气候变化研究进展 ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (3): 294-304.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.274
所属专题: “碳中和”目标下的关键节点——2035美丽中国低碳发展路径研究专栏
• “碳中和”目标下的关键节点——2035美丽中国低碳发展路径研究专栏 • 上一篇 下一篇
基于混合LCA的新疆地区电力生产水足迹分析及碳中和目标下的变化
闫书琪1, 李素梅1, 吕鹤1, 陈莎1( ), 刘影影1, 王宏涛2, 刘会政3, 陈前利4
), 刘影影1, 王宏涛2, 刘会政3, 陈前利4
- 1 北京工业大学环境科学系,北京 100124
2 中国质量认证中心,北京 100070
3 北京工业大学经济与管理学院,北京 100124
4 新疆农业大学管理学院,乌鲁木齐 830052
-
收稿日期:2021-12-06修回日期:2022-01-13出版日期:2022-05-30发布日期:2022-04-29 -
通讯作者:陈莎 -
作者简介:闫书琪,男,硕士研究生。 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFF0215700)
Water footprint analysis of electricity production in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region based on a hybrid LCA model and its changes under carbon neutralization target
YAN Shu-Qi1, LI Su-Mei1, LYU He1, CHEN Sha1( ), LIU Ying-Ying1, WANG Hong-Tao2, LIU Hui-Zheng3, CHEN Qian-Li4
), LIU Ying-Ying1, WANG Hong-Tao2, LIU Hui-Zheng3, CHEN Qian-Li4
- 1 Department of Environmental Science, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
2 China Quality Certification Center, Beijing 100070, China
