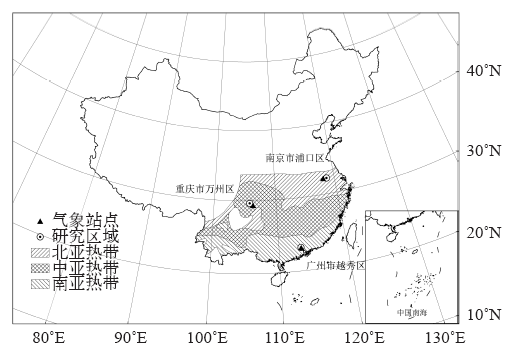
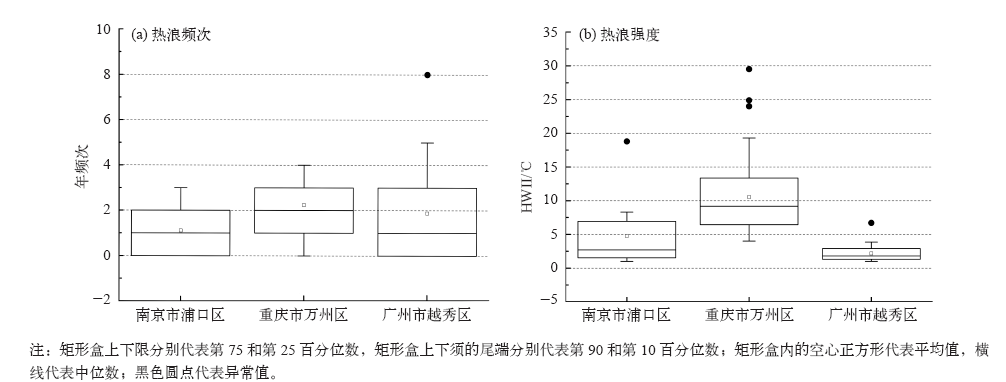
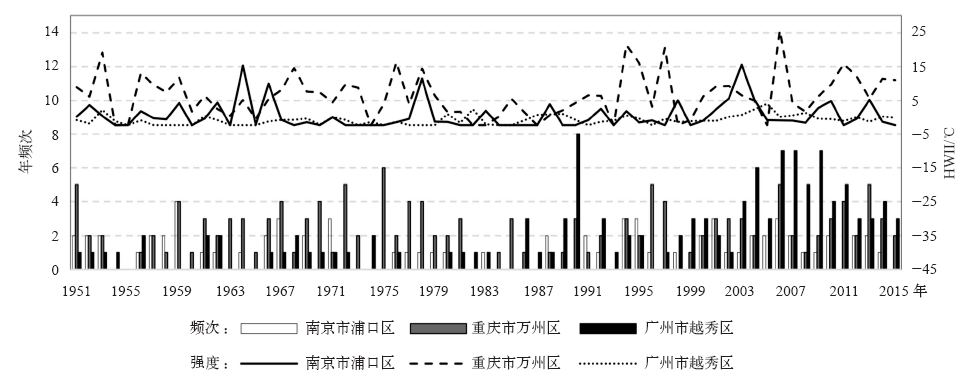
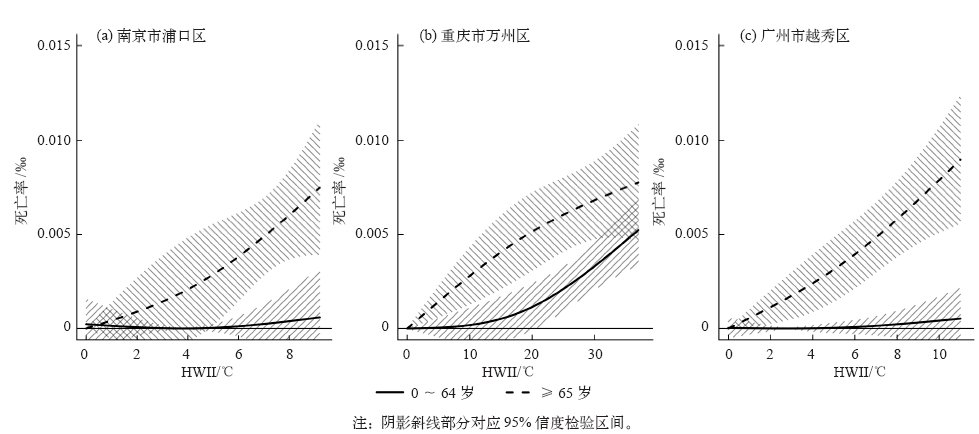
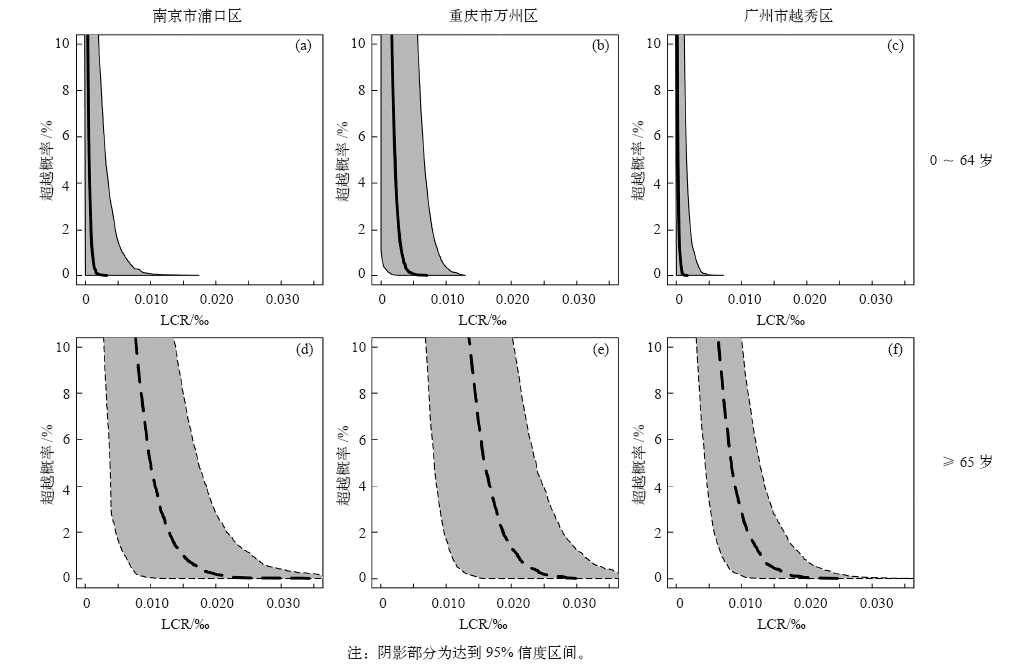
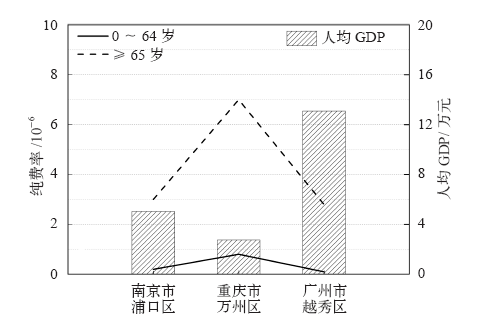
| [1] | Zuo J, Pullen S, Palmer J , et al. Impacts of heat waves and corresponding measures: a review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015,92:1-12 | | [2] | Gao J, Sun Y, Liu Q , et al. Impact of extreme high temperature on mortality and regional level definition of heat wave: a multi-city study in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015,505:535-544 | | [3] | Guo Y, Li S, Zhang Y , et al. Extremely cold and hot temperatures increase the risk of ischaemic heart disease mortality: epidemiological evidence from China[J]. Heart, 2012,99(3):195-203 | | [4] | 吴凡, 景元书, 李雪源 , 等. 南京地区高温热浪对心脑血管疾病日死亡人数的影响[J]. 环境卫生学杂志, 2013,4:288-292 | | [5] | Ma W, Zeng W, Zhou M , et al. The short-term effect of heat waves on mortality and its modifiers in China: an analysis from 66 communities[J]. Environment International, 2015,75:103-109 | | [6] | Anderson G B, Bell M L . Heat waves in the United States: mortality risk during heat waves and effect modification by heat wave characteristics in 43 U. S. communities[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2011,119(2):210-218 | | [7] | 许遐祯, 郑有飞, 尹继福 , 等. 南京市高温热浪特征及其对人体健康的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2011,12:2815-2820 | | [8] | 程义斌, 金银龙, 李永红 , 等. 武汉市高温对心脑血管疾病死亡的影响[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2009,3:224-225 | | [9] | Peng Z, Wang Q, Kan H , et al. Effects of ambient temperature on daily hospital admissions for mental disorders in Shanghai, China: a time-series analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017,590:281-286 | | [10] | Wolf T , McGregor G, Analitis A . Performance assessment of a heat wave vulnerability index for Greater London, United Kingdom[J]. Weather Climate and Society, 2014,6(1):32-46 | | [11] | Gasparrini A, Armstrong B . The impact of heat waves on mortality[J]. Epidemiology, 2011,22(1):68-73 | | [12] | Robine J M, Cheung S L, Roy S L , et al. Report on excess mortality in Europe during summer 2003 [R]. G. A. EU Community Action Programme for Public Health, 2007 | | [13] | Agence France-Press. Russian heat wave caused 11,000 deaths in Moscow: official. 