 [2020-07-12]. http://www.chinapower.com.cn/zxy/jznxdb/20200604/21216.html (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 生态环境部. 关于公布全国燃煤机组脱硫脱硝设施等重点大气污染减排工程名单的公告[EB/OL]. 2014 [2020-07-12]. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Notice on the list of key air pollution emission reduction projects such as desulfurization and denitrification facilities of coal-fired power units in China[EB/OL]. 2014 [2020-07-12]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgg/201407/t20140711_278584.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 中国电力企业联合会. 电力工业统计资料汇编(2019)[M]. 北京: 中国电力企业联合会, 2020. |
| China Electricity Council. Compilation of statistics of electric power industry (2019)[M]. Beijing: China Electricity Council, 2020 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 电力规划设计总院. 火电工程限额设计参考造价指标(2019年水平)[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2020. |
| China Electric Power Planning & Engineering Institute. Reference cost index for quota design of thermal power project (2019)[M]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2020 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] |
Hu B, Zhai H. The cost of carbon capture and storage for coal-fired power plants in China[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2017, 65: 23-31
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2017.08.009 URL |
| [28] |
Li B H, Zhang N, Smith R. Simulation and analysis of CO2 capture process with aqueous Monoethanolamine solution[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 161: 707-717
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.07.010 URL |
| [29] | Li K K, Cousins A, Yu H, et al. Systematic study of aqueous Monoethanolamine-based CO2 capture process: model development and process improvement[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2016, 4: 23-39 |
| [30] |
Li K, Wardhaugh L, Feron P, et al. Systematic study of aqueous Monoethanolamine (MEA)-based CO2 capture process (II): techno-economic assessment of the MEA process and its improvements[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 165: 648-659
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.12.109 URL |
| [31] |
Oh S Y, Binns M, Cho H, et al. Energy minimization of MEA-based CO2 capture process[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 169: 353-362
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.02.046 URL |
| [32] |
Singh S, Lu H R, Cui Q, et al. China baseline coal-fired power plant with post-combustion CO2 capture: 2. Techno-economics[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2018, 78: 429-436
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2018.09.012 URL |
| [33] |
Ye B, Jiang J, Zhou Y, et al. Technical and economic analysis of amine-based carbon capture and sequestration at coal-fired power plants[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 222: 476-487
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.050 URL |
| [34] |
Rubin E S. Understanding the pitfalls of CCS cost estimates[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2012, 10: 181-190
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2012.06.004 URL |
| [35] |
Zhai H, Rubin E S. A techno-economic assessment of hybrid cooling systems for coal- and natural-gas-fired power plants with and without carbon capture and storage[J]. Environmental Science Technology, 2016, 50: 4127-4134
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b00008 URL |
| [36] |
Zhai H, Rubin E S. Technical and economic assessments of ionic liquids for pre-combustion CO2 capture at IGCC power plants[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 114: 2166-2172
doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1353 URL |
| [37] |
Wei Y M, Kang J N, Liu L C, et al. A proposed global layout of carbon capture and storage in line with a 2℃ climate target[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2021, 11: 112-118
doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-00960-0 URL |
| [38] |
Wei N, Li X C, Wang Q, et al. Budget-type techno-economic model for onshore CO2 pipeline transportation in China[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2016, 51: 176-192
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2016.05.010 URL |
| [39] |
Wei N, Li X C, Dahowski R T, et al. Economic evaluation on CO2-EOR of onshore oil fields in China[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2015, 37: 170-181
doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.01.014 URL |
| [40] | 魏宁, 姜大霖, 刘胜男, 等. 国家能源集团燃煤电厂CCUS改造的成本竞争力分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40 (4): 1258-1265, 1416. |
| Wei N, Jiang D L, Liu S N, et al. Cost competitiveness analysis of retrofitting CCUS to coal-fired power plants[J]. Proceedings of The CSEE, 2020, 40 (4): 1258-1265, 1416 (in Chinese) | |
| [41] |
Sun L L, Dou H G, Li Z P, et al. Assessment of CO2 storage potential and carbon capture, utilization and storage prospect in China[J]. Journal of The Energy Institute, 2018, 91: 970-977
doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2017.08.002 URL |
| [42] | 能源基金会. 中国现代化的新征程: “十四五”到碳中和的新增长故事[EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-11-08]. https://www.efchina.org/Reports-en/report-lceg-20201210-en. |
| Energy Foundation. Comprehensive report on China’s carbon neutrality 2020: a new journey of China’s modernization: The 14th Five-year Plan to carbon neutrality[EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-11-08]. https://www.efchina.org/Reports-en/report-lceg-20201210-en. (in Chinese) |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||