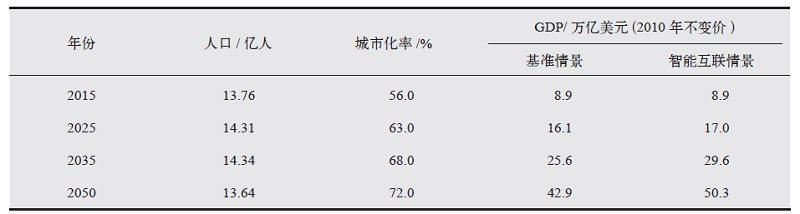
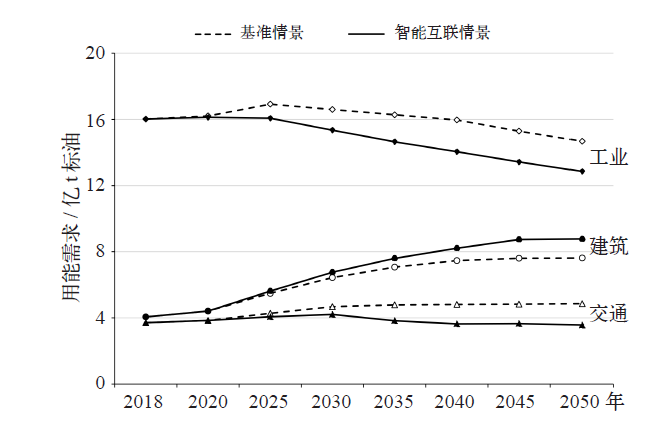
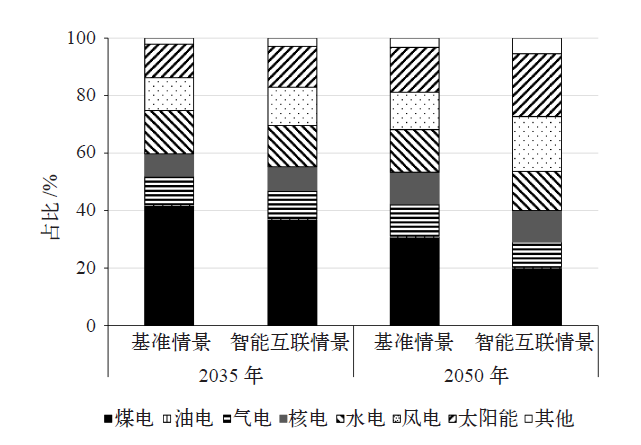
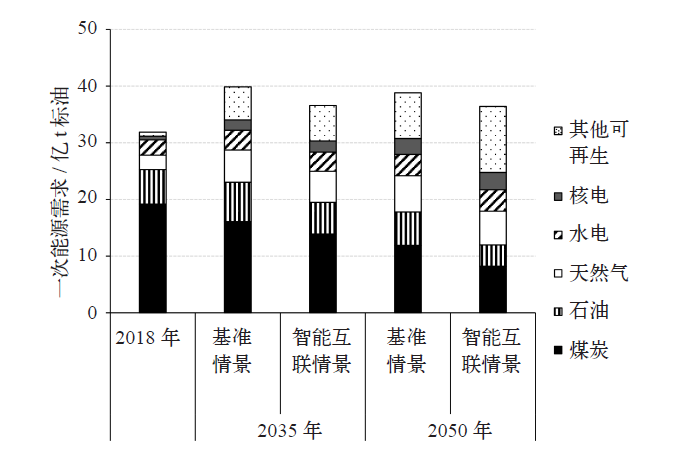
| [1] |
王利宁. 建设能源命运共同体是全世界人民的共同诉求[N]. 石油商报, 2019-04-25 (05).
|
|
Wang L N. Building a community with a shared energy future is the common aspiration of people all over the world [N]. Oil Business Daily, 2019-04-25 (05)(in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
王庆扬, 谢沛荣, 熊尚坤, 等. 5G关键技术与标准综述[J]. 电信科学, 2017 (11):118-128.
|
|
Wang Q Y, Xie P R, Xiong S K, et al. Overview of 5G key technologies and standards[J]. Telecom Science, 2017 (11):118-128 (in Chinese)
|
| [3] |
项立刚. 5G时代[M]. 北京: 中国人民大学出版社, 2019.
