Climate Change Research ›› 2021, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (2): 195-203.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.103
• Adaptation to Climate Change • Previous Articles Next Articles
Nature-based Solution: potential and economic benefits of carbon removal or carbon emission reduction through forestry approaches
TIAN Hui-Ling1, ZHU Jian-Hua1,2,3( ), LI Chen-Yu1, XIAO Wen-Fa1,2,3
), LI Chen-Yu1, XIAO Wen-Fa1,2,3
- 1 Research Institute of Forest Ecology, Environment and Protection, Chinese Academy of Forestry/Key Laboratory of Forest Ecology and Environment of National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Beijing 100091, China
2 Scientific and Technological Collaborative Innovation Center for the Yangtze River Economic Belt Ecological Conservation, National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Beijing 100091, China
3 Co-innovation Center for Sustainable Forestry in Southern China, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing 210037, China
-
Received:2020-05-25Revised:2020-07-02Online:2021-03-30Published:2021-04-02 -
Contact:ZHU Jian-Hua E-mail:zhucool@caf.ac.cn
Cite this article
TIAN Hui-Ling, ZHU Jian-Hua, LI Chen-Yu, XIAO Wen-Fa. Nature-based Solution: potential and economic benefits of carbon removal or carbon emission reduction through forestry approaches[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(2): 195-203.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.103
| [1] |
Eggermont H, Balian E, Azevedo J, et al. Nature-based Solutions: new influence for environmental management and research in Europe[J]. GAIA: Ecological Perspectives for Science and Society, 2015, 24(4):243-248
doi: 10.14512/gaia.24.4.9 URL |
| [2] | Cohen-Shacham E, Walters G, Janzen C, et al. Nature-based Solutions to address global societal challenges [R/OL]. 2016 [2020-05-03]. https://www.iucn.org/commissions/commission-ecosystem-management/our-work/nature-based-solutions |
| [3] | MacKinnonm K, Sobrevila C, Hickey V. Biodiversity, climate change, and adaptation: Nature-based Solutions from the World Bank portfolio [R/OL]. Washington, DC: World Bank, 2008 [2020-05-03]. http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/149141468320661795/Biodiversity-climate-change-and-adaptation-nature-based-solutions-from-the-World-Bank-portfolio |
| [4] | IUCN. No time to lose: make full use of Nature-based Solutions in the post-2012 climate change regime [R/OL]. 2009 [2020-05-03]. https://www.iucn.org/sites/dev/files/import/downloads/iucn_position_paper_unfccc_cop_15.pdf |
| [5] |
Griscoma B W, Adamsa J, Ellis P W, et al. Natural climate solutions[J]. PNAS, 2017, 114(44):11645-11650
URL pmid: 29078344 |
| [6] | 中国国家发展和改革委员会. 中国应对气候变化国家方案[R/OL]. 2007 [2020-05-03]. http://www.ce.cn/xwzx/gnsz/szyw/200706/04/t20070604_11594800.shtml. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. China’s national climate change program [R/OL]. 2007 [2020-05-03]. http://www.ce.cn/xwzx/gnsz/szyw/200706/04/t20070604_11594800.shtml (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 李艳芳. 落实NbS的切实行动: 深度发掘林业碳汇的价值[J]. 可持续发展经济导刊, 2019 (11):19-20. |
| Li Y F. Exploring the value of forestry carbon sink is an important action to implement NbS[J]. Economic Guide for Sustainable Development, 2019 (11):19-20 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] |
Pan Y, Birdsey R A, Fang J, et al. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests[J]. Science, 2011, 333: 988-993
URL pmid: 21764754 |
| [9] | European Union. Towards an EU research and innovation policy agenda for Nature-based Solutions & renaturing cities [R/OL]. 2015 [2020-05-06]. https://publications.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/fb117980-d5aa-46df-8edc-af367cddc202 |
| [10] | 张小全, 谢茜, 曾楠. 基于自然的气候变化解决方案[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(3):336-344. |
| Zhang X Q, Xie X, Zeng N. Nature-based Solutions to address climate change[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(3):336-344 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | Shukla P R, Skea J, Calvo Buendia E, et al. Summary for policymakers [M/OL]//IPCC. Climate change and land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems. 2019 [2020-05-03]. https://www.ipcc.ch/srccl/chapter/summary-for-policymakers/ |
