气候变化研究进展 ›› 2018, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (4): 362-370.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2017.198
1975—2016年秦巴山区极端气温事件的空间差异性分析
- 1 成都信息工程大学大气科学学院高原大气与环境四川省重点实验室,成都 610225
2 南京信息工程大学气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心,南京 210044
3 中国气象局国家气候中心,北京 100081
4 辽宁省桓仁满族自治县气象局,本溪 117200
Spatial heterogeneity of temperature extremes in the Qinling-Daba Mountains region in 1975-2016
Wei XIANG1,Zhi-Gang CHENG1( ),Bo-Tao ZHOU2,3,Xin BIN1,Dong-Lei FENG1,4
),Bo-Tao ZHOU2,3,Xin BIN1,Dong-Lei FENG1,4
- 1 College of Atmospheric Sciences, Chengdu University of Information Technology and The Key Laboratory of Plateau Atmosphere and Environment of Sichuan Province, Chengdu 610225, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
3 National Climate Center, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
4 Huanren Manchu Autonomous County Meteorological Burea, Benxi 117200, China
摘要:
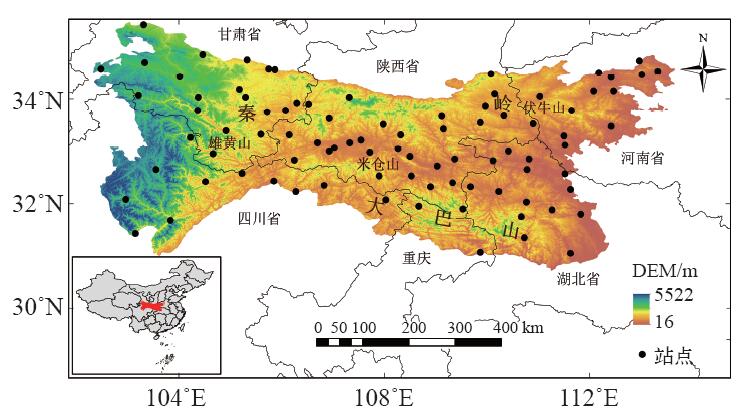
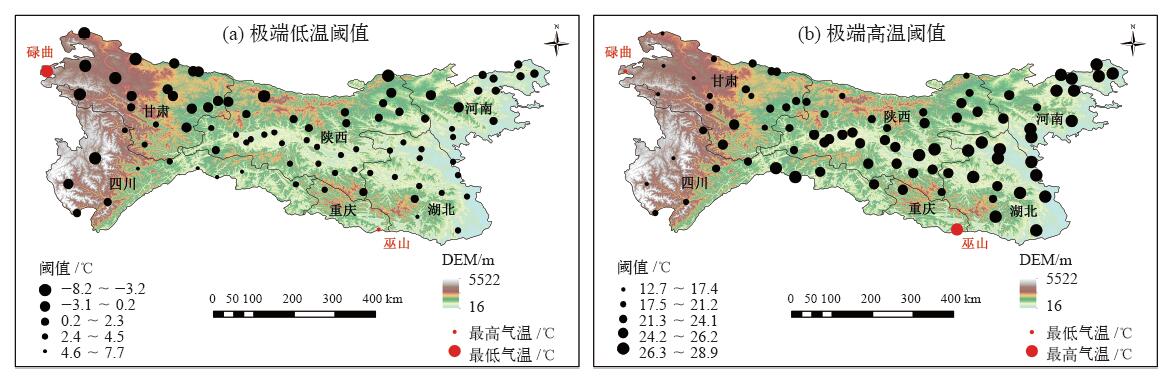
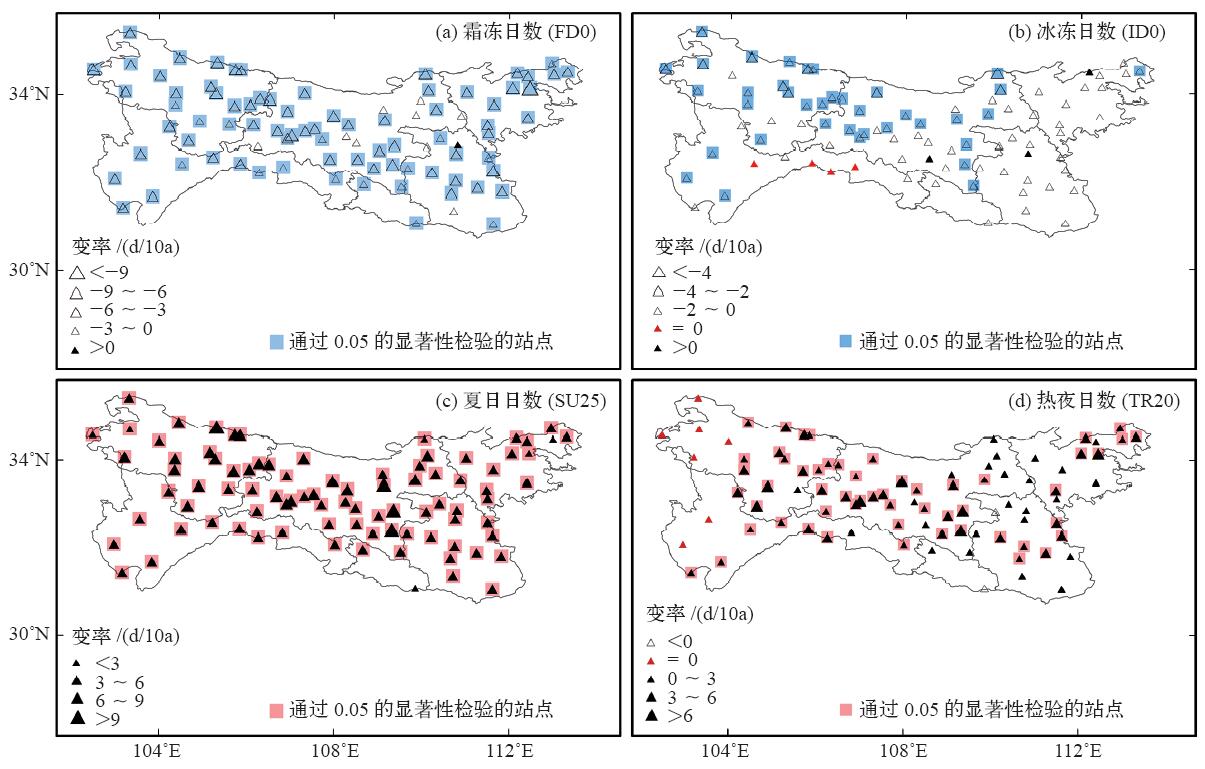
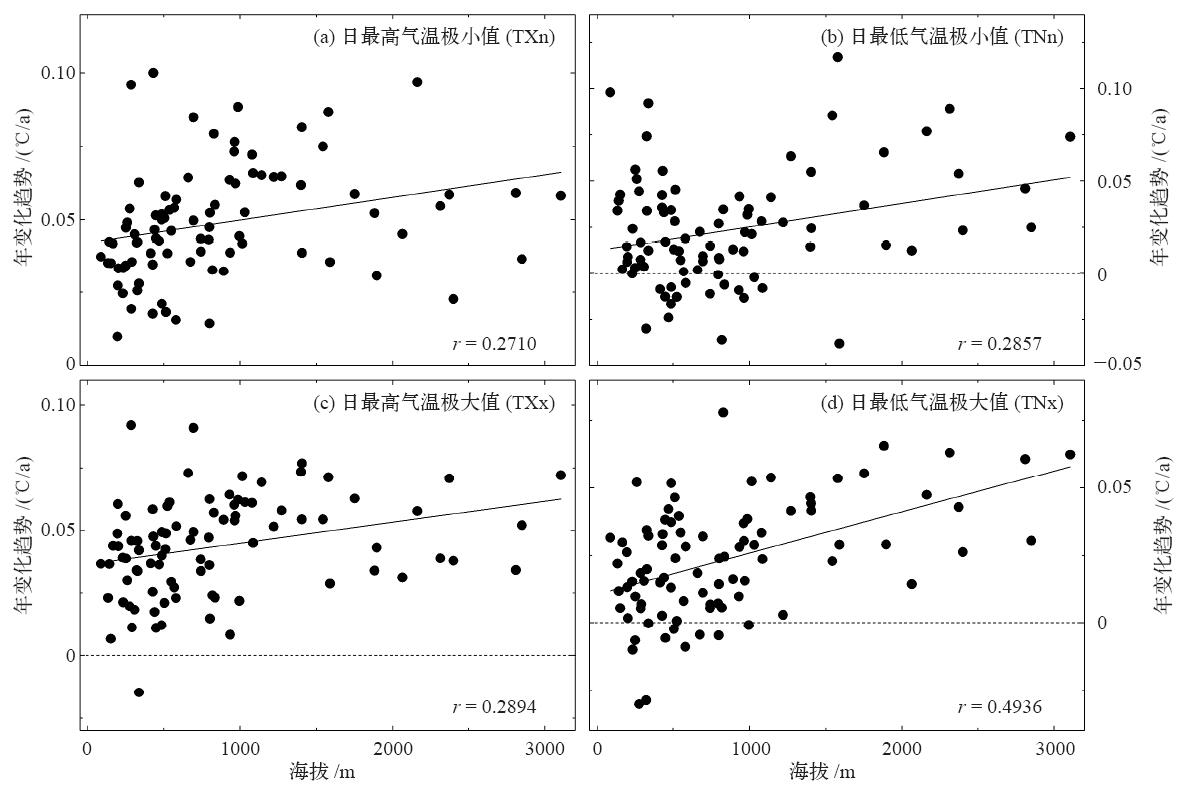
利用秦巴山区88个气象站1975—2016年的逐日气温数据,结合16个极端气温指数分析了秦巴山区极端气温阈值的空间分布及极端气温事件变化趋势的海拔依赖性。结果表明:极端气温阈值存在明显的空间分布差异,表现为极端低温阈值与极端高温阈值由西北向东南均有增温趋势;总体来看,极端气温暖事件(SU25、TR20、TX90P、TN90P、WSDI)增加幅度大于冷事件(FD0、ID0、TX10P、TN10P、CSDI)减少幅度,且变化趋势较冷事件更显著;全区霜冻日数、夏日日数、冷夜日数、暖昼日数及高温极值(TXx、TXn)变化均比较显著;区域作物生长期西部增长趋势较东部显著,多数站点变化幅度在3~6 d/10a之间;海拔越高发生极端低温事件的气温越低,极端低温阈值变化趋势为-0.36℃/100m;海拔越低发生极端高温事件的气温越高,极端高温变化趋势达0.5℃/100m,且均通过99%的信度检验;区域极端气温极值指数的变化趋势与海拔呈显著正相关,具有明显的海拔依赖性,表现为海拔越高,极值指数增加趋势越明显。