气候变化研究进展 ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (6): 670-682.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.006
中国60城市站1901—2019年日降水数据集的构建
战云健1( ), 陈东辉1(
), 陈东辉1( ), 廖捷1, 鞠晓慧1, 赵煜飞1, 任国玉2,3
), 廖捷1, 鞠晓慧1, 赵煜飞1, 任国玉2,3
- 1 中国气象局国家气象信息中心,北京 100081
2 中国气象局国家气候中心,北京 100081
3 中国地质大学(武汉)环境学院,武汉 430074
-
收稿日期:2022-01-11修回日期:2022-02-24出版日期:2022-11-30发布日期:2022-04-29 -
通讯作者:陈东辉 -
作者简介:战云健,男,高级工程师,zhanyj@cma.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划“不同温升情景下区域气象灾害风险预估”(2019YFA0606904);“国家气象科学数据中心建设”专项资金;国家重点科技研发计划项目“全球变化及应对”重点专项(2018YFA0605603)
Construction of a daily precipitation dataset of 60 city stations in China for the period 1901-2019
ZHAN Yun-Jian1( ), CHEN Dong-Hui1(
), CHEN Dong-Hui1( ), LIAO Jie1, JU Xiao-Hui1, ZHAO Yu-Fei1, REN Guo-Yu2,3
), LIAO Jie1, JU Xiao-Hui1, ZHAO Yu-Fei1, REN Guo-Yu2,3
- 1 National Meteorological Information Center, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
2 National Climate Center, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
3 School of Environmental Studies, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan 430074, China
-
Received:2022-01-11Revised:2022-02-24Online:2022-11-30Published:2022-04-29 -
Contact:CHEN Dong-Hui
摘要:
近年来中国区域降水的极端化问题得到学术界的广泛关注,有关研究也获得了大量成果。但是,目前国内外常用的高分辨率降水资料序列多从1951年左右开始,普遍缺少20世纪早期中国的逐日降水资料,对于近一百多年中国极端降水变化特征及其机理,目前还不清楚。基于多来源的1901—1950年原始观测报表数字化逐日降水资料,补充先前未录入的“无降水”和缺测数据,研发质量控制方案并开展质量控制,补充录入检出的缺失和错误数据并再次质控,结合1951年以来的现代降水日值资料,建立中国60个城市站1901—2019年降水日值数据集。数据集评估结果显示,早期中国东部地区的台站较为密集,数据完整性和正确性较好,但中国西部的台站数量少且完整性和正确性偏低。本数据集构建的年总降水量累积值序列与已有的月降水量数据基本一致。基于该数据集,研究发现重庆站近百年来的降水未出现显著的趋势性变化。该数据集使后续分析研究中国极端降水的百年尺度长期变化特征成为可能。
引用本文
战云健, 陈东辉, 廖捷, 鞠晓慧, 赵煜飞, 任国玉. 中国60城市站1901—2019年日降水数据集的构建[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(6): 670-682.
ZHAN Yun-Jian, CHEN Dong-Hui, LIAO Jie, JU Xiao-Hui, ZHAO Yu-Fei, REN Guo-Yu. Construction of a daily precipitation dataset of 60 city stations in China for the period 1901-2019[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(6): 670-682.

