气候变化研究进展 ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (4): 468-481.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.261
CMIP6与CMIP5对历史大气层顶和地表辐射收支模拟的时空对比
万梓文1,2, 王伟1,2( ), 吕恒1,2, 仇培宇3, 李雨竹1,2, 卢阳4
), 吕恒1,2, 仇培宇3, 李雨竹1,2, 卢阳4
- 1 南京信息工程大学气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心,南京 210044
2 南京信息工程大学江苏省农业气象重点实验室,南京 210044
3 中国气象科学研究院,北京 100081
4 广东省佛山市顺德区气象局,佛山 528399
-
收稿日期:2021-11-10修回日期:2022-01-07出版日期:2022-07-30发布日期:2022-06-01 -
通讯作者:王伟 -
作者简介:万梓文,男,硕士研究生 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2019YFA0607202)
Comparison between CMIP6 and CMIP5 models in simulating historical spatiotemporal variations in radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface
WAN Zi-Wen1,2, WANG Wei1,2( ), LYU Heng1,2, QIU Pei-Yu3, LI Yu-Zhu1,2, LU Yang4
), LYU Heng1,2, QIU Pei-Yu3, LI Yu-Zhu1,2, LU Yang4
- 1 Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters (CIC-FEMD), Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology (NUIST), Nanjing 210044, China
2 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Agricultural Meteorology, NUIST, Nanjing 210044, China
3 Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, Beijing 100081, China
4 Meteorological Bureau of Shunde District, Foshan 528399, China
-
Received:2021-11-10Revised:2022-01-07Online:2022-07-30Published:2022-06-01 -
Contact:WANG Wei
摘要:
基于云和地球辐射能量系统观测数据集(CERES),对比分析了耦合模式比较计划第五(CMIP5)和第六阶段(CMIP6)模拟的历史大气层顶和地表辐射收支的年际变化和空间分布,明确了多模式间不确定性大的关键区域。结果表明:在年际尺度上,除地表向上长波辐射外,CMIP6的辐射分量的集合均值较CMIP5更接近于CERES观测值,全球地表向下短波辐射的高估和大气逆辐射的低估在CMIP6中分别降低了1.9 W/m2和3.3 W/m2。除大气逆辐射外,CMIP6的辐射分量在多模式间的一致性较CMIP5提高。在北极,CMIP6对大气层顶反射短波、大气层顶出射长波和地表向下短波辐射的模拟偏差较CMIP5大。在南北纬60°,CMIP6对大气逆辐射的模拟偏差较CMIP5大。其他区域CMIP6的辐射分量更接近CERES观测值。CMIP6模拟的地表向下短波辐射和大气逆辐射的不确定性较大区域面积较CMIP5减小,但不确定性极大区域面积无变化。地表净辐射的不确定性空间分布在两代CMIP间变化甚小。青藏高原、赤道太平洋、热带雨林、阿拉伯半岛和南极洲沿海依然是地球系统模式模拟辐射收支不确定性极大的关键区域。
引用本文
万梓文, 王伟, 吕恒, 仇培宇, 李雨竹, 卢阳. CMIP6与CMIP5对历史大气层顶和地表辐射收支模拟的时空对比[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 468-481.
WAN Zi-Wen, WANG Wei, LYU Heng, QIU Pei-Yu, LI Yu-Zhu, LU Yang. Comparison between CMIP6 and CMIP5 models in simulating historical spatiotemporal variations in radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(4): 468-481.

