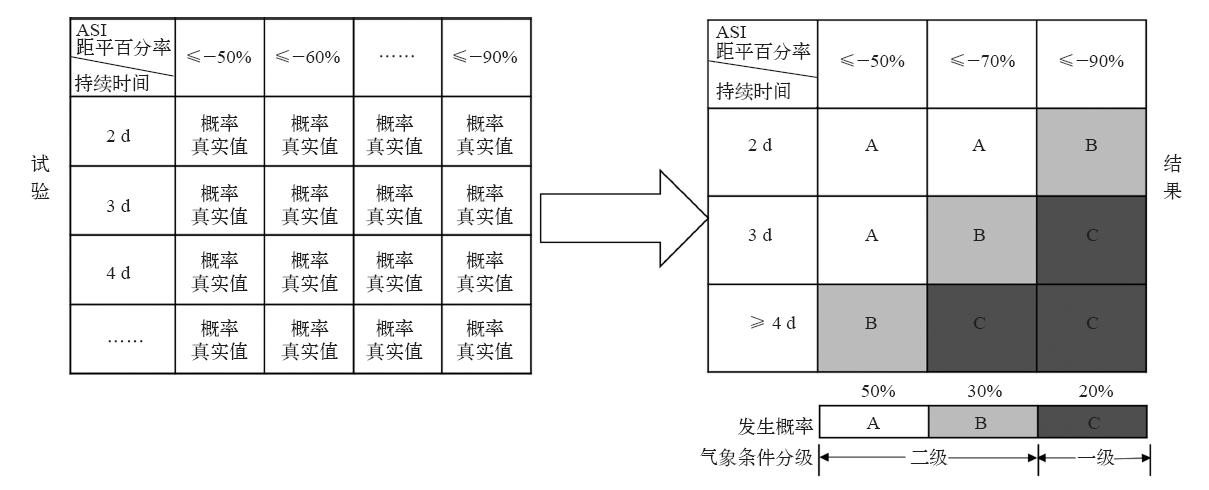
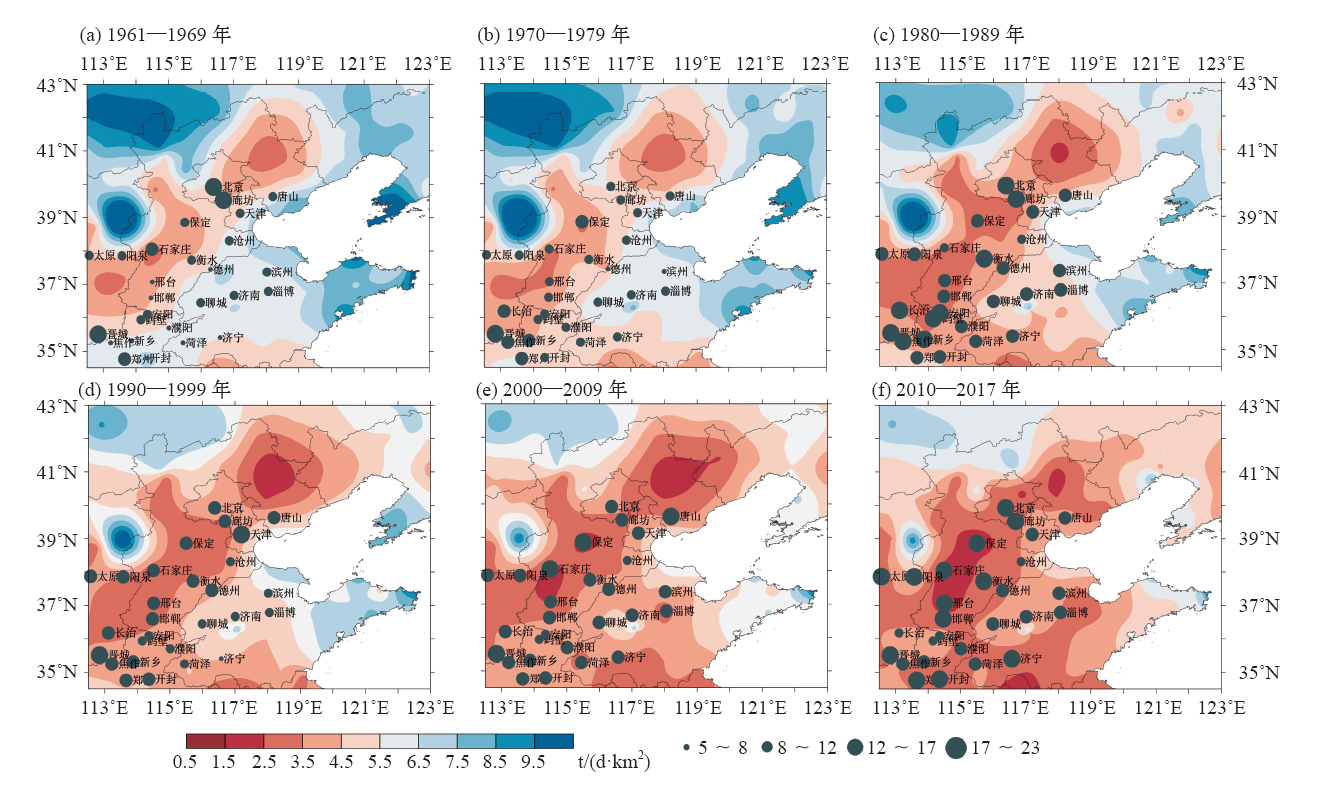
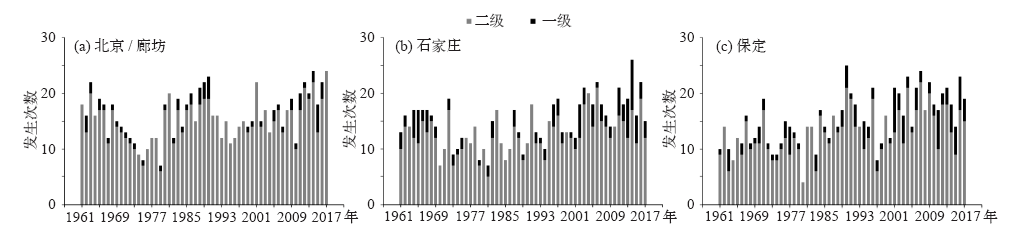
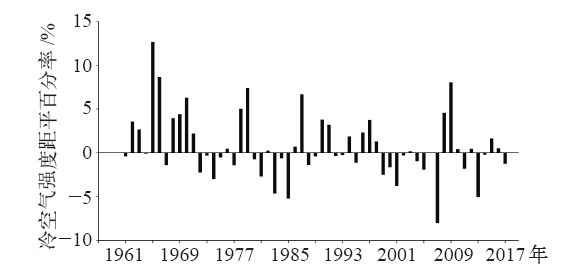
| [1] | 吴兑 . 近十年中国灰霾天气研究综述[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012,32(2):257-269. | | [1] | Wu D . Hazy weather research in China in the last decade: a review[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012,32(2):257-269 (in Chinese) | | [2] | 丁一汇, 王会军 . 近百年中国气候变化科学问题的新认识[J]. 科学通报, 2016,61(10):1029-1041. | | [2] | Ding Y H, Wang H J . Newly acquired knowledge on the scientific issues related to climate change over the recent 100 years in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016,61(10):1029-1041 (in Chinese) | | [3] | 张人禾, 李强, 张若楠 . 2013年1月中国东部持续性强雾霾天气产生的气象条件分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014,44(1):27-36. | | [3] | Zhang R H, Li Q, Zhang R N . Meteorological conditions for the persistent severe fog and haze event over eastern China in January 2013[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2014,44(1):27-36 (in Chinese) | | [4] | 蒋伊蓉, 朱蓉, 朱克云 , 等. 京津冀地区重污染天气过程的污染气象条件模拟研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015,35(9):2681-2692. | | [4] | Jiang Y R, Zhu R, Zhu K Y , et al. Numerical simulation on the air pollution potential in the severe air pollution episodes in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015,35(9):2681-2692 (in Chinese) | | [5] | 段云霞, 李德勤, 田莉 , 等. 沈阳市一次持续性重污染天气过程特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2016,34(5):803-810. | | [5] | Duan Y X, Li D Q, Tian L , et al. Characteristic analysis of a continuous and serious pollution weather process in Shenyang[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2016,34(5):803-810 (in Chinese) | | [6] | 杨晓亮, 杨敏 . 一次雾霾过程中气象因子与细颗粒物浓度关系的研究[J]. 干旱气象, 2014,32(5):781-787. | | [6] | Yang X L, Yang M . Relationship between mereorological factors and fine particulate matter concentration during a fog and haze weather process[J]. Journal of Arid Meteorology, 2014,32(5):781-787 (in Chinese) | | [7] | Wu P, Ding Y H, Liu Y J . Atmospheric circulation and dynamic mechanism for persistent haze events in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Advances Atmospheric Sciences, 2017,34(4):429-440 | | [8] | 张恒德, 吕梦瑶, 张碧辉 , 等. 2014年2月下旬京津冀持续重污染过程的静稳天气及传输条件分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016,36(12):4340-4351. | | [8] | Zhang H D, Lü M Y, Zhang B H , et al. Analysis of the stagnant meteorological situation and the transmission condition of continuous heavy pollution course from February 20 to 26, 2014 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2016,36(12):4340-4351 (in Chinese) | | [9] | 丁一汇, 柳艳菊 . 