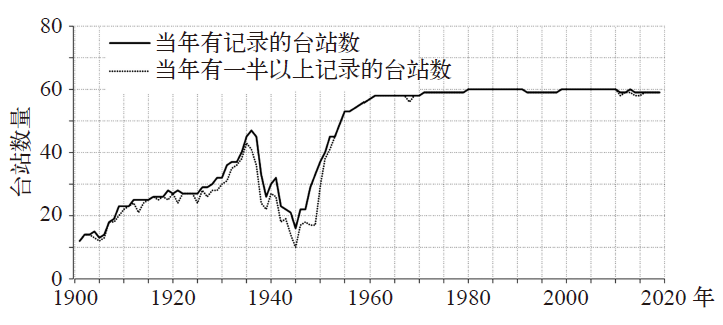
图3 1901—2019年60个城市台站数据实有率(a)、正确率(b)、可疑率(c)、站址差异数据所占比率(d)以及估测为0数据所占比率(e)的时间变化
Fig. 3 Variation of the valid rate (a), correct rate (b), suspicious rate (c), the rate of data with different locations (d), and the rate of data estimated to be 0 (e) for 60 stations from 1901 to 2019

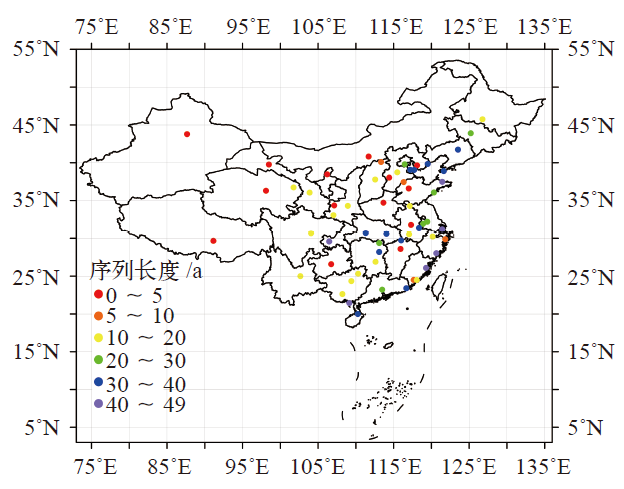
图4 1901—2019年中国60城市站逐日降水资料实有率(a)和正确率(b)空间分布
Fig. 4 Geographic distribution of the valid rate (a) and the correct rate (b) for 60 stations from 1901 to 2019

图5 1901—1950年中国60城市站逐日降水资料实有率(a)、可疑率(b)、站址差异数据所占比率(c)以及估测为0数据所占比率(d)空间分布
Fig. 5 Geographic distribution of the valid rate (a), the suspicious rate (b), the rate of data with different locations (c), and the rate of data estimated to be 0 (d) for 60 stations from 1901 to 1950
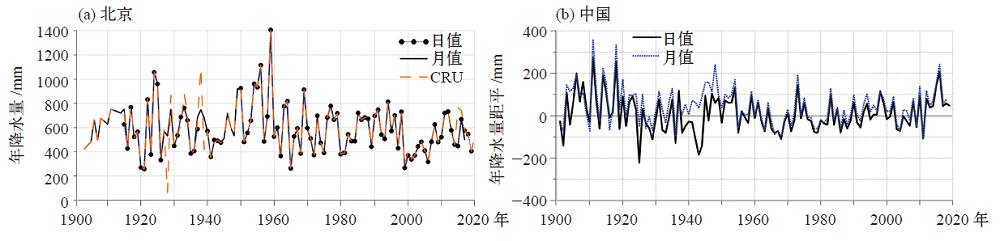
图6 1901—2019年北京(a)以及中国区域平均(b)的日值和月值累加成的年降水量时间序列
Fig. 6 Time series of annual precipitation accumulated by daily and monthly precipitation in Beijing (a) and regional average in China (b) from 1901 to 2019
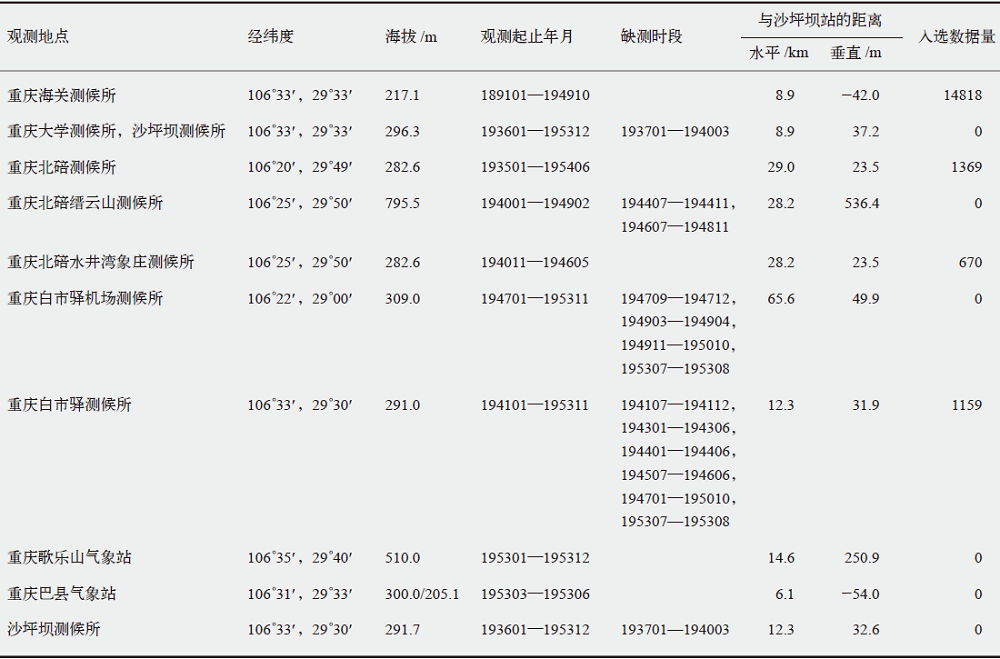 |
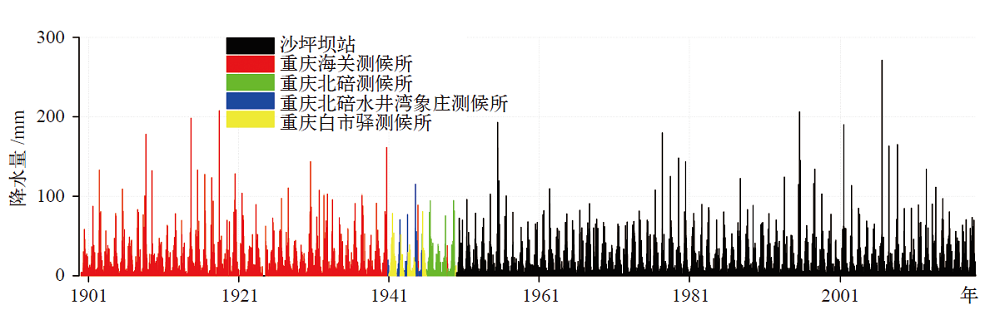
表1 重庆市解放前和解放初期(1954年之前)全部气象观测台站基本信息、与沙坪坝站的距离以及本数据集的选用情况
Table 1 The basic information, distance to Shapingba station, and the selection status in this dataset of all the meteorological observation stations before 1954 in Chongqing
 |
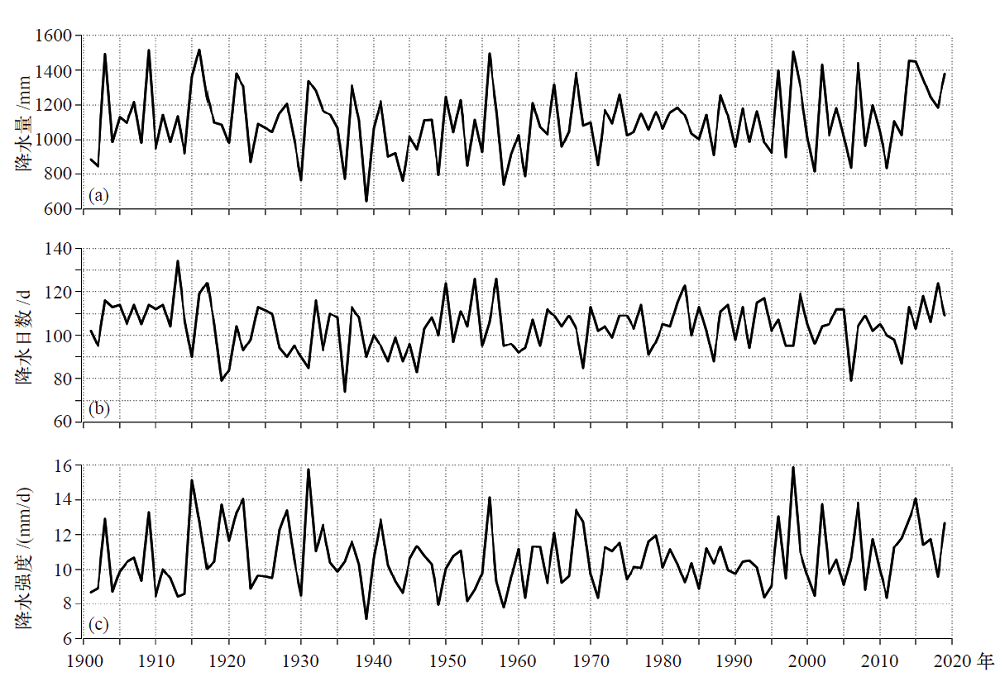
图9 1901—2019年重庆年降水量(a)、年降水日数(b)和年平均日降水强度(c)时间序列
Fig. 9 Time series of annual precipitation (a), precipitation days (b), and precipitation intensity (c) above 0.1 mm in Chongqing from 1901 to 2019
| [1] | 翟盘茂, 王萃萃, 李威. 极端降水事件变化的观测研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007, 3 (3): 144-148. |
| Zhai P M, Wang C C, Li W. A review on study of change in precipitation extremes[J]. Climate Change Research, 2007, 3 (3): 144-148 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 丁一汇. 人类活动与全球气候变化及其对水资源的影响[J]. 中国水利, 2008, 2: 20-27. |
| Ding Y H. Human activity and the global climate change and its impact on water resources[J]. China Water Resources, 2008, 2: 20-27 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 黄荣辉, 杜振彩. 全球变暖背景下中国旱涝气候灾害的演变特征及趋势[J]. 自然杂志, 2010, 32 (4): 187-195, 201. |