图1 CMIP5(1850—2005年)、CMIP6(1850—2014年)和CERES(2001—2018年)的大气层顶(TOA)和地表(SFC)辐射收支的年际变化 注:蓝色阴影和红色阴影分别为CMIP5和CMIP6多模式间1倍标准差。
Fig. 1 Interannual variations in radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface for CMIP5 from 1850 to 2005, CMIP6 from 1850 to 2014 and CERES from 2001 to 2018. (Blue and red shading areas represent the one standard derivation among Earth System Models in CMIP5 and CMIP6, respectively)
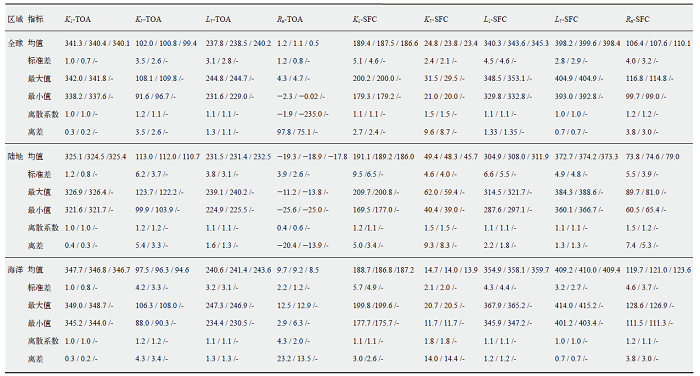 |
表3 2001—2005年CMIP5 / CMIP6 / CERES大气层顶和地表辐射收支统计数据
Table 3 Statistics of radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface for CMIP5 / CMIP6 / CERES from 2001 to 2005
 |

图2 2001—2005年平均的CERES大气层顶和地表辐射收支全球分布以及CERES、CMIP5、CMIP6的纬向分布
Fig. 2 Geographical distribution of radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface from CERES and zonal means from CERES, CMIP5 and CMIP6 for the period 2001-2005

图3 2001—2005年平均的CMIP5、CMIP6与CERES大气层顶和地表辐射收支差值的全球和纬向分布
Fig. 3 Geographical distribution and zonal mean of CMIP5, CMIP6 radiation budgets deviation relative to CERES observation at the top of atmosphere and the surface for the period 2001-2005

图4 2001—2005年平均的CMIP5、CMIP6大气层顶和地表辐射收支多模式间不确定性的空间分布
Fig. 4 Geographical distribution of regions with large inter-model variability in radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface from CMIP5 models and CMIP6 models for the period 2001-2005
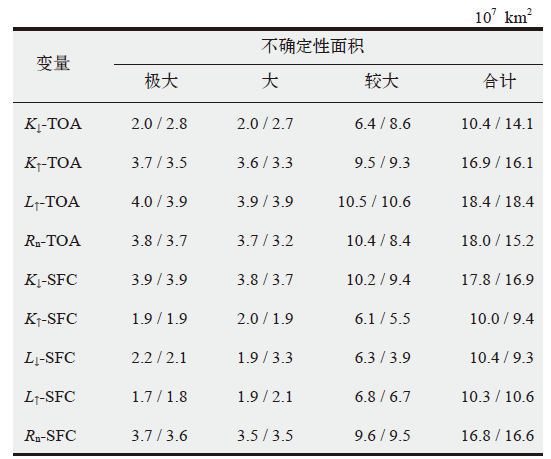 |
表4 CMIP5 / CMIP6大气层顶和地表辐射分量模式间不确定性大的区域面积的统计值
Table 4 Area of regions with large inter-model variability for radiation budgets at the top of atmosphere and the surface from CMIP5 models and CMIP6 models
 |
| [1] |
Stephens G L, Li J, Wild M, et al. An update on Earth’s energy balance in light of the latest global observations[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5 (10): 691-696. DOI: 10.1038/ngeo1580
doi: 10.1038/ngeo1580 URL |
| [2] |
Wild M. The global energy balance as represented in CMIP6 climate models[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2020, 55 (16): 553-577. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-020-05282-7
doi: 10.1007/s00382-020-05282-7 URL |
| [3] |
Wild M, Folini D, Hakuba M Z, et al. The energy balance over land and oceans: an assessment based on direct observations and CMIP5 climate models[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2015, 44 (11-12): 3393-3429. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-014-2430-z
doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2430-z URL |
| [4] |
Loeb N, Natividad M S, Su W Y, et al. CERES Top-of-Atmosphere Earth radiation budget climate data record: accounting for in-orbit changes in instrument calibration[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8 (182): 1-14. DOI: 10.3390/rs8030182
doi: 10.3390/rs8030182 URL |
| [5] |
Allen M R, Ingram J W. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle[J]. Nature: International Weekly Journal of Science, 2002, 419 (6903): 228-232. DOI: 10.1038/nature01092
doi: 10.1038/nature01092 |
| [6] |
DeAngelis A M, Qu X, Zelinka M D, et al. An observational radiative constraint on hydrologic cycle intensification[J]. Nature, 2015, 528 (7581): 249-253. DOI: 10.1038/nature15770
doi: 10.1038/nature15770 URL |
| [7] | Lee X. Fundamentals of boundary-layer meteorology[M]. Gewerbestrasse: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 22-24 |
| [8] |
Wang W, Chakraborty T C, Xiao W, et al. Ocean surface energy balance allows a constraint on the sensitivity of precipitation to global warming[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12 (2115): 1-9. DOI: 10.1038/S41467-021-22406-7
doi: 10.1038/S41467-021-22406-7 URL |
| [9] |
Wild M. Short-wave and long-wave surface radiation budgets in GCMs: a review based on the IPCC-AR4/CMIP3 models[J]. Dynamic Meteorology and Oceanography, 2008, 60 (5): 932-945. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0870.2008.00342.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0870.2008.00342 |
| [10] |
周天军, 陈梓明, 邹立维, 等. 中国地球气候系统模式的发展及其模拟和预估[J]. 气象学报, 2020, 78 (3): 332-350. DOI: 10.11676/qxxb2020.029.