3 College of Economics and Management, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
4 College of Management, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi 830052, China
-
Received:2021-12-06Revised:2022-01-13Online:2022-05-30Published:2022-04-29 -
Contact:CHEN Sha
摘要:
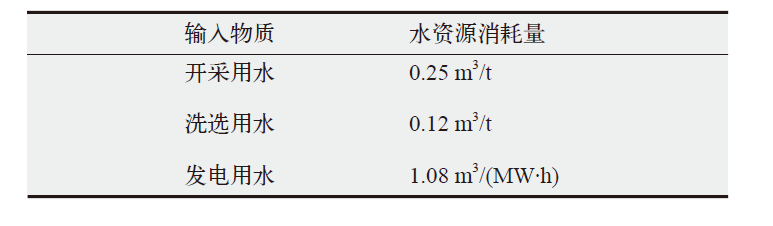
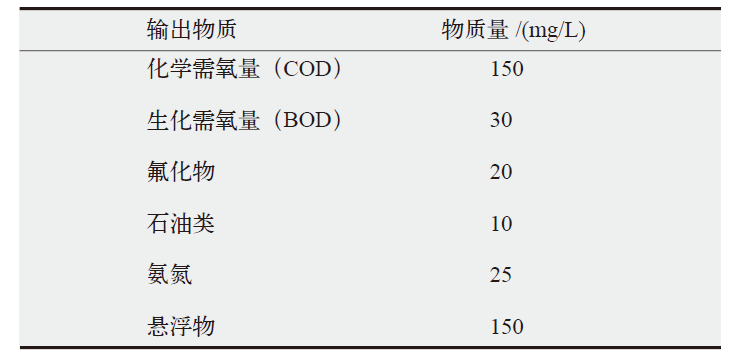
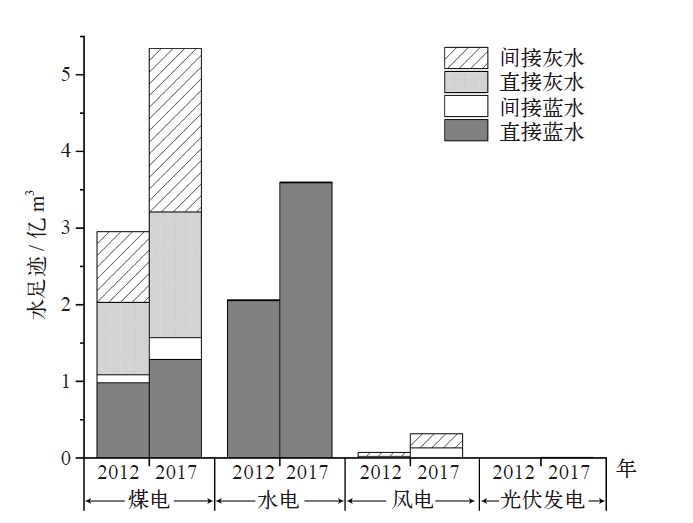
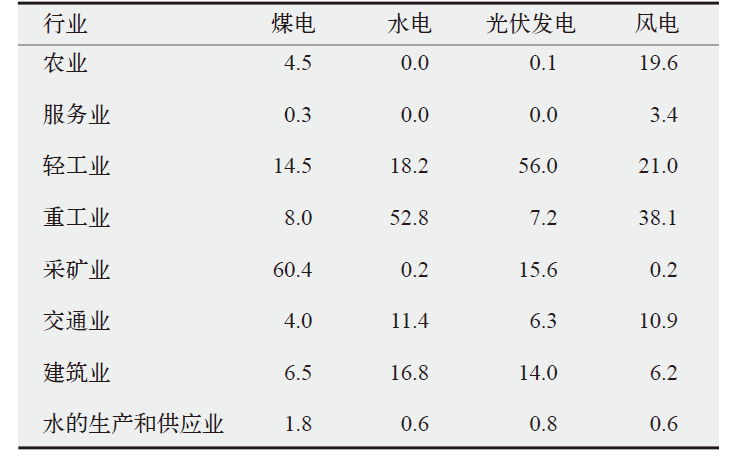
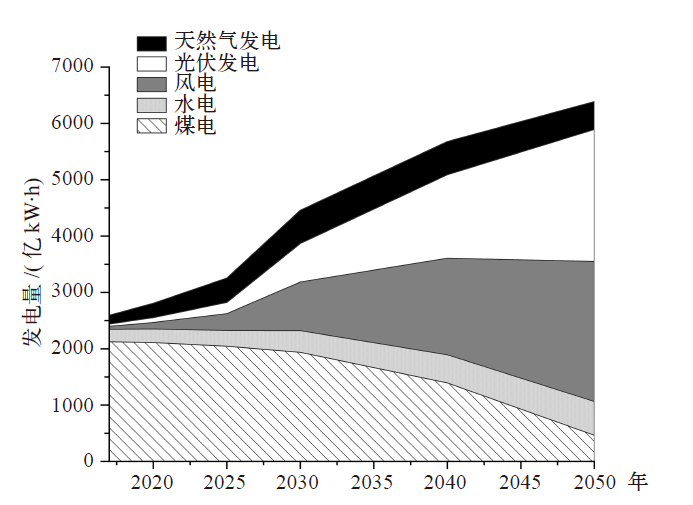
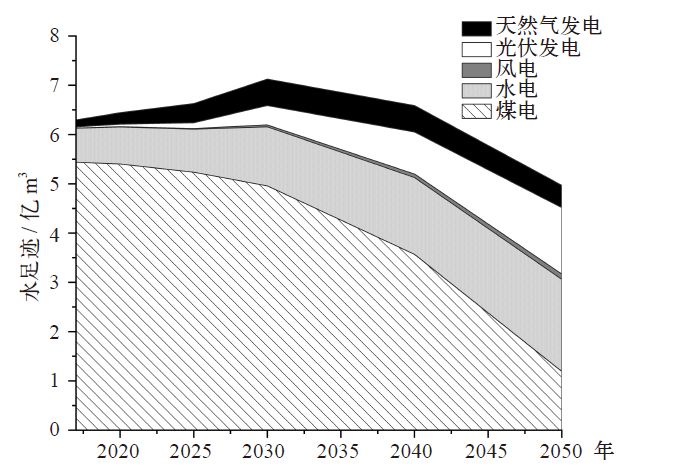
新疆是我国电力生产的主要地区,同时存在严重的水资源短缺问题。作为综合评价指标,水足迹可以用来量化分析电力生产中的水资源消耗及其水环境影响。文中基于投入产出和生命周期的混合生命周期模型对新疆地区2012年和2017年电力生产水足迹进行了量化研究,并对不同发电技术的水足迹贡献部门进行了分析。结果发现:因电力生产结构的变化和燃煤发电技术革新,新疆电力生产的单位水足迹由2012年的4.26×10-3 m3/(kW∙h)下降到2017年的3.08×10-3 m3/(kW∙h)。对不同发电技术的水足迹贡献部门分析发现,煤电和水电的间接水足迹分别主要来自采矿业和重工业,占比分别为60.3%和52.8%。风电和光伏发电的间接水足迹分别主要来自重工业和轻工业,占比分别为38.1%和56.0%。最后针对碳中和目标下新疆电力结构转型带来的水足迹变化进行分析,2017—2050年高比例的可再生能源发电将使新疆电力生产单位水足迹下降75%。
引用本文
闫书琪, 李素梅, 吕鹤, 陈莎, 刘影影, 王宏涛, 刘会政, 陈前利. 基于混合LCA的新疆地区电力生产水足迹分析及碳中和目标下的变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(3): 294-304.
