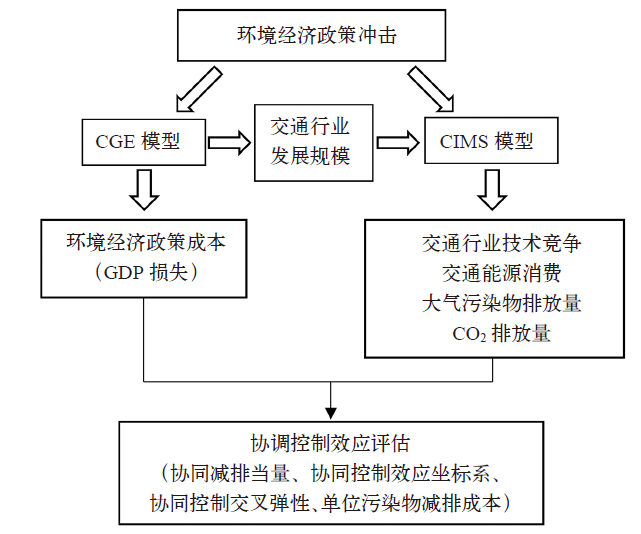
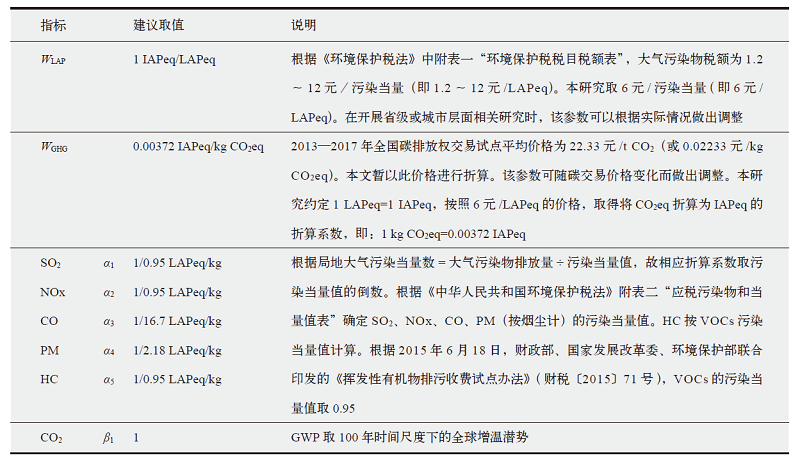
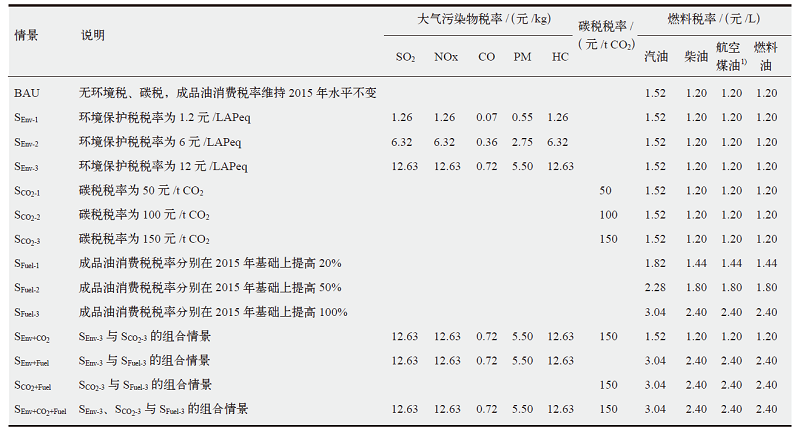
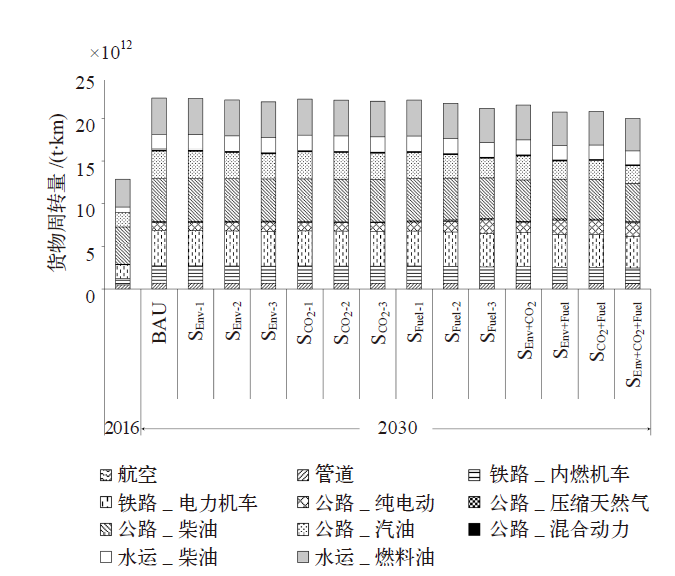
| [1] |
生态环境部,国家统计局,农业农村部. 关于发布《第二次全国污染源普查公报》的公告[EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-04-19]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/202006/t20200610_783547.html.
