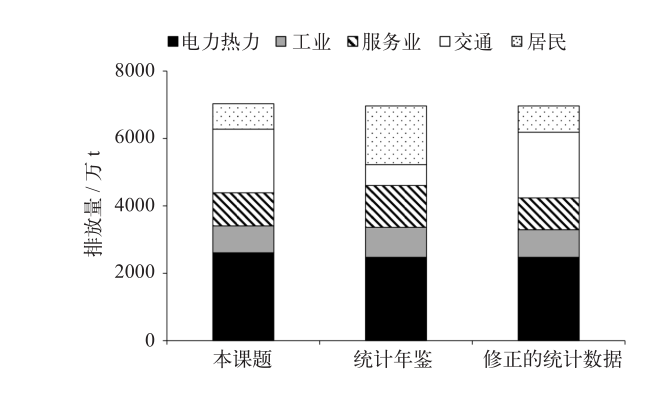
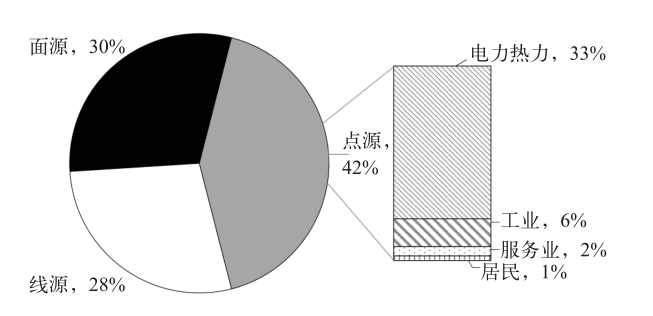
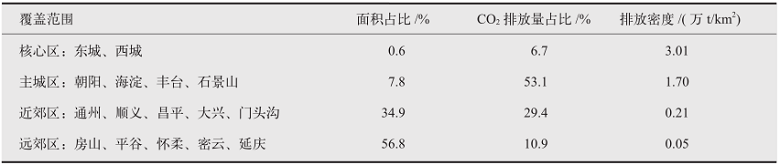
Climate Change Research ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (2): 188-195.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.192
• Greenhouse Gas Emissions • Previous Articles Next Articles
A high spatial resolution CO2 emission inventory in Beijing
LIAO Hong-Yun1( ), ZHAO Meng1(
), ZHAO Meng1( ), LI Yan-Xia2
), LI Yan-Xia2
- 1 Energy Research Institute of National Development and Reform Commission, Beijing 100038, China
2 Key Laboratory of Enhanced Heat Transfer and Energy Conservation, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
-
Received:2021-08-27Revised:2021-09-16Online:2022-03-30Published:2022-01-06
Cite this article
LIAO Hong-Yun, ZHAO Meng, LI Yan-Xia. A high spatial resolution CO2 emission inventory in Beijing[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(2): 188-195.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.192
| [1] | 蒋小谦, 房伟权, 庄贵阳, 等. 城市温室气体核算工具2.0 [R/OL]. 2015 [2021-03-10]. http://www.wri.org.cn/node/41204. |
| Jiang X Q, Fang W Q, Zhuang G Y, et al. Urban greenhouse gas accounting tools [R/OL]. 2015 [2021-03-10]. http://www.wri.org.cn/node/41204 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 绿色创新发展中心. 低碳试点城市峰值研究及绿色转型工作进展情况概览 [R/OL]. 2017 [2021-03-10]. http://www.igdp.cn. |
| Innovative Green Development Program. Overview of research on peak value of low carbon pilot cities and progress of green transformation [R/OL]. 2017 [2021-03-10]. http://www.igdp.cn (in Chinese) | |
| [3] |
Oda T, Maksyutov S, Andres R J. The open-source data inventory for anthropogenic CO2, version 2016 (ODIAC2016): a global monthly fossil fuel CO2 gridded emissions data product for tracer transport simulations and surface flux inversions[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2018, 10(1):87-107
doi: 10.5194/essd-10-87-2018 URL |
| [4] | Janssens-Maenhout G, Crippa M, Guizzardi D, et al. EDGAR v4.3.2 global atlas of the three major greenhouse gas emissions for the period 1970 & 2012[J]. Earth System Science Data Discussions, 2019, 11:959-1002 |
| [5] | Zheng B, Tong D, Li M, et al. Trends in China's anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 18(19):14095-14111 |
| [6] | Wang R S, Tao P, Ciais P, et al. High-resolution mapping of combustion processes and implications for CO2 emissions[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 12(8):21211-21239 |
| [7] | Liu M, Wang H, Oda T, et al. Refined estimate of China's CO2 emissions in spatiotemporal distributions[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 13(21):10873-10882 |
| [8] |
Cai B S, Liang S, Zhou J, et al. China high resolution emission database (CHRED) with point emission sources, gridded emission data, and supplementary socioeconomic data[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2018, 129:232-239
doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.036 URL |
| [9] |
Han P F, Zeng N, Oda T, et al. A city-level comparison of fossil-fuel and industry processes-induced CO2 emissions over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from eight emission inventories[J]. Carbon Balance and Management, 2020, 15(1). DOI: 10.1186/s13021-020-00163-2
doi: 10.1186/s13021-020-00163-2 |
| [10] | 王庆一. 中国能源统计系统改革的几点建议 [R/OL]. 自然资源保护协会, 2014 [2021-06-01]. http://www.nrdc.cn/information/informationinfo?id=122&cook=2. |
| Wang Q Y. Recommendations for China energy statistics [R/OL]. Natural Resources Defense Council, 2014 [2021-06-01]. http://www.nrdc.cn/information/informationinfo?id=122&cook=2 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 北京统计局. 北京统计年鉴2018 [M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018. |
| Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Beijing statistical yearbook 2018 [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2018 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 北京市统计局. 北京市2019年国民经济和社会发展统计公报 [EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-02-12]. http://tjj.beijing.gov.cn/tjsj_31433/tjgb_31445/ndgb_31446/202003/t20200302_1673343.html. |
| Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics. Statistical bulletin of Beijing's national economic and social development in 2019 [EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-02-12] http://tjj.beijing.gov.cn/tjsj_31433/tjgb_31445/ndgb_31446/202003/t20200302_1673343.html (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 生态环境部. 北京2013—2018年大气污染治理历程 [R/OL]. 2019 [2021-02-12]. https://www.cenews.com.cn/pollution_ctr/xydt/201909/t20190925_910689.html. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of The People's Republic of China. The course of air pollution control in Beijing from 2013 to 2018[R/OL]. 2019 [2021-02-12]. https://www.cenews.com.cn/pollution_ctr/xydt/201909/t20190925_910689.html (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 全国汽车标准化技术委员会. GB/T 15089 机动车辆及挂车分类2001[R/OL]. 2001 [2020-01-01]. https://www.waizi.org.cn/bz/88997.html. |