YAN Shu-Qi, LI Su-Mei, LYU He, CHEN Sha, LIU Ying-Ying, WANG Hong-Tao, LIU Hui-Zheng, CHEN Qian-Li. Water footprint analysis of electricity production in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region based on a hybrid LCA model and its changes under carbon neutralization target[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(3): 294-304.
| [1] |
Xiang X, Jia S. China’s water-energy nexus: assessment of water-related energy use[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2019, 144: 32-38
doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.01.009 URL |
| [2] | United Nations Water. The United Nations world water development[R/OL]. 2019 [2021-10-01]. https://www.un.org/zh/global-issues/water |
| [3] | 李悦, 崔玉杰. 中国能源消费总量的预测及影响因素分析[J]. 低碳经济, 2020, 9 (1): 1-9. |
|
Li Y, Cui Y J. Prediction of total energy consumption in China and analysis of its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Low Carbon Economy, 2020, 9 (1): 1-9 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.12677/JLCE.2020.91001 URL |
|
| [4] |
Zhang C, Zhong L, Liang S, et al. Virtual scarce water embodied in inter-provincial electricity transmission in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 187: 438-448
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.11.052 URL |
| [5] | Xu L J, Fan X C, Wang W Q, et al. Renewable and sustainable energy of Xinjiang and development strategy of node areas in the “Silk Road Economic Belt”[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 79: 274-285 |
| [6] | Xu L, Eli W, Abudula A. Construction and practice of fine-grained energy management research center of engineering and technology[J]. Experimental Technology & Management, 2014, 31 (11): 153-155 |
| [7] |
Hoekstra A Y, Chapagain A K. Water footprints of nations: water use by people as a function of their consumption pattern[J]. Water Resources Management, 2006, 21 (1): 35-48
doi: 10.1007/s11269-006-9039-x URL |
| [8] | Hua E, Wang X, A. Engel B, et al. Water competition mechanism of food and energy industries in WEF nexus: a case study in China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2021, 254 (3): 106941 |
| [9] |
Tandon S A, Kolekar N, Kumar R. Water and energy footprint assessment of bottled water industries in India[J]. Natural Resources, 2014, 5 (2): 68-72
doi: 10.4236/nr.2014.52007 URL |
| [10] |
Ming J, Liao X, Zhao X. Grey water footprint for global energy demands[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2020, 14 (1): 201-208
doi: 10.1007/s11707-019-0760-1 URL |
| [11] |
Anna T, William H, Paul C, et al. A methodology for industrial water footprint assessment using energy-water-carbon nexus[J]. Processes, 2021, 9 (2). DOI: 10.3390/pr9020393
doi: 10.3390/pr9020393 |
| [12] |
Chini C M, Peer R A M. The traded water footprint of global energy from 2010 to 2018 [J]. Scientific Data, 2021, 8 (1). DOI: 10.1038/s41597-020-00795-6
doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-00795-6 |
| [13] | Hoekstra A, Chapagain A, Aldaya M M, et al. The water footprint assessment manual: setting the global standard[M]. London: Earthscan, 2011 |
| [14] | 钱逸颖, 董会娟, 田旭, 等. 应对水资源危机的中国水足迹研究综述[J]. 生态经济, 2018, 34 (7): 162-166. |
| Qian Y Y, Dong H J, Tian X, et al. A review of the research on China’s water footprint responding to water crisis[J]. Ecological Economy, 2018, 34 (7): 162-166 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 陈莎, 吕鹤, 李素梅, 等. 面向水资源可持续利用的综合水足迹评价方法[J]. 水资源保护, 2021, 37 (4): 7. |
| Chen S, Lyu H, Li S M, et al. Methods of comprehensive water footprint assessment for sustainable utilization of water resources[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2021, 37 (4): 7 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | Jia C, Yan P, Liu P, et al. Energy industrial water withdrawal under different energy development scenarios: a multi-regional approach and a case study of China[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 135: 110224 |