近50年我国雾和霾的长期变化特征及其与大气湿度的关系[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014,44(1):37-48. | | [9] | Ding Y H, Liu Y J . Analysis of long-term variations of fog and haze in China in recent 50 years and their relations with atmospheric humidity[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2014,44(1):37-48 (in Chinese) | | [10] | Chen H P, Wang H J . Haze days in North China and the associated atmospheric circulations based on daily visibility data from 1960 to 2012[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2015,120(12):5895-5909 | | [11] | 尹志聪, 王会军, 袁东敏 . 华北黄淮冬季霾年代际增多与东亚冬季风的减弱[J]. 科学通报, 2015,60(15):1395-1400. | | [11] | Yin Z C, Wang H J, Yuan D M . Interdecadal increase of haze in winter over North China and the Huang-Huai area and the weakening of the East Asia winter monsoon[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015,60(15):1395-1400 (in Chinese) | | [12] | 吴萍, 丁一汇, 柳艳菊 , 等. 中国中东部冬季霾日的形成与东亚冬季风和大气湿度的关系[J]. 气象学报, 2016,74(3):352-366. | | [12] | Wu P, Ding Y H, Liu Y J , et al. Influence of the East Asian winter monsoon and atmospheric humidity on the wintertime haze frequency over central-eastern China[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2016,74(3):352-366 (in Chinese) | | [13] | Cai W J, Li K, Liao H , et al. Weather conditions conductive to Beijing severe haze more frequent under climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2017,7(4):257-262 | | [14] | Han Z Y, Zhou B T, Xu Y , et al. Projected changes in haze pollution potential in China: an ensemble of regional climate model simulations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics, 2017,17(16):1-46 | | [15] | 朱蓉, 张存杰, 梅梅 . 大气自净能力指数的气候特征与应用研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018,38(10):3601-3610. | | [15] | Zhu R, Zhang C J, Mei M . The climate characteristics of atmospheric self-cleaning ability index and its application in China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018,38(10):3601-3610 (in Chinese) | | [16] | 国家技术监督局,国家环境保护局. 