气候变化研究进展 ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (5): 557-566.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.144
• IPCC第六次评估报告WGIII专栏 • 上一篇 下一篇
对IPCC AR6报告建筑章节的介绍和解读
- 1 国家发展和改革委员会能源研究所,北京 100038
2 清华大学建筑学院建筑节能研究中心,北京 100084
Interpretation of IPCC AR6 on buildings
BAI Quan1( ), HU Shan2(
), HU Shan2( ), GU Li-Jing1
), GU Li-Jing1
- 1 Energy Research Institute of National Development and Reform Commission, Beijing 100038, China
2 Building Energy Research Center, School of Architecture, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
摘要:
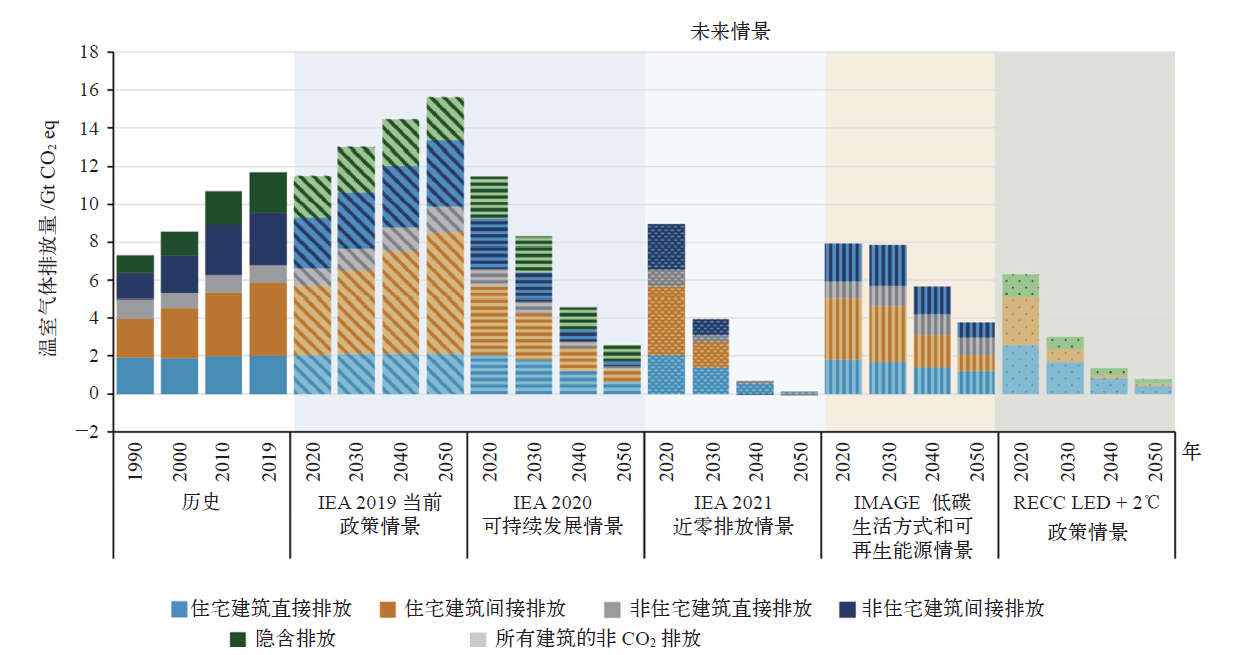
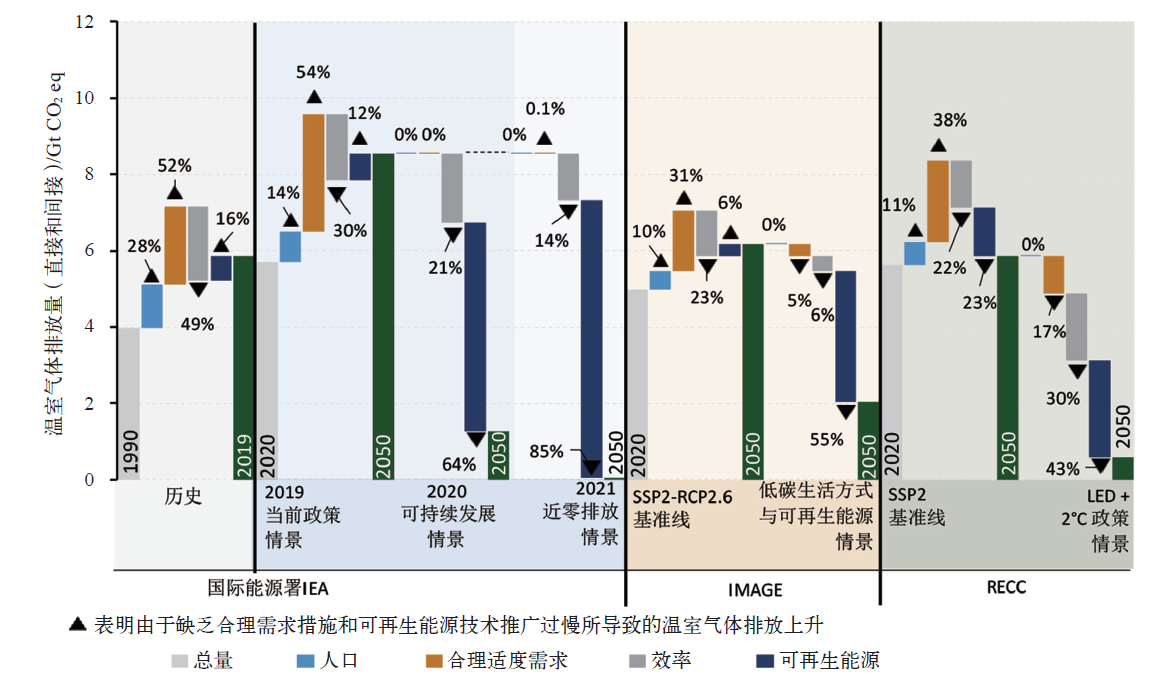
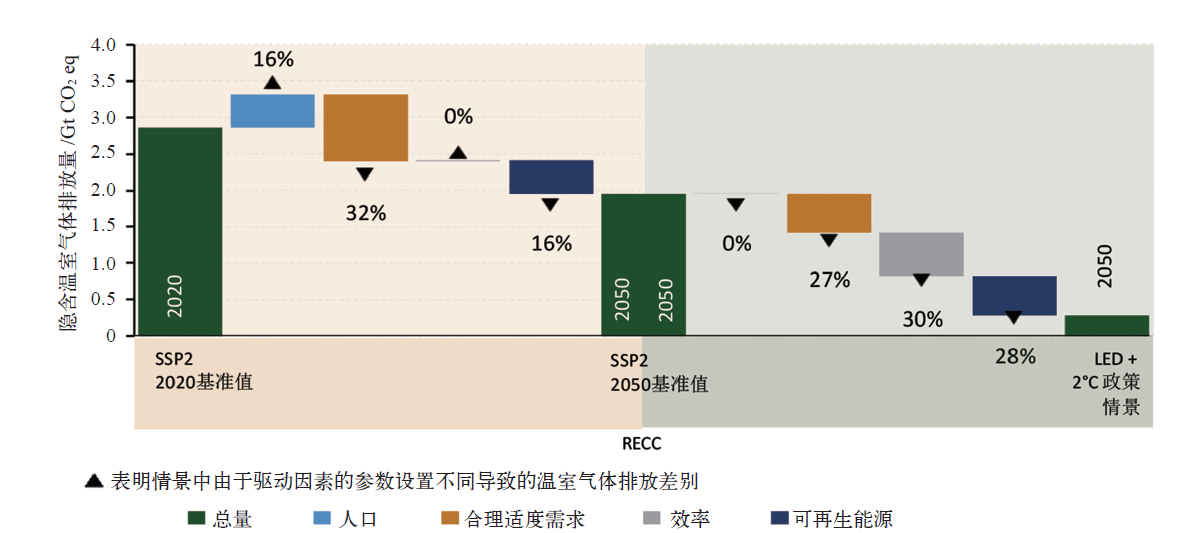
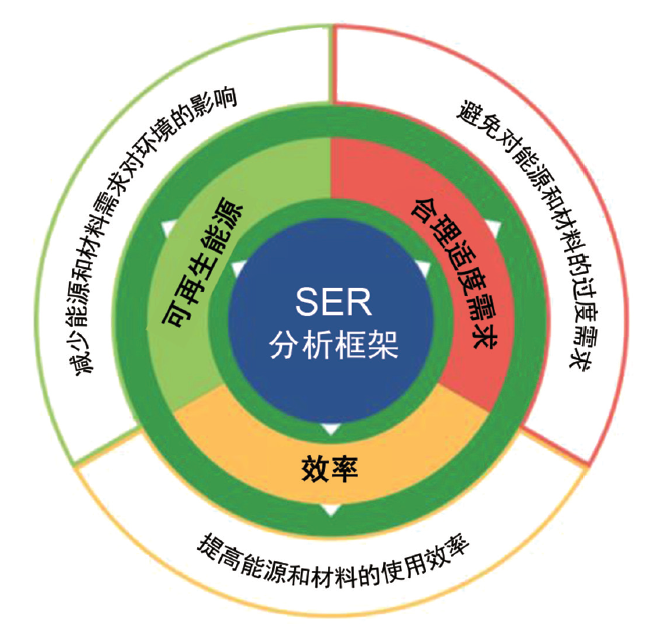