| Huang R H, Du Z C. Evolution characteristics and trend of droughts and floods in China under the background of global warming[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2010, 32 (4): 187-195, 201 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013 |
| [5] | 符淙斌, 黄燕. 亚洲的全球变化问题[J]. 气候与环境研究, 1996, 2: 97-112. |
| Fu C B, Huang Y. Global change in Aisa[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 1996, 2: 97-112 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 肖国举, 张强, 王静. 全球气候变化对农业生态系统的影响研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18 (8): 1877-1885. |
| Xiao G J, Zhang Q, Wang J. Impact of global climate change on agro-ecosystem: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18 (8): 1877-1885 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] |
Zhai P M, Zhang X B, Wan H, et al. Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2005, 18 (7): 1096-1108
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-3318.1 URL |
| [8] | 闵屾, 钱永甫. 我国近40年各类降水事件的变化趋势[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 47 (3): 105-110. |
| Min S, Qian Y F. Trends in all kinds of precipitation events in China over the past 40 years[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2008, 47 (3): 105-110 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | Tu K, Yan Z W, Dong W J. Climatic jumps in precipitation and extremes in drying North China during 1954-2006[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 2010, 88 (1): 29-42 |
| [10] |
Ren G Y, Liu H B, Chu Z Y, et al. Multi-time-scale climatic variations over Eastern China and implications for the south-north water diversion project[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2011, 12 (8): 600-617
doi: 10.1175/2011JHM1321.1 URL |
| [11] | 任国玉, 任玉玉, 战云健, 等. 中国大陆降水时空变异规律: II. 现代变化趋势[J]. 水科学进展, 2015, 26 (4): 451-465. |
| Ren G Y, Ren Y Y, Zhan Y J, et al. Spatial and temporal patterns of precipitation variability over mainland China: II. recent trends[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2015, 26 (4): 451-465 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | Cao L, Yan Z, Ping Z, et al. Climatic warming in China during 1901-2015 based on an extended dataset of instrumental temperature records[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2017, 12 (6): 064005 |
