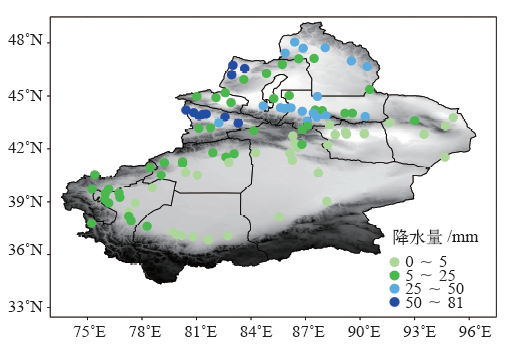
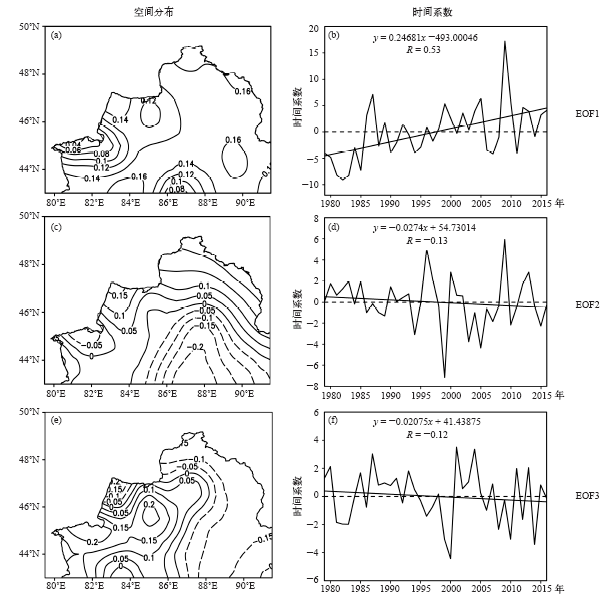
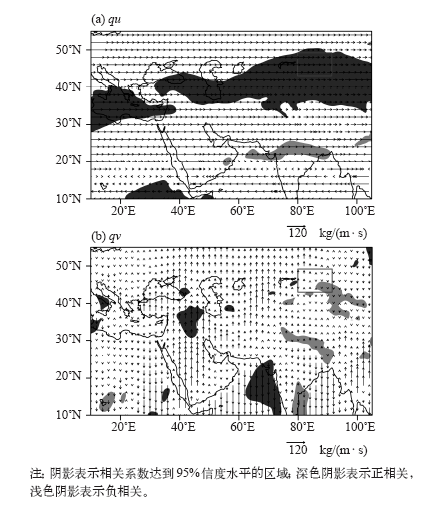
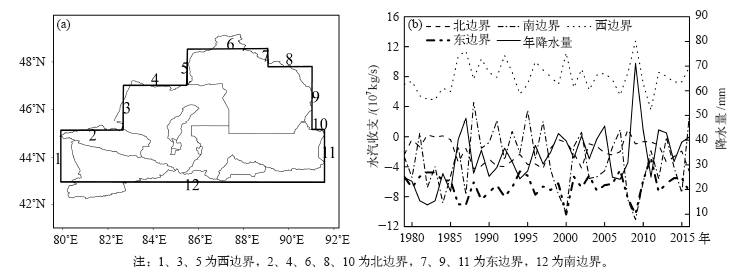
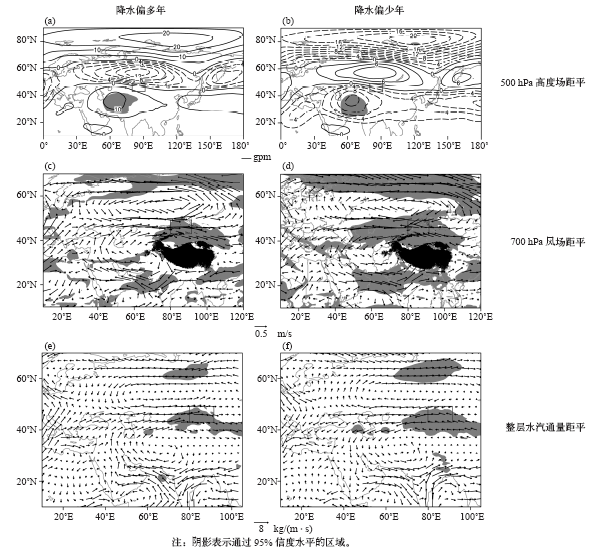
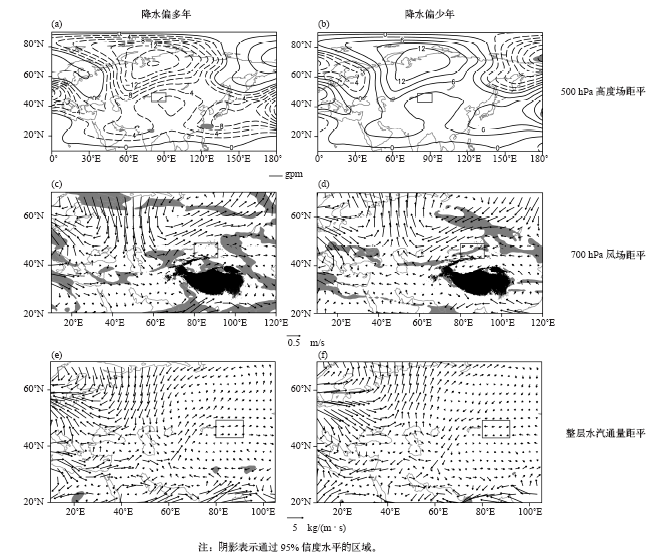
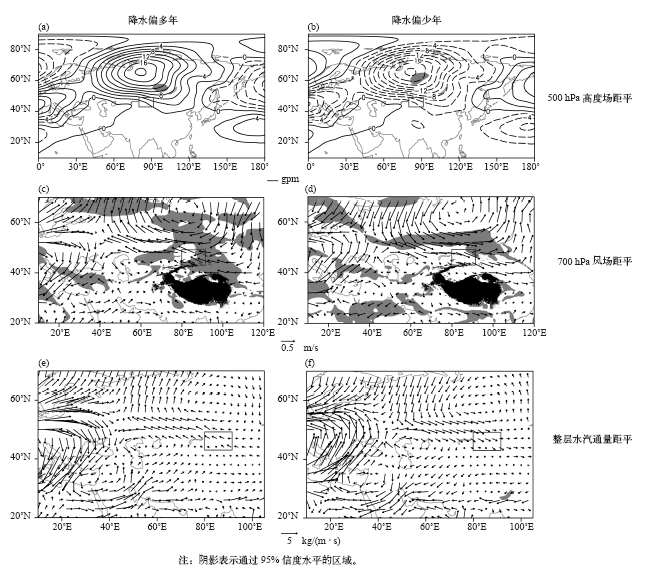
| [1] | 张家宝, 邓子风 . 新疆降水概论[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1987: 278-280 | | [2] | 张庆云, 陶诗言 . 亚洲中高纬度环流对东亚夏季降水的影响[J]. 气象学报, 1998,56(2):199-211 | | [3] | 黄荣辉, 张振洲, 黄刚 , 等. 夏季东亚季风区水汽输送特征及其与南亚季风区水汽输送的差别[J]. 大气科学, 1998,22(4):460-469 | | [4] | 黄荣辉, 刘永, 冯涛 . 20世纪90年代末中国东部夏季降水和环流的年代际变化特征及其内动力成因[J]. 科学通报, 2013 ( 8):617-628 | | [5] | Brimelow J C, Reuter G W . Transport of atmospheric moisture during three extreme rainfall events over the Mackenzie River Basin[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2005,6(4):423-440 | | [6] | Wang H, He S . The North China/Northeastern Asia severe summer drought in 2014[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015,28(17):6667-6681 | | [7] | 施能 . 近40年东亚冬季风强度的多时间尺度变化特征及其与气候的关系[J]. 应用气象学报, 1996,7(2):175-182 | | [8] | 黄荣辉, 刘永, 皇甫静亮 , 等. 20世纪90年代末东亚冬季风年代际变化特征及其内动力成因[J]. 大气科学, 2014,38(4):627-644 | | [9] | 肖晓, 陈文, 范广洲 , 等. 20世纪90年代末东亚冬季风年代际变化的外强迫因子分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2016,21(2):197-209 | | [10] | 钱维宏, 张玮玮 . 我国近46年来的寒潮时空变化与冬季增暖[J]. 大气科学, 2007,31(6):1266-1278 | | [11] | 靳立亚, 符娇兰, 陈发虎 . 西北地区空中水汽输送时变特征及其与降水的关系[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自科版, 2006,42(1):1-6 | | [12] | 黄荣辉, 陈际龙 . 我国东、西部夏季水汽输送特征及其差异[J]. 大气科学, 2010,34(6):1035-1045 | | [13] | 何金海, 刘芸芸, 常越 . 西北地区夏季降水异常及其水汽输送和环流特征分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2005,23(1):10-16 | | [14] | 陈活泼, 孙建奇, 范可 . 