| [17] | 姜小云. 基于生命周期评价的我国区域电力水足迹特征研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2019. |
| Jiang X Y. Study on water footprint of regional electricity production in China based on life cycle assessment[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2019 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Xie X, Jiang X, Zhang T, et al. Study on impact of electricity production on regional water resource in China by water footprint[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 152 (C): 165-178
doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.01.025 URL |
| [19] |
Zhu X, Guo R, Chen B, et al. Embodiment of virtual water of power generation in the electric power system in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 151: 345-354
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.04.082 URL |
| [20] | 朱永楠, 姜珊, 赵勇, 等. 我国煤电生产水足迹评价[J]. 水电能源科学, 2019, 37 (9): 28-31. |
| Zhu Y N, Jiang S, Zhao Y, et al. Water footprint evaluation of coal-fired power generation in China[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2019, 37 (9): 28-31 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] |
Zhang C, Anadon L D. Life cycle water use of energy production and its environmental impacts in China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47 (24): 14459-14467
doi: 10.1021/es402556x URL |
| [22] | Macknick J, Newmark R, Heath G, et al. Operational water consumption and withdrawal factors for electricity generating technologies: a review of existing literature[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2012, 7 (4): 189-190 |
| [23] | Meldrum J, Nettles-Anderson S, Heath G, et al. Life cycle water use for electricity generation: a review and harmonization of literature estimates[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2013, 8 (1): 015031 |
| [24] | Liu J, Zhao D, Gerbens-Leenes P W, et al. China’s rising hydropower demand challenges water sector[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5 (1): 11446 |
| [25] | 檀勤良, 姚洵睿, 艾柄均. 考虑生命周期的中国煤电水足迹评估[J]. 华北电力大学学报: 社会科学版, 2020 (5): 41-50. |
| Tan Q L, Yao X R, Ai B J. Water footprint assessment of coal-fired power generation in China based on life cycle theory[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University: Social Sciences, 2020 (5): 41-50 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
Chai L, Liao X, Yang L, et al. Assessing life cycle water use and pollution of coal-fired power generation in China using input-output analysis[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 231: 951-958
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.09.178 URL |
| [27] |
Ma X T, Yang D L, Shen X X, et al. How much water is required for coal power generation: an analysis of gray and blue water footprints[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 636 (1): 547-557
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.309 URL |
| [28] |
Wu X D, Ji X, Li C, et al. Water footprint of thermal power in China: implications from the high amount of industrial water use by plant infrastructure of coal-fired generation system[J]. Energy Policy, 2019, 132: 452-461
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2019.05.049 URL |
| [29] | 谭圣林, 邱国玉, 熊育久. 投入产出法在虚拟水消费与贸易研究中的新应用[J]. 自然资源学报, 2014, 29 (2): 355-364. |
| Tan S L, Qiu G Y, Xiong Y J. New application of the input-output framework in the study of virtual water consumption and trade[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2014, 29 (2): 355-364 (in Chinese) | |
| [30] |
孙才志, 郑靖伟. 基于投入产出表的中国水资源消耗结构路径分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 2021, 40 (3): 370-381.