| [13] |
Li Q, Peng J, Shen Y. Development of China homogenized monthly precipitation dataset during 1900-2009[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2012, 22 (4): 579-593
doi: 10.1007/s11442-012-0948-8 |
| [14] | Png I P L, Chen Y, Chu J, et al. Temperature, precipitation and sunshine across China, 1912-51: a new daily instrumental dataset[J]. Geoscience Data Journal, 2020: 1-13 |
| [15] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 中华人民共和国国家标准: 地面标准气候值统计方法(GB∕T 34412—2017)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of The People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. National standard of the People’s Republic of China: statistical method for surface standard climate normals (GB∕T 34412—2017)[S]. Beijing: Standard Press of China, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 中国气象局气候变化中心. 中国气候变化蓝皮书[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021. |
| Climate Change Center of China Meteorological Administration. Blue book on climate change in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] |
Yang S, Xu W, Xu Y, et al. Development of a global historic monthly mean precipitation dataset[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2016, 30: 217-231
doi: 10.1007/s13351-016-5112-4 URL |
| [18] |
Harris I, Osborn T J, Jones P, et al. Version 4 of the CRU TS monthly high-resolution gridded multivariate climate dataset[J]. Scientific Data, 2020, 7 (1): 109
doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0453-3 pmid: 32246091 |
| [19] | 战云健, 任国玉, 王朋岭, 等. 中国区域平均降水量序列构建方法比较研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2021, 26 (1): 45-57. |
| Zhan Y J, Ren G Y, Wang P L, et al. Construction method for regionally average precipitation time series in China[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2021, 26 (1): 45-57 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 战云健, 任国玉, 王朋岭. 数据处理方法对中国区域平均降水序列精度的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15 (6): 584-595. |
| Zhan Y J, Ren G Y, Wang P L. The influence of data processing on constructing regional average precipitation time series[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15 (6): 584-595 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 张铭明, 李建, 甘玉婷, 等. 基于GWR 模型的中国中东部降水与海拔高度关系特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2021, 40 (1): 1-11. |
