所属专题: IPCC第六次评估报告WGIII解读专栏
• • 下一篇
IPCC第六次评估报告历史排放趋势和驱动因素相关核心结论解读
谭显春1, 3,戴瀚程2,顾佰和1,黄 晨2,朱开伟1,马啸天2,闫洪硕1, 3,刘心远2,朱衍磊2
- 1 中国科学院科技战略咨询研究院,北京100190; 2 北京大学环境科学与工程学院,北京100871; 3 中国科学院大学公共政策与管理学院,北京100049
Analysis on the Key Findings Related to Emission Trends and Drivers from the Working Group Ⅲ Contribution to the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report
TAN Xian-Chun1, 3, DAI Han-Cheng2, GU Bai-He1, HUANG Chen2, ZHU Kai-Wei1, MA Xiao-Tian2, YAN Hong-Shuo1, 3, LIU Xin-Yuan2, ZHU Yan-Lei2
- 1 Institutes of Science and Development, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China;
2 College of Environmental Sciences and Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China;
3 School of Public Policy and Management, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
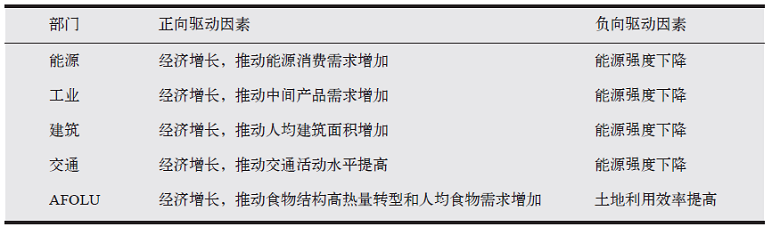
摘要: IPCC报告第三工作组中“排放历史趋势和驱动因素”章节是历次评估报告的核心内容之一。2022年4月发布的第六次评估报告(AR6),在简要回顾1850-2019年历史累计排放趋势后,主要分析了1990—2019年期间温室气体排放趋势与驱动因素。相比于第五次评估报告(AR5),在历史排放趋势方面,AR6在时间尺度上重点分析2010—2019年的近期变化,在研究内容上更加突出1.5℃温控目标的重要性,强化了对土地利用变化相关温室气体排放的关注,强调生产与消费视角下碳排放趋势及其区域演变趋势,探究了新冠肺炎疫情对全球碳排放的短期影响;在驱动因素方面,除了考虑全球和区域层面,还增加了基于能源、工业、建筑、交通、农林及其它土地利用(AFOLU)等部门视角的经济驱动因素分解及地区间差异分析,系统体现全球、区域和部门三层次下驱动因素的异同,指出区域层面存在能源转型成效,肯定了现有气候政策对气候减缓的积极影响以及突出技术变革与创新对气候减缓的益处,明确了化石能源基础设施碳锁定效应的不利影响等。最后,结合本章节关键结论的基础上,评估了相关结论对我国低碳发展的可能影响和启示。