2010 [Z/OL]. 2010 [2018-02-20]. | | [14] | World Bank . World development report 2014: risk and opportunity: managing risk for development [R]. Washington DC: World Bank, 2013 | | [15] | Tseng C, Chen C . Natural disaster management mechanisms for probabilistic earthquake loss[J]. Natural Hazards, 2012,60(3):1055-1063 | | [16] | Paudel Y , Botzen W J W, Aerts J C J H. Influence of climate change and socio-economic development on catastrophe insurance: a case study of flood risk scenarios in the Netherlands[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2015,15:1717-1729 | | [17] | Chantarat S, Barrett C B, Mude A G , et al. Using weather index insurance to improve drought response for famine prevention[J]. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 2007,89:1262-1268 | | [18] | Ye T, Li Y, Gao Y , et al. Designing index-based livestock insurance for managing snow disaster risk in Eastern Inner Mongolia, China[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2017,23:160-168 | | [19] | 刘凯文, 刘可群, 邓爱娟 , 等. 基于开花期地域差异的中稻高温热害天气指数保险设计[J]. 中国农业气象, 2017,10:679-688 | | [20] | 张静, 张朝, 陶福禄 . 中国南方双季稻区天气指数保险的选择分析[J]. 保险研究, 2017,7:13-21 | | [21] | 易沵泺, 王季薇, 王铸 , 等. 草原牧区雪灾天气指数保险设计: 以内蒙古东部地区为例[J]. 保险研究, 2015,5:69-77 | | [22] | Zhang J, Liu S, Han J , et al. Impact of heat waves on non-accidental deaths in Jinan, China, and associated risk factors[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 2016,60(9):1367-1375 | | [23] | Saha S, Brock J W, Vaidyanathan A , et al. Spatial variation in hyperthermia emergency department visits among those with employer-based insurance in the United States: a case-crossover analysis[J]. Environmental Health, 2015,14:20 | | [24] | Tian Z, Li S, Zhang J , et al. The characteristic of heat wave effects on coronary heart disease mortality in Beijing, China: a time series study[J]. Plos One, 2013,8(9):e77321 | | [25] | Son J, Lee J, Anderson B G , et al. The impact of heat waves on mortality in