| Zhang M M, Li J, Gan Y T, et al. Analysis of the relationship between precipitation and altitude over central and eastern China based on the geographically weighted regression model[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2021, 40 (1): 1-11 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 王霞, 王瑛, 林齐根, 李宁, 张馨仁, 周笑影. 气候变化背景下中国滑坡灾害人口风险评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 166-176. |
| [2] | 孙晨, 汪方, 周月华, 李兰. CWRF模式对长江流域极端降水气候事件的模拟能力评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(1): 44-57. |
| [3] | 王倩之, 刘凯, 汪明. NEX-GDDP降尺度数据对中国极端降水指数模拟能力的评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(1): 31-43. |
| [4] | 汤秭晨, 李清泉, 王黎娟, 伍丽泉. CMIP6年代际试验对中国气温预测能力的初步评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(2): 162-174. |
| [5] | 袁志逸, 李振宇, 康利平, 谭晓雨, 周新军, 李晓津, 李超, 彭天铎, 欧训民. 中国交通部门低碳排放措施和路径研究综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(1): 27-35. |
| [6] | 潘金玉, 苏布达, 王艳君, 景丞, 翟建青, 姜彤. 共享社会经济路径(SSPs)下2020—2050年中国分产业产值时空变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(6): 725-737. |
| [7] | 丁凯熙, 张利平, 佘敦先, 张琴, 向竣文. 全球升温1.5℃和2.0℃情景下澜沧江流域极端降水的变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(4): 466-479. |
| [8] | 张奇谋,王润,姜彤,陈松生. RCPs情景下汉江流域未来极端降水的模拟与预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(3): 276-286. |
| [9] | 王岱,孙银川,游庆龙. 太平洋年代际振荡对中国冬季最低气温年代际变化的贡献[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(1): 70-77. |
| [10] | 马欣,王文涛,张雪艳,吴绍洪,刘燕华. 基于哥本哈根学派的中国气候安全化比较分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(6): 693-699. |
| [11] | 廖要明,陈德亮,刘秋锋. 中国地气温差时空分布及变化趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(4): 374-384. |
| [12] | 尹红,孙颖. 基于ETCCDI指数2017年中国极端温度和降水特征分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(4): 363-373. |
| [13] | 李彩瑛,阎建忠,花晓波,张镱锂. 农户生计对气候变化的敏感性研究综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(3): 290-300. |
| [14] | 孙茹,韩雪,潘婕,熊伟,居辉. 全球1.5℃和2.0℃升温对中国小麦产量的影响研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(6): 573-582. |
| [15] | 贺冰蕊,翟盘茂. 中国1961—2016年夏季持续和非持续性极端降水的变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5): 437-444. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||