|
|
Xiang L G. 5G era [M]. Beijing: China Renmin University Press, 2019 (in Chinese)
|
| [4] |
克劳斯·施瓦布. 第四次工业革命转型的力量[M]. 北京: 中信出版集团, 2016.
|
|
Klaus S. The fourth industrial revolution [M]. Beijing: Citic Publishing Group, 2016 (in Chinese)
|
| [5] |
王毅, 陈启鑫, 张宁, 等. 5G通信与泛在电力物联网的融合:应用分析与研究展望[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43(5):1575-1585.
|
|
Wang Y, Chen Q X, Zhang N, et al. Fusion of the 5G communication and the ubiquitous electric internet of things: application analysis and research prospects[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(5):1575-1585 (in Chinese)
|
| [6] |
赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌, 等. 人工智能应用于地球系统科学[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(1):126-129.
|
|
Zhao Z C, Luo Y, Huang J B, et al. Artificial intelligence applies to Earth system science[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(1):126-129 (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
刘朝全, 姜学峰. 2019年国内外油气行业发展报告[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2020.
|
|
Liu C Q, Jiang X F. Domestic and foreign oil and gas industry development report in 2019 [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2020 (in Chinese)
|
| [8] |
中国石油经济技术研究院. 2050世界与中国能源展望[R]. 北京, 2019.
|
|
CNPC Economics & Technology Research Institute. 2050 world and China energy outlook [R]. Beijing, 2019 (in Chinese)
|
| [9] |
刘钊. 能源和数字革命背景下能源系统与信息技术融合的技术架构研究[J]. 电工材料, 2019 (6):23-26.
|
|
Liu Z. Research on technical architecture of integration of energy system and information technology under the background of digital revolution[J]. Electrical Material, 2019 (6):23-26 (in Chinese)
|
| [10] |
惠春琳. 能源数字化: 重塑全球能源发展态势[J]. 学习时报, 2019 (6):2.
|
|
Hui C L. Energy digitalization: reshaping the global energy development trend[J]. Study Times, 2019 (6):2 (in Chinese)
|
| [11] |
王林. 油气行业数字化转型, 人工智能是关键[J]. 中国石化报, 2019 (12):7.
|
|
Wang L. Artificial intelligence is the key to the digital transformation of the oil and gas industry[J]. China Petrochemical News, 2019 (12):7 (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
代红才. 泛在电力物联网推动我国能源转型发展与业态创新[J]. 电力时代, 2020 (1):20-21.
|
|
Dai H C. Pan in the power of things to accelerate the development of China’s energy transformation and the innovation of the formats[J]. Power Era, 2020 (1):20-21 (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
刘素蔚, 于灏. 能源企业数字化转型五大趋势[J]. 国家电网, 2019: 59-61.
|
|
Liu S W, Yu H. Five trends of digital transformation of energy enterprises[J]. State Grids, 2019: 59-61 (in Chinese)
|
| [14] |
International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Global renewables outlook: energy transformation 2050 [R/OL]. 2020 [2020-01-21]. https://www.irena.org/publications/2020/Apr/Global-Renewables-Outlook-2020
|
| [15] |
Joint Global Change Research Institute (JGCRI). Global Change Assessment Model (GCAM) 2018 [EB/OL]. 2018 [2018-10-24]. http://jgcri.github.io/gcam-doc/
|
| [16] |
Wang L, Chen H, Chen W. Co-control of carbon dioxide and air pollutant emissions in China from a cost-effective perspective[J]. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2019 (7242):1-21
|
| [17] |
王利宁, 杨雷, 陈文颖, 等. 国家自主决定贡献的减排力度评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(6):71-78.
|
|
Wang L N, Yang L, Chen W Y, et al. Assessment of carbon reduction effect of the nationally determined contributions[J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(6):71-78 (in Chinese)
|
| [18] |
Pan X Z, Chen W Y, Clarke L E, et al. China’s energy system transformation towards the 2 degrees goal: implications of different effort-sharing principles[J]. Energy Policy, 2017, 103(4):116-126
|
| [19] |
International Energy Agency (IEA). Digitalization potential impact on transport, buildings and industry [EB/OL]. 2020 [2020-05-02]. https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/digitalisation-potential-impact-on-transport-buildings-and-industry
|
 ), CHEN Wen-Ying2(
), CHEN Wen-Ying2( ), DAI Jia-Quan1, XIANG Zheng-Jian1, GONG Jin-Shuang1
), DAI Jia-Quan1, XIANG Zheng-Jian1, GONG Jin-Shuang1