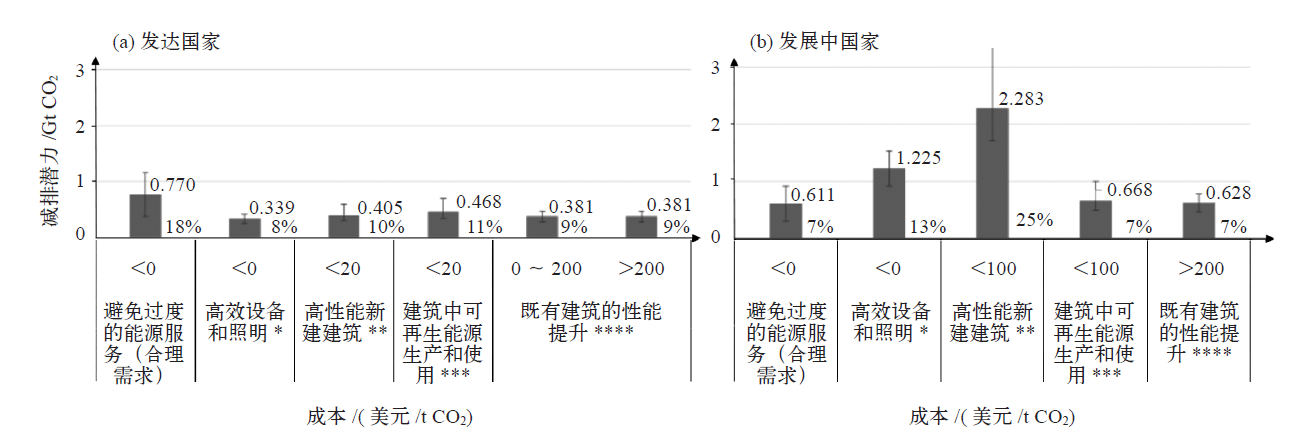
IPCC于2022年4月正式发布了第六次评估报告(AR6)第三工作组(WGIII)报告《气候变化2022:减缓气候变化》,该报告以已发布的第一和第二工作组报告作为基础,评估了各领域减缓气候变化的进展。报告的第九章建筑章节系统全面地评估了全球建筑领域的温室气体排放现状、趋势和驱动因素,综述并评估了建筑减缓气候变化的措施、潜力、成本和政策。报告主要结论认为,全球建筑领域有可能在2050年实现温室气体净零排放,但如果政策措施执行不力,将有可能在建筑领域形成长达几十年的高碳锁定效应。报告的主要结论将成为全球建筑领域应对气候变化行动的重要参考,对于我国建筑领域实现碳达峰、碳中和目标也有非常重要的借鉴意义。