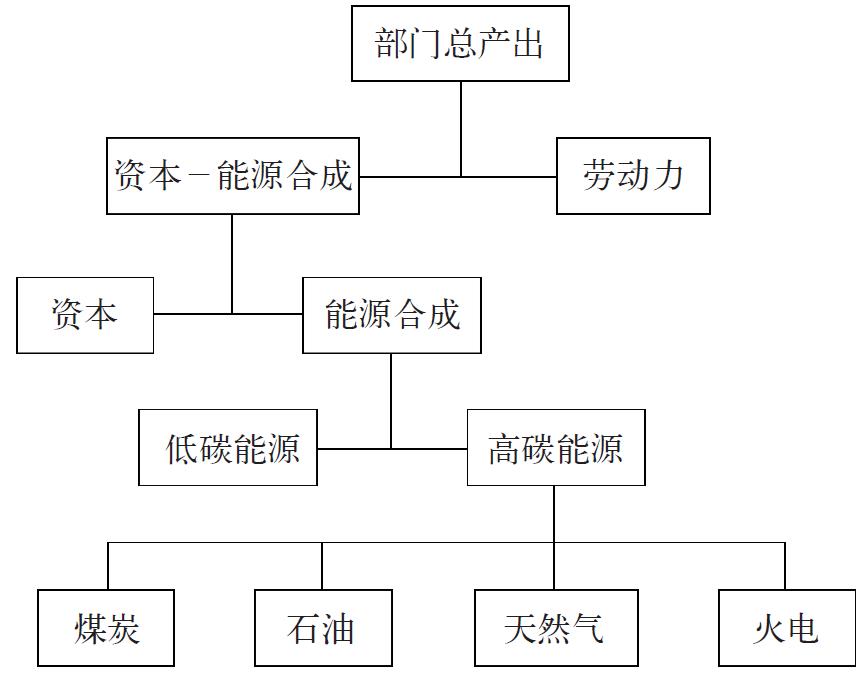
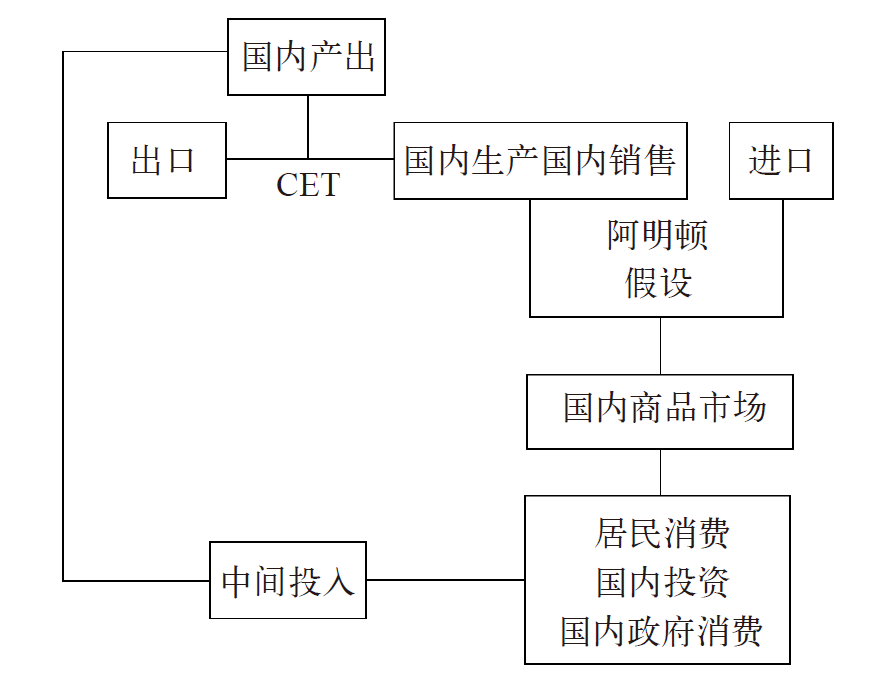
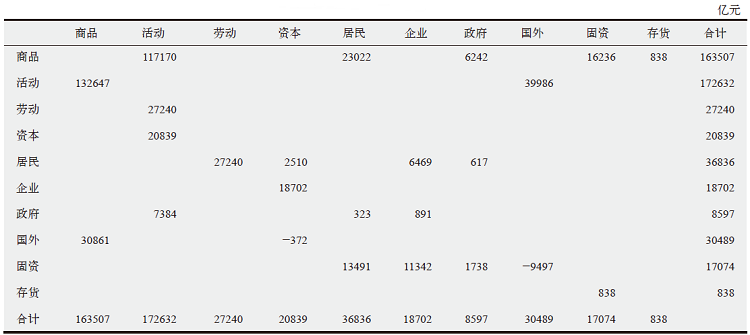
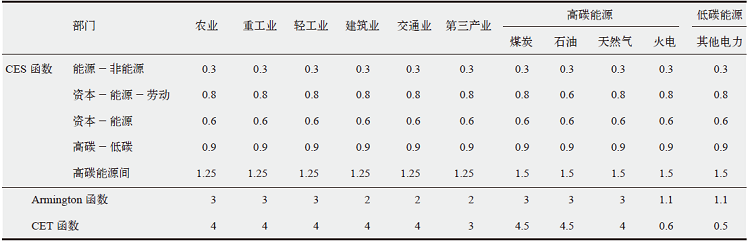
| [1] |
苏明, 傅志华, 许文, 等. 我国开征碳税问题研究[J]. 经济研究参考, 2009 (72):2-16.
|
|
Su M, Fu Z H, Xu W, et al. Research on the issue of levying carbon tax in China[J]. Review of Economic Research, 2009 (72):2-16 (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
Nicoletti G, Oliveira-Martins J. Global effects of the European carbon tax[M]//Carraro C, Siniscalco D. The European carbon tax: an economic assessment. Berlin: Springer Netherlands, 1993
|
| [3] |
Allan G, Lecca P, Mcgregor P, et al. The economic and environmental impact of a carbon tax for Scotland: a Computable General Equilibrium analysis[J]. Ecological Economics, 2014,100(100):40-50
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2014.01.012
URL
|
| [4] |
Mohammed T. A CGE analysis of the macroeconomic effects of carbon dioxide emission reduction on the Algerian economy[J]. Advances in Applied Economic Research, 2017: 1-20
|
| [5] |
Meng X. Will Australian carbon tax affect the resources boom? Results from a CGE model[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2012,21(4):495-507
doi: 10.1007/s11053-012-9187-z
URL
|
| [6] |