seven major cities in Korea[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2012,120(4):566-571 | | [26] | Ma W, Xu X, Peng L , et al. Impact of extreme temperature on hospital admission in Shanghai, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2011,409:3634-3637 | | [27] | Chen K, Bi J, Chen J , , et al. Influence of heat wave definitions to the added effect of heat waves on daily mortality in Nanjing,China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 506- 507:18-25 | | [28] | 冯灵芝, 熊伟, 居辉 , 等. RCP情景下长江中下游地区水稻生育期内高温事件的变化特征[J]. 中国农业气象, 2015,4:383-392 | | [29] | 陈敏, 耿福海, 马雷鸣 , 等. 近138年上海地区高温热浪事件分析[J]. 高原气象, 2013,2:2597-2607 | | [30] | Anderson G B, Bell M L . Weather-related mortality: how heat, cold, and heat waves affect mortality in the United States[J]. Epidemiology, 2009,20(2):205-213 | | [31] | Guo Y, Gasparrini A, Armstrong B , et al. Global variation in the effects of ambient temperature on mortality: a systematic evaluation[J]. Epidemiology, 2014,25(6):781-789 | | [32] | Wang C, Zhang Z, Zhou M , et al. Nonlinear relationship between extreme temperature and mortality in different temperature zones: a systematic study of 122 communities across the mainland of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017,586:96-106 | | [33] | Grossi P, Kunreuther H . Catastrophe modeling: a new approach to managing risk[M]. Springer US, 2005 | | [34] | ?str?m D O, Forsberg B, Rockl?v J . Heat wave impact on morbidity and mortality in the elderly population: a review of recent studies[J]. Maturitas, 2011,69(2):99-105 | | [35] | Tan J, Zheng Y, Song G , et al. Heat wave impacts on mortality in Shanghai, 1998 and 2003[J]. International Journal of Biometeorology, 2007,51(3):193-200 | | [36] | IPCC. Climate change 2014: synreport report [R]. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth assessment report of the IPCC. IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland, 2014: 1-151 | | [37] | Mills E . Synergisms between climate change mitigation and adaptation: an insurance perspective[J]. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2007,12(5):809-842 |
|
 ),Zhao ZHANG(
),Zhao ZHANG( ),Bin HOU
),Bin HOU