doi: 10.11676/qxxb2020.029 |
|
Zhou T J, Chen Z M, Zou L W, et al. Development of climate and Earth System Models in China[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2020, 78 (3): 332-350. DOI: 10.11676/qxxb2020.029 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11676/qxxb2020.029 |
|
| [11] |
周天军, 邹立维, 陈晓龙. 第六次国际耦合模式比较计划(CMIP6) 评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15 (5): 445-456. DOI: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2019.193.
doi: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2019.193 |
|
Zhou T J, Zou L W, Chen X L. Commentary on the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6)[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15 (5): 445-456. DOI: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2019.193 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2019.193 |
|
| [12] |
赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 从检验CMIP5气候模式看CMIP6地球系统模式的发展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14 (6): 643-648. DOI: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2018.036.
doi: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2018.036 |
|
Zhao Z C, Luo Y, Huang J B. The detection of the CMIP5 climate model to see the development of CMIP6 Earth System Models[J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14 (6): 643-648. DOI: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2018.036 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.12006/.issn.1673-1719.2018.036 |
|
| [13] |
Wild M, Folini D, Schaer C, et al. The global energy balance from a surface perspective[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2013, 40 (11-12): 3107-3134. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-012-1569-8
doi: 10.1007/s00382-012-1569-8 URL |
| [14] |
Taylor K E, Stouffer R J, Meehl G A. An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design[J]. Bulletin of The American Meteorological Society, 2012, 93 (4): 485-498. DOI: 10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00094.1
doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00094.1 URL |
| [15] |
Veronika E, Sandrine B, Meehl G A, et al. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2016, 9 (5): 1937-1958. DOI: 10.5194/gmd-9-1937-2016
doi: 10.5194/gmd-9-1937-2016 URL |
| [16] |
Thornhill G, Collins W, Olivié D, et al. Climate-driven chemistry and aerosol feedbacks in CMIP6 Earth System Models[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2021, 21 (2): 1105-1126. DOI: 10.5194/acp-21-1105-2021
doi: 10.5194/acp-21-1105-2021 |
| [17] |
Wild M. Validation of general circulation model radiative fluxes using surface observations[J]. Journal of Climate, 1995, 8 (5): 1309-1324. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(1995)0082.0.CO;2
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1995)0082.0.CO;2 URL |
| [18] |
Wild M, Long C N, Ohmura A. Evaluation of clear-sky solar fluxes in GCMs participating in AMIP and IPCC-AR4 from a surface perspective[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2006, 111 (D1): 1-15. DOI: 10.1029/2005JD006118
doi: 10.1029/2005JD006118 |
| [19] |
赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌. 评估43个CMIP5模式模拟全球能量平衡能力[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2015 (3): 227-230. DOI: 10.3969/.issn.1673-1719.2015.03.010.