新疆夏季降水年代际转型的归因分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012,55(6):1844-1851 | | [15] | 史玉光, 孙照渤 . 新疆水汽输送的气候特征及其变化[J]. 高原气象, 2008,27(2):310-319 | | [16] | Huang W, Feng S, Chen J , et al. Physical mechanisms of summer precipitation variations in the Tarim Basin in Northwestern China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015,28(9):3579-3591 | | [17] | 杨莲梅, 张庆云 . 新疆北部汛期降水年际和年代际异常的环流特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2007,50(2):412-419 | | [18] | 杨莲梅, 张云惠, 汤浩 . 2007年7月新疆三次暴雨过程的水汽特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2012,31(4):963-973 | | [19] | 戴新刚, 李维京, 马柱国 . 近十几年新疆水汽源地变化特征[J]. 自然科学进展, 2006,16(12):1651-1656 | | [20] | 杨莲梅, 刘雯 . 新疆北部持续性暴雪过程成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 2016,35(2):507-519 | | [21] | 杨莲梅, 杨涛, 贾丽红 , 等. 新疆大~暴雪气候特征及其水汽分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2005,27(3):389-396 | | [22] | 张书萍, 祝从文 . 2009年冬季新疆北部持续性暴雪的环流特征及其成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 2011,35(5):833-846 | | [23] | 张俊兰, 崔彩霞, 陈春艳 . 北疆典型暴雪天气的水汽特征研究[J]. 高原气象, 2013,32(4):1115-1125 | | [24] | 杨莲梅, 史玉光, 汤浩 . 新疆北部冬季降水异常成因[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010,21(4):491-499 | | [25] | Yatagai A . Evaluation of hydrological balance and its variability in arid and semi-arid regions of Eurasia from ECMWF 15 year reanalysis[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2003,17(14):2871-2884 | | [26] | 魏凤英 . 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 气象出版社, 2007: 37-41 | | [27] | 杨莲梅, 关学锋, 张迎新 . 亚洲中部干旱区降水异常的大气环流特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018,35(2):249-259 |
|
 ),Lian-Mei YANG1,2(
),Lian-Mei YANG1,2( )
)