郭正权, 张兴平, 郑宇花. 能源价格波动对能源-环境-经济系统的影响研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2018,26(11):22-30.
|
|
Guo Z Q, Zhang X P, Zheng Y H. Impacts of energy price fluctuations on energy-environment-economy system in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2018,26(11):22-30 (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
翁智雄, 马忠玉, 蔡松锋. 中国碳税政策的经济与环境影响研究: 基于动态CGE模型分析[J]. 中国物价, 2018 (8):10-13.
|
|
Weng Z X, Ma Z Y, Cai S F. Analysis on the economic and environmental impacts of China's carbon tax policy[J]. China Price, 2018 (8):10-13 (in Chinese)
|
| [8] |
李娜, 石敏俊, 袁永娜. 低碳经济政策对区域发展格局演进的影响: 基于动态多区域CGE模型的模拟分析[J]. 地理学报, 2010,65(12):1569-1580.
doi: 10.11821/xb201012012
URL
|
|
Li N, Shi M J, Yuan Y N. Impacts of carbon tax policy on regional development in China: a dynamic simulation based on a multi-regional CGE model[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2010,65(12):1569-1580 (in Chinese)
|
| [9] |
王文举, 范允奇. 碳税对区域能源消费、经济增长和收入分配影响实证研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2012,21(4):442-447.
|
|
Wang W J, Fan Y Q. Empirical research on effects of carbon taxation on regional energy consumption, economic growth and income distribution[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2012,21(4):442-447 (in Chinese)
|
| [10] |
梁伟. 基于CGE模型的环境税“双重红利”研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2013.