|
|
Ministry of Ecology and Environment, National Bureau of Statistics, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs. Announcement of publishing the “second national survey of pollution sources bulletin” [EB/OL]. 2020 [2021-04-19]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk01/202006/t20200610_783547.html (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
生态环境部. 中华人民共和国气候变化第二次两年更新报告 [R/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-20]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/ydqhbh/wsqtkz/201907/P020190701765971866571.pdf.
|
|
Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Second biennial update report on climate change of the People’s Republic of China [R/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-20]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/ydqhbh/wsqtkz/201907/P020190701765971866571.pdf (in Chinese)
|
| [3] |
北京市生态环境局. 北京市PM2.5来源解析正式发布 [EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-04-19]. http://sthjj.beijing.gov.cn/bjhrb/index/xxgk69/zfxxgk43/fdzdgknr2/xwfb/607219/index.html.
|
|
Beijing Municipal Ecology and Environmental Bureau. Beijing released the PM2.5 source analysis result [EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-04-19]. http://sthjj.beijing.gov.cn/bjhrb/index/xxgk69/zfxxgk43/fdzdgknr2/xwfb/607219/index.html (in Chinese)
|
| [4] |
北京市生态环境局. 最新科研成果新一轮北京市PM2.5来源解析正式发布[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-04-19]. http://sthjj.beijing.gov.cn/bjhrb/index/xxgk69/zfxxgk43/fdzdgknr2/xwfb/832588/index.html.
|
|
Beijing Municipal Ecology and Environmental Bureau. Beijing released the latest scientific research results of PM2.5 source [EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-04-19]. http://sthjj.beijing.gov.cn/bjhrb/index/xxgk69/zfxxgk43/fdzdgknr2/xwfb/832588/index.html (in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
中国新闻网. 济南PM2.5源解析结果:燃煤扬尘对污染贡献率超半 [EB/OL]. 2014 [2021-04-19]. http://www.chinanews.com/sh/2014/10-30/6734238.shtml.
|
|
China News. Jinan released PM2.5 source analysis results: coal-burning dust contributes more than half of pollution [EB/OL]. 2014 [2021-04-19]. http://www.chinanews.com/sh/2014/10-30/6734238.shtml (in Chinese)
|
| [6] |
济南市人民政府网. 济南市2017年度环境空气PM10、PM2.5来源解析结果发布[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-04-19]. http://www.jinan.gov.cn/art/2018/5/18/art_28939_2636331.html.
|
|
Jinan Government. Jinan released the source analysis results of PM10 and PM2.5 in 2017 [EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-04-19]. http://www.jinan.gov.cn/art/2018/5/18/art_28939_2636331.html (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
生态环境部. 关于统筹和加强应对气候变化与生态环境保护相关工作的指导意见[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-04-19]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/202101/t20210113_817221.html.
|
|
Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Guiding opinions on coordinating and strengthening the work related to climate change and ecological environmental protection [EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-04-19]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk03/202101/t20210113_817221.html (in Chinese)
|
| [8] |
生态环境部. 中华人民共和国环境保护税法(2018年修正)[Z]. 北京: 中国法制出版社, 2018.
|
|
Ministry of Ecology and Environmental of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental protection law of the People’s Republic of China (2018 revision)[Z]. Beijing: China Legal Publishing House, 2018 (in Chinese)
|
| [9] |
Beevers S D, Carslaw D C. The impact of congestion charging on vehicle emissions in London[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39:1-5
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.10.001
URL
|
| [10] |
Brand C, Anable J, Tran M. Accelerating the transformation to a low carbon passenger transport system: the role of car purchase taxes, feebates, road taxes and scrappage incentives in the UK[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2013, 49:132-148
doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2013.01.010
URL
|
| [11] |
Gupta M, Bandyopadhyay K R, Sanjay K S. Measuring effectiveness of carbon tax on Indian road passenger transport: a system dynamics approach[J]. Energy Economics, 2019, 81:341-354
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2019.03.013
URL
|
| [12] |
周全, 葛察忠, 李红祥. 国际绿色交通经验及借鉴[J]. 环境保护, 2011 (22):67-69.