| National Technical Committee of Auto Standardization. GB/T 15089 classification of power-driven vehicles and trailers. [R/OL]. 2001 [2020-01-01]. https://www.waizi.org.cn/bz/88997.html (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 36670—2018 城市道路交通组织设计规范 [R/OL]. 2018 [2021-02-12]. https://max.book118.com/html/2018/1024/7122021024001154.shtm. |
| National Standardization Administration. GB/T 36670—2018 guideline on the design of traffic operation of urban roads [R/OL]. 2018 [2021-02-12]. https://max.book118.com/html/2018/1024/7122021024001154.shtm (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 国家发展和改革委员会应对气候变化司. 省级温室气体清单编制指南(试行) [R/OL]. 2011 [2021-02-12]. http://cn.edcmee.org.cn/ptfb/zcbz/202106/P020210601177040314696.pdf. |
| Department of Climate Change, National Development and Reform Commission. Guidelines for the compilation of provincial greenhouse gas inventories (Trial) [R/OL]. 2011 [2021-02-12]. http://cn.edcmee.org.cn/ptfb/zcbz/202106/P020210601177040314696.pdf (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 陈操操, 邱大庆, 于凤菊, 等. 北京市燃气工业锅炉CO2排放因子及不确定性分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(8):1-10. |
| Chen C C, Qiu D Q, Yu F J, et al. Carbon dioxide emissions factor of nature gas boiler and its uncertainty in Beijing[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(8):1-10 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Li Y, Lv C, Yang N, et al. A study of high temporal-spatial resolution greenhouse gas emissions inventory for on-road vehicles based on traffic speed-flow model: a case of Beijing[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 277:122419
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122419 URL |
| [19] | 国家统计局. 中国能源统计年鉴2018 [M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018. |
| National Bureau of Statistics. China energy statistical yearbook 2018 [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2018 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 徐新良. 中国GDP空间分布公里网格数据集 [DB/OL]. 中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心数据注册与出版系统, 2017 [2020-01-01]. http://www.resdc.cn/DOI. |
| Xu X L. Kilometer grid data set of China's GDP spatial distribution [DB/OL]. Data Registration and Publishing System of Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017 [2020-01-01]. http://www.resdc.cn/DOI (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 戴彦德, 康艳兵, 熊小平, 等. 2050中国能源和碳排放情景暨能源转型与低碳发展路线图[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2017. |
| Dai Y D, Kang Y B, Xiong X P, et al. Energy development and carbon emission scenarios towards 2050 energy transition and low carbon development roadmap for China [M]. Beijing: China Environment Press, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | IPCC. 2019 refinement to the 2006 IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories [R/OL]. 2019 [2020-01-01]. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/2019-refinement-to-the-2006-ipcc-guidelines-for-national-greenhouse-gas-inventories/ |
| [23] | 联合国环境规划署. 北京二十年大气污染治理历程与展望 [R/OL]. 2019 [2021-02-12]. http://sthjj.beijing.gov.cn/bjhrb/index/ztzl/bj20ndqwrzllcyzw/index.html. |
| UNEP. A review of 20 years' air pollution control in Beijing [R/OL]. 2019 [2021-02-12]. http://sthjj.beijing.gov.cn/bjhrb/index/ztzl/bj20ndqwrzllcyzw/index.html (in Chinese) |
| [1] | YANG Nan, LI Yan-Xia, ZHAO Meng, LYU Chen, LIU Zhong-Liang, CHEN Sha. Establishment of a CO2 direct emission accounting model for cement clinker manufacturers [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(1): 79-87. |
| [2] | Rui-Qiang YUAN, Ya-Nan WANG, Peng WANG, Shi-Qin WANG, Yu-Hong CHEN. An analysis of precipitation concentration variation characteristics and influential factors in Shanxi province, China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(1): 11-20. |
| [3] | . National Greenhouse Gas Emission Inventory Development in the Context of International Climate Negotiation [J]. Climate Change Research, 2012, 8(5): 372-377. |
| [4] | Songli Zhu. Good Practices in Australia for Greenhouse Gas Inventory Development [J]. Climate Change Research, 2011, 7(3): 204-209. |
| [5] | Tao Yun. Evolutional Characteristics of Utilizable Precipitation over Yunnan Province from 1961 to 2006 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2010, 6(01): 8-14. |
| [6] | Cao Guoliang;Zhang Xiaoye; Wang Yaqiang;et al.. Inventory of Black Carbon Emission from China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2007, 03(00): 75-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||