制定地方大气污染物排放标准的技术方法: GB/T 13201—91 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1991. | | [16] | National Bureau of Technical Supervision, National Bureau of Environmental Protection. Techanical methods for making local emission standards of air pollutants: GB/T 13201-91 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1991 ( in Chinese) | | [17] | 梅梅, 朱蓉 . 污染防治重点区域大气扩散条件变化趋势及成因[J]. 环境影响评价, 2017,39(5):1-6. | | [17] | Mei M, Zhu R . Variation trend and genesis analysis of atmospheric diffusion conditions in key areas for pollution control[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2017,39(5):1-6 (in Chinese) | | [18] | 张恒德, 张碧辉, 吕梦瑶 , 等. 北京地区静稳天气综合指数的初步构建及其在环境气象中的应用[J]. 气象, 2017,43(8):998-1004. | | [18] | Zhang H D, Zhang B H, Lü M Y , et.al. Development and application of stable weather index of Beijing in environmental meteorology[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2017,43(8):998-1004 (in Chinese) | | [19] | Wang J X L, Angell J K . Air stagnation climatology for the United States (1948-1998) [R/OL]. NOAA. Air Resources Laboratory ATLAS No.1, 1999 [ 2018- 09- 20]. http://www.arl.noaa.gov/documents/reports/atlas.pdf | | [20] | 王遵娅, 司东, 段丽瑶 . 冷空气过程检测指标: QX/T 393—2017 [S]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2018. | | [20] | Wang Z Y, Si D, Duan L Y. Monitoring indices of cold air processes: QX/T 393—2017 [S]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2018 ( in Chinese) | | [21] | 张爱英, 任国玉, 郭军 , 等. 近30年我国高空风速变化趋势分析[J]. 高原气象, 2009,28(3):680-686. | | [21] | Zhang A Y, Ren G Y, Guo J , et al. Change trend analyses on upper-air wind speed over China in the past 30 years[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2009,28(3):680-686 (in Chinese) | | [22] | Yin Z C, Wang H J, Chen H P . Understanding severe winter haze events in the North China Plain in 2014: roles of climate anomalies[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2017,17(3):1641-1651 | | [23] | Wang H J, Chen H P, Liu J P , et al. Arctic sea ice decline intensified haze pollution in eastern China[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2015,8(1):1-9 | | [24] | Zhao S, Li J, Cheng S . Decadal variability in the occurrence of wintertime haze in central eastern China tied to the Pacific Decadal Oscillation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016,6(1):27424 | | [25] | Xu X, Zhao T, Liu F , et al. Climate modulation of the Tibetan Plateau on haze in China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions, 2016,15(3):28915-28937 |
|