|
|
Liang W. Study of double dividend of environmental tax based on CGE model: a case study of Shandong province[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2013 (in Chinese)
|
| [11] |
韦晓倩. 征收碳税对我国区域经济发展和环境质量的影响研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2011.
|
|
Wei X Q. The impact of carbon tax on regional economy and environment: the analysis based on a CGE model[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2011 (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
周丹, 赵子健. 基于地区CGE模型的碳税效应研究: 以上海为例[J]. 生态经济, 2015,31(4):24-28.
|
|
Zhou D, Zhao Z J. The effects analysis of carbon tax based on CGE model: taking Shanghai as an example[J]. Ecological Economy, 2015,31(4):24-28 (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
郭正权. 基于CGE模型的我国低碳经济发展政策模拟分析[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2011.
|
|
Guo Z Q. The low-carbon economic development policy analysis based on CGE model in China[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology, 2011 (in Chinese)
|
| [14] |
国家统计局能源统计司. 中国能源统计年鉴2013 [M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2013.
|
|
Department of energy statistics of the National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. China's energy statistical yearbook 2013[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2013 (in Chinese)
|
| [15] |
张欣. 可计算一般均衡模型的基本原理与编程[M]. 上海: 格致出版社, 2010.
|
|
Zhang X. The basic principles and programming of the basic principles and programming of the general equilibrium model can be calculated [M]. Shanghai: Gezhi Publishing House, 2010 (in Chinese)
|
| [16] |
范金, 杨中卫, 赵彤. 中国宏观社会核算矩阵的编制[J]. 世界经济文汇, 2010 (4):103-119.
|
|
Fan J, Yang Z W, Zhao T. Compilation of China's macro-social accounting matrix[J]. World Economic Papers, 2010 (4):103-119 (in Chinese)
|
| [17] |
卢启程, 李怡佳, 邹平. 省级社会核算矩阵的编制研究[J]. 统计与决策, 2011 (4):28-31.
|
|
Lu Q C, Li Y J, Zou P. Research on the compilation of provincial social accounting matrix[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2011 (4):28-31 (in Chinese)
|
| [18] |
王韬, 马成, 林聪. SAM平衡的SG-RAS与SG-CE方法[J]. 统计研究, 2012,29(12):88-95.
|
|
Wang T, Ma C, Lin C. SG-RAS/SG-CE methods for SAM balancing[J]. Statistical Research, 2012,29(12):88-95 (in Chinese)
|
| [19] |
李蒙娟. 基于动态CGE模型的工业碳税政策效应模拟分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江财经大学, 2018.
|
|
Li M J. Simulation analysis of industrial carbon tax policy effect based on dynamic CGE model[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Finance & Economics, 2018 (in Chinese)
|
| [20] |
胡青. 基于CGE模型的碳税政策对中国经济结构影响研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017.
|
|
Hu Q. Research on the impact of carbon tax policy on China's economic structure and carbon emission reduction based on CGE model[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017 (in Chinese)
|
| [21] |
樊星, 马树才, 朱连洲. 中国碳减排政策的模拟分析: 基于中国能源CGE模型的研究[J]. 生态经济, 2013 (9):50-54.
|
|
Fan X, Ma S C, Zhu L Z. A simulation analysis of Chinese reduction policies based on CGE model[J]. Ecological Economy, 2013 (9):50-54 (in Chinese)
|
| [22] |
国家发展和改革委员会能源研究所. 中国可持续发展能源暨碳排放情景分析综合报告[R]. 2003.
|
|
Energy Research Institute of The National Development and Reform Commission. China's sustainable development energy and carbon emissions scenario analysis comprehensive report[R]. 2003 (in Chinese)
|
| [23] |
徐卓顺. 可计算一般均衡(CGE)模型: 建模原理、参数估计方法与应用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2009.
|
|
Xu Z S. Modeling principles, parameter estimation methods and applications of Computable General Equilibrium model[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2009 (in Chinese)
|
 ), CAI Xiao-Ting, ZHANG Da-Quan, ZHANG Yu-Fan
), CAI Xiao-Ting, ZHANG Da-Quan, ZHANG Yu-Fan