| [12] | Masson-Delmotte V P, Zhai H O, Pörtner D, , et al. Summary for policymakers [M/OL]//IPCC. Global warming of 1.5℃. 2018 [2020-05-03]. https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15/chapter/spm/ |
| [13] | UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme). The emissions gap report 2015 [M]. Nairobi: UNEP, 2015: 98 |
| [14] | UNEP. Compendium of contributions Nature-based Solutions [R]. Nairobi: Nature-based Solutions (NbS) Facilitation Team, 2019: 22-171 |
| [15] | IPCC. Climate change 2014: mitigation of climate change [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2015 |
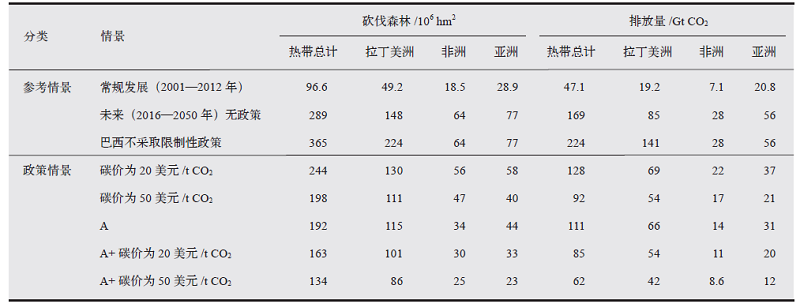
| [16] | Busch J, Engelmann J. Cost-effectiveness of reducing emissions from tropical deforestation, 2016-2050[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2018, 13: 1748-9326 |
| [17] | 柯水发, 李周, 张莹. 中国应对气候变化的造林行动及绿色就业潜力测算[J]. 林业经济, 2012 (7):34-40. |
| Ke S F, Li Z, Zhang Y. A forestation action to tackle climate change and green employment potential estimation[J]. Forestry Economy, 2012 (7):34-40 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Yao Y, Piao S, Wang T. Future biomass carbon sequestration capacity of Chinese forests[J]. Science Bulletin, 2018, 63: 1108-1117
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.07.015 URL |
| [19] |
He N, Wen D, Zhu J, et al. Vegetation carbon sequestration in Chinese forests from 2010 to 2050[J]. Global Change Biology, 2016, 23(4):1575-1584
doi: 10.1111/gcb.13479 URL pmid: 27562684 |
| [20] |
Zhang C, Ju W, Chen J, et al. Sustained biomass carbon sequestration by China’s forests from 2010 to 2050[J]. Forests, 2018, 9(11):689
doi: 10.3390/f9110689 URL |
| [21] | 李奇, 朱建华, 冯源, 等. 中国森林乔木林碳储量及其固碳潜力预测[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(3):287-294. |
| Li Q, Zhu J H, Feng Y, et al. Carbon storage and carbon sequestration potential of the forest in China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(3):287-294 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] |
Yang Y H, Li P, Ding J Z, et al. Increased topsoil carbon stock across China’s forests[J]. Global Change Biology, 2014, 20: 2687-2696
URL pmid: 24453073 |
| [23] |
Shi S W, Han P F. Estimating the soil carbon sequestration potential of China’s grain for green project[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2014, 28: 1279-1294
doi: 10.1002/2014GB004924 URL |
| [24] | 方精云, 黄耀, 朱江玲, 等. 森林生态系统碳收支及其影响机制[J]. 中国基础科学, 2015, 17(3):20-25. |
| Fang J Y, Huang Y, Zhu J L, et al. Forest ecosystem carbon budget and its influence mechanism[J]. Basic Science in China, 2015, 17(3):20-25 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 吴庆标, 王效科, 段晓男, 等. 中国森林生态系统植被固碳现状和潜力[J]. 生态学报, 2008 (2):517-524. |
| Wu Q B, Wang X K, Duan X N. Carbon sequestration and its potential by forest ecosystems in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008 (2):517-524 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
Deng L, Liu S, Kim D G, et al. Past and future carbon sequestration benefits of China’s grain for green program[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2017, 47: 13-20
doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2017.09.006 URL |
| [27] |
Liu D, Chen Y, Cai W, et al. The contribution of China’s grain to green program to carbon sequestration[J]. Landscape Ecology, 2014, 29(10):1675-1688
doi: 10.1007/s10980-014-0081-4 URL |
| [28] | 朱教君, 郑晓. 关于三北防护林体系建设的思考与展望: 基于40年建设综合评估结果[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(5):1600-1610. |
| Zhu J J, Zheng X. Thoughts and prospects on the construction of Three North Shelterbelt system: based on the comprehensive assessment results of 40 years of construction[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(5):1600-1610 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] |
Chu X, Zhan J, Li Z, et al. Assessment on forest carbon sequestration in the Three-North Shelterbelt program region, China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 215: 382-389
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.296 URL |
| [30] |
Zhou W M, Lewis B J, Wu S N, et al. Biomass carbon storage and its sequestration potential of afforestation under natural forest protection program in China[J]. Chinese Geographical Science, 2014, 24(4):406-413
doi: 10.1007/s11769-014-0702-5 URL |
| [31] |
Liu B, Zhang L, Lu F, et al. Greenhouse gas emissions and net carbon sequestration of the Beijing-Tianjin sand source control project in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 225: 163-172