|
|
Zhou Q, Ge C Z, Li H X. International experience and reference of green transportation[J]. Environmental Protection, 2011 (22):67-69 (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
何平林, 乔雅, 宁静, 等. 环境税双重红利效应研究:基于OECD 国家能源和交通税的实证分析[J]. 中国软科学, 2019 (4):33-49.
|
|
He P L, Qiao Y, Ning J, et al. An empirical study on the double dividend effect of environmental tax: based on the energy tax and vehicle traffic tax in OECD countries[J]. China Soft Science, 2019 (4):33-49 (in Chinese)
|
| [14] |
冯相昭, 蔡博峰. 中国道路交通系统的碳减排政策综述[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2012, 22(8):10-15.
|
|
Feng X Z, Cai B F. A review on policies of reducing carbon emission in China’s urban road transport system[J]. China Population’ Resources and Environment, 2012, 22(8):10-15 (in Chinese)
|
| [15] |
Mao X Q, Yang S Q, Liu Q, et al. Achieving CO2 emission reduction and the co-benefits of local air pollution abatement in the transportation sector of China[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2012, 21:1-13
|
| [16] |
符淼, 孙宇. 交通碳税对我国碳排放、社会福利及税收收入的影响分析:基于TREMOVE模型[J]. 重庆工商大学学报: 社会科学版, 2015, 32(2):8-15.
|
|
Fu M, Sun Y. Analysis on the impact of transportation carbon taxes on CO2 emissions’ social welfare and tax revenue in China: based on TREMOVE model[J]. Journal of Chongqing Technology and Business University: Social Sciences Edition, 2015, 32(2):8-15 (in Chinese)
|
| [17] |
杨升. 我国道路交通环境税政策对居民健康影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2016.
|
|
Yang S. The study on residents’ health effect of China’s road transport environmental tax[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2016 (in Chinese)
|
| [18] |
Liu L, Wang K, Wan S S, et al. Assessing energy consumption, CO2 and pollutant emissions and health benefits from China’s transport sector through 2050[J]. Energy Policy, 2018, 116:382-396
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2018.02.019
URL
|
| [19] |
张强. 丝绸之路经济带(国内段)交通运输低碳发展及税收政策研究[D]. 陕西: 陕西师范大学, 2018.
|
|
Zhang Q. Research on low-carbon development and tax policy of transportation in the Silk Road Economic Belt (domestic section)[D]. Shaanxi: Shaanxi Normal University, 2018 (in Chinese)
|
| [20] |
Qiu R, Xu J P, Xie H P, et al. Carbon tax incentive policy towards air passenger transport carbon emissions reduction[J]. Transportation Research Part D, 2020, 85:102441
doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2020.102441
URL
|
| [21] |
毛显强, 曾桉, 刘胜强, 等. 钢铁行业技术减排措施硫、氮、碳协同控制效应评价研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012 (5):1253-1260.
|
|
Mao X Q, Zeng A, Liu S Q, et al. Assessment of SO2, NOx and CO2 co-control effects by technological reduction measures in iron & steel industry[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012 (5):1253-1260 (in Chinese)
|
| [22] |
邢有凯, 毛显强, 冯相昭, 等. 城市蓝天保卫战行动协同控制局地大气污染物和温室气体效果评估: 以唐山市为例[J]. 中国环境管理, 2020, 12(4):20-28.
|
|
Xing Y K, Mao X Q, Feng X Z, et al. An effectiveness evaluation of co-controlling local air pollutants and GHGs by implementing blue sky defense action at city level: a case study of Tangshan city[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 12(4):20-28 (in Chinese)
|
| [23] |
Hu T, Mao X Q, Lu X D, et al. Air pollutants and greenhouse gas emissions co-control evaluation in the People’s Republic of China[R/OL]. 2020 [2021-02-20]. https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/664391/eawp-029-air-pollutants-ghg-co-control-evaluation-prc.pdf
|
 ), LIU Zheng-Yan3, MAO Xian-Qiang1(
), LIU Zheng-Yan3, MAO Xian-Qiang1( ), GAO Yu-Bing1,4, HE Feng1,4, YU Hong5
), GAO Yu-Bing1,4, HE Feng1,4, YU Hong5