doi: 10.3969/.issn.1673-1719.2015.03.010 |
|
Zhao Z C, Luo Y, Huang J B. Assessment of global energy balance as simulated by 43 CMIP5 climate models[J]. Climate Change Reasearch, 2015 (3): 227-230. DOI: 10.3969/.issn.1673-1719.2015.03.010 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3969/.issn.1673-1719.2015.03.010 |
|
| [20] |
Wild M, Hakuba M Z, Folini D, et al. The cloud-free global energy balance and inferred cloud radiative effects: an assessment based on direct observations and climate models[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018, 52 (7-8): 4787-4812. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-018-4413-y
doi: 10.1007/s00382-018-4413-y URL |
| [21] |
Wild M, Folini D, Henschel F, et al. Projections of long-term changes in solar radiation based on CMIP5 climate models and their influence on energy yields of photovoltaic systems[J]. Solar Energy, 2015, 116 (6): 12-24. DOI: 10.1016/j.solener.2015.03.039
doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2015.03.039 URL |
| [22] |
Wild M, Ohmura A, Gilgen H, et al. Evaluation of downward longwave radiation in General Circulation Models[J]. Journal of Climate, 2001, 14 (15): 3227-3239. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(2001)0142.0.CO;2
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2001)0142.0.CO;2 URL |
| [23] |
Loeb N G, Doelling D R, Wang H, et al. Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Energy Balanced and Filled (EBAF) top-of-atmosphere (TOA) edition-4.0 data product[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017 (1): 895-918. DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0208.1
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0208.1 |
| [24] |
Trenberth K E, Fasullo J T, Kiehl J. Earth’s global energy budget[J]. Bulletin of The American Meteorological Society, 2009, 90 (3): 311-323. DOI: 10.1175/2008BAMS2634.1
doi: 10.1175/2008BAMS2634.1 URL |
| [25] |
Loeb N G, Wielicki B A, Doelling D R, et al. Toward optimal closure of the Earth’s Top-of-Atmosphere radiation budget[J]. Journal of Climate, 2009, 22 (3): 748-766. DOI: 10.1175/2008JCLI2637.1
doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2637.1 URL |
| [26] |
Von Schuckmann K, Palmer M D, Trenberth K E, et al. An imperative to monitor Earth’s energy imbalance[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2016, 6: 138-144. DOI: 10.1038/nclimate2876
doi: 10.1038/nclimate2876 URL |
| [27] |
Kato S, Rose F G, Rutan D A, et al. Surface irradiances of edition 4.0 Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System (CERES) Energy Balanced and Filled (EBAF) data product[J]. Journal of Climate, 2018, 31 (11): 4501-4527. DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0523.1
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0523.1 URL |
| [28] |
Li J, Sun Z, Liu Y, et al. Top-of-Atmosphere radiation budget and cloud radiative effects over the Tibetan Plateau and adjacent monsoon regions from CMIP6 simulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2021, 126 (9): 1-26. DOI: 10.1002/essoar.10505197.1
doi: 10.1002/essoar.10505197.1 |
| [29] |
Zhang X T, Liang S L, Wild M, et al. Analysis of surface incident shortwave radiation from four satellite products[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015 (165): 186-202. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.05.015
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.05.015 |
| [30] |
Gui S, Liang S, Li L. Evaluation of satellite-estimated surface longwave radiation using ground-based observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2010, 115 (D18): 1-16. DOI: 10.1029/2009JD013635
doi: 10.1029/2009JD013635 |
| [31] |
黄禄丰, 朱再春, 黄萌田, 等. 基于CMIP6模式优化集合平均预估21世纪全球陆地生态系统总初级生产力变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (5): 514-524. DOI: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.221.
doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.221 |
|
Huang L F, Zhu Z C, Huang M T, et al. Projection of gross primary productivity change of global terrestrial ecosystem in the 21st century based on optimal ensemble averaging of CMIP6 models[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17 (5): 514-524. DOI: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.221 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.221 |
|
| [32] |
Fläschner D, Mauritsen T, Stevens B. Understanding the intermodel spread in global-mean hydrological sensitivity[J]. Journal of Climate, 2016, 29 (2): 801-817. DOI: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0351.1
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0351.1 URL |
| [33] |
Jung M, Reichstein M, Margolis H A, et al. Global patterns of land-atmosphere fluxes of carbon dioxide, latent heat, and sensible heat derived from eddy covariance, satellite, and meteorological observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2011, 116 (G3): 1-16. DOI: 10.1029/2010JG001566
doi: 10.1029/2010JG001566 |
| [34] |
Zhou C, Zelinka M D, Dessler A E, et al. The relationship between interannual and long-term cloud feedbacks[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42 (23): 10463-10469. DOI: 10.1002/2015GL066698
doi: 10.1002/2015GL066698 |
| [35] |
Zhou L J, Zhang M H, Bao Q, et al. On the incident solar radiation in CMIP5 models[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42 (6): 1930-1935. DOI: 10.1002/2015GL063239
doi: 10.1002/2015GL063239 URL |
| [36] |
Dolinar E K, Dong X, Xi B, et al. Evaluation of CMIP5 simulated clouds and TOA radiation budgets using NASA satellite observations[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2015, 44 (7-8): 2229-2247
doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2158-9 URL |
| [37] |
Schwarz M, Folini D, Yang S, et al. Changes in atmospheric shortwave absorption as important driver of dimming and brightening[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2020, 13: 110-115. DOI: 10.1038/s41561-019-0528-y
doi: 10.1038/s41561-019-0528-y URL |
| [1] | 黄禄丰, 朱再春, 黄萌田, 赵茜, 马伟蕊, 曾辉. 基于CMIP6模式优化集合平均预估21世纪全球陆地生态系统总初级生产力变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 514-524. |
| [2] | 张稼乐,潘志华,匡文慧,潘宇鹰,韩国琳,王佳琳,黄娜,张子源,尹文娟. 1984—2014年北京地区不透水地表的时空变化及其温度效应研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(3): 296-305. |
| [3] | 纪多颖,张倩,骆祉丞,陈扬馨. CMIP6二氧化碳移除模式比较计划(CDRMIP)概况与评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 457-464. |
| [4] | 宋振亚,鲍颖,乔方利. FIO-ESM v2.0模式及其参与CMIP6的方案[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 558-565. |
| [5] | 曹剑,马利斌,李娟,王斌,王波. NUIST-ESM模式及其参与CMIP6的方案[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 566-570. |
| [6] | 辛晓歌,吴统文,张洁,张芳,李伟平,张艳武,路屹雄,房永杰,颉卫华,张莉,董敏,史学丽,李江龙,储敏,刘茜霞,颜京辉. BCC模式及其开展的CMIP6试验介绍[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 533-539. |
| [7] | 林岩銮,黄小猛,梁逸爽,秦怡,徐世明,黄文誉,徐芳华,刘利,王勇,彭怡然,王兰宁,薛巍,付昊桓,张广俊,王斌,李锐喆,张诚,卢麾,阳坤,罗勇,白玉琪,宋振亚,王敏琦,赵文婕,张峰,徐敬蘅,赵曦,陆春松,骆亦其,陈奕兆,胡勇,唐强,陈德训,杨广文,宫鹏. 清华大学CIESM模式及其参与CMIP6的方案[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 545-550. |
| [8] | 容新尧,李建,陈昊明,辛羽飞,苏京志,华莉娟,张正秋. CAMS-CSM模式及其参与CMIP6的方案[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(5): 540-544. |
| [9] | 杨世莉,董文杰,丑洁明,刘昌新. 对地球系统模式与综合评估模型双向耦合问题的探讨[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(4): 335-342. |
| [10] | 吴启蒙,吴立广,曹剑. NUIST地球系统模式模拟热带气旋活动的气候特征分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(2): 107-118. |
| [11] | 徐文慧, 李庆祥, 杨溯, 许艳. 近百年全球地表月气温数据的概况与初步整合[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(5): 358-364. |
| [12] | 高蕾, 陈海山, 孙善磊. 基于MODIS卫星资料研究三峡工程对库区地表温度的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(3): 226-234. |
| [13] | 赵宗慈 罗勇 黄建斌. 对地球系统模式评估方法的回顾[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9(1): 1-8. |
| [14] | 刘波 姜彤 任国玉 Klaus Fraedrich. 2050年前长江流域地表水资源变化趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(003): 145-150. |
| [15] | 马柱国 任小波. 1951-2005年中国区域气候变化与干旱化趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007, 03(04): 195-201. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||