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.184 URL |
| [32] | 李怒云, 苏迪. 我国林业碳汇的发展趋势与展望[N/OL]. 2018-10-28 [2020-05-08]. http://www.tanpaifang.com/tanhui/2018/1028/62393.html. |
| Li N Y, Su D. The development trend and prospect of China’s forestry carbon sink [N/OL]. 2018-10-28 [2020-05-08]. http://www.tanpaifang.com/tanhui/2018/1028/62393.html (in Chinese) | |
| [33] |
He B, Miao L, Cui X, et al. Carbon sequestration from China’s afforestation projects[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(7):5491-5499
doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4559-4 URL |
| [34] |
Lin B, Ge J. Valued forest carbon sinks: how much emissions abatement costs could be reduced in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 224: 455-464
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.221 URL |
| [35] | 罗明. 依靠自然的力量着眼可持续发展[N]. 中国自然资源报, 2019-11-07 (3). |
| Luo M. Rely on the power of nature for sustainable development [N]. China Natural Resources News, 2019 -11-07 (3)(in Chinese) | |
| [36] | 罗明, 应凌霄, 周妍. 基于自然解决方案的全球标准之准则透析与启示[J]. 中国土地, 2020 (4):9-13. |
| Luo M, Ying L X, Zhou Y. Dialysis and inspiration of global standards based on natural solutions[J]. Chinese Land, 2020 (4):9-13 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | ZHANG Meng-Rong, CHEN Sha, LI Su-Mei. Case analysis of GHG emission and reduction from food consumption of Beijing relish restaurant based on life cycle [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(2): 140-150. |
| [2] | AN Yan, GU Bai-He, WANG Yi, TAN Xian-Chun, ZHAI Han-Bing. Advances, problems and strategies of policy for Nature-based Solutions in the fields of climate change in China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(2): 184-194. |
| [3] | CHEN Nan, LIN Xuan-Chen. Estimation of uncertainty based on emission reduction targets in NDC/INDCs [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(2): 223-235. |
| [4] | WANG Ke, LIU Fang-Ming, YIN Ming-Jian, LIU Jun-Ling. Research on China’s carbon emissions pathway under the 1.5℃ target [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(1): 7-17. |
| [5] | Xiao-Quan ZHANG, Xi XIE, Nan ZENG. Nature-based Solutions to address climate change [J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(3): 336-344. |
| [6] | Xiao-Ting CHEN, Ying CHEN. The scientific and political views of carbon budget for global climate governance [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(6): 632-639. |
| [7] | Yuan LIU,Dan-Ni SUN,Jian-Jun ZHANG,Ke-An WU,Jing ZHENG. Measures analysis for HFC-23 emission mitigation in China under the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(4): 423-428. |
| [8] | Jing WU, Qian-Ting ZHU, Shi-Qi WANG, Zheng WANG. Game simulation on emission reduction under the background of the Paris Agreement [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(2): 182-190. |
| [9] | Huang Ying, Guo Hongxu, Xie Pengcheng, Liao Cuiping, Zhao Daiqing. Study on Carbon Emission Reduction Calculation of Subway Travel—Take Guangzhou as an Example [J]. Climate Change Research, 2017, 13(3): 284-291. |
| [10] | Huang Wei, Gao Qingxian, Cao Guoliang, Ma Zhanyun, Zhang Weiding, Chao Qingchen. Effect of China’s Urban Symbiosis Development on GHG Emission Reduction [J]. Climate Change Research, 2017, 13(1): 76-82. |
| [11] | He Jiankun. Global Low-Carbon Transition and China’s Response Strategies [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(5): 357-365. |
| [12] | Liu Kan, Zheng Wenru, Li Yijie . Analysis and Suggestions on the HFC-23 Abatement Policy in China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(3): 179-184. |
| [13] | Cui Tiening, Lu Ting . Exploratory Study on Voluntary Emission Reduction System of Urban Public Bicycle— Take Beijing as an Example [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(2): 112-117. |
| [14] | Liu Yu, Hu Xiaohong. Economic and Environmental Implications of Raising China’s Emission Standard for Thermal Power Plants: An Environmentally Extended CGE Model-Based Analysis [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(2): 154-161. |
| [15] | Wang Wenjun, Xie Pengcheng, Hu Jilian, Wang Le, Zhao Daiqing. Analysis of the Relative Mitigation Cost Advantages of Carbon Tax and ETS for the Cement Industry [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(1): 53-60. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||