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2021.03.002 |
| Sun C Z, Zheng J W. Structural path analysis of water resources consumption in China based on input-output table[J]. Progress in Geography, 2021, 40 (3): 370-381 (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 孙才志, 刘淑彬. 基于MRIO模型的中国省(市)区水足迹测度及空间转移格局[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34 (5): 945-956. |
|
Sun C Z, Liu S B. Water footprint and space transfer at provincial level of China based on MRIO model[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2019, 34 (5): 945-956 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20190504 URL |
|
| [32] |
Liao X, Zhao X, Liu W, et al. Comparing water footprint and water scarcity footprint of energy demand in China’s six megacities[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 269. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115137
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115137 |
| [33] | 杨文娟, 赵荣钦, 张战平, 等. 河南省不同产业碳水足迹效率研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2019, 34 (1): 92-103. |
|
Yang W J, Zhao R Q, Zhang Z P, et al. Industrial carbon and water footprint efficiency of Henan province based on input-output analysis[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2019, 34 (1): 92-103 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20190108 URL |
|
| [34] |
Okadera T, Geng Y, Fujita T, et al. Evaluating the water footprint of the energy supply of Liaoning province, China: a regional input-output analysis approach[J]. Energy Policy, 2015, 78: 148-157
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2014.12.029 URL |
| [35] |
Liao X, Chai L, Xu X, et al. Grey water footprint and interprovincial virtual grey water transfers for China’s final electricity demands[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 227: 111-118
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.179 URL |
| [36] | 刘秀丽, 郭丕斌, 王昕. 煤炭资源型地区产业能-水足迹效率及影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40 (24): 8999-9010. |
| Liu X L, Guo P B, Wang X. Industrial energy-water footprint efficiency and its influencing factors in coal resources-based areas[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40 (24): 8999-9010 (in Chinese) | |
| [37] | 梁赛, 王亚菲, 徐明, 等. 环境投入产出分析在产业生态学中的应用[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36 (22): 7217-7227. |
| Liang S, Wang Y F, Xu M, et al. Environmental input-output analysis in industrial ecology[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36 (22): 7217-7227 (in Chinese) | |
| [38] | 王长波, 张力小, 庞明月. 生命周期评价方法研究综述: 兼论混合生命周期评价的发展与应用[J]. 自然资源学报, 2015, 30 (7): 1232-1242. |
| Wang C B, Zhang L X, Pang M Y. A review on hybrid life cycle assessment: development and application[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2015, 30 (7): 1232-1242 (in Chinese) | |
| [39] |
Feng K, Hubacek K, Siu Y L, et al. The energy and water nexus in Chinese electricity production: a hybrid life cycle analysis[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 39: 342-355
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.080 URL |
| [40] |
Li X, Feng K, Siu Y L, et al. Energy-water nexus of wind power in China: the balancing act between CO2 emissions and water consumption[J]. Energy Policy, 2012, 45: 440-448
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2012.02.054 URL |
| [41] |
Lindner S, Legault J, Guan D. Disaggregating the electricity sector of China’s input-output table for improved environmental life-cycle assessment[J]. Economic Systems Research, 2013, 25. DOI: 10.1080/09535314.2012.746646
doi: 10.1080/09535314.2012.746646 |
| [42] |
Lindner S, Guan D. A hybrid-unit energy input-output model to evaluate embodied energy and life cycle emissions for China’s economy[J]. Journal of Industrial Ecology, 2014, 18 (2): 201-211
doi: 10.1111/jiec.12119 URL |
| [43] |
Wan L, Wang C, Cai W. Impacts on water consumption of power sector in major emitting economies under INDC and longer term mitigation scenarios: an input-output based hybrid approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 184: 26-39
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.10.013 URL |
| [44] |
Joshi S. Product environmental life-cycle assessment using input-output techniques[J]. Journal of Industrial Ecology, 1999, 3: 95-120
doi: 10.1162/108819899569449 URL |
| [45] | 马忠, 张芯瑀, 冯浩源. 基于混合LCA模型的酒店服务业水足迹量化研究: 以张掖市为例[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38 (9): 3780-3786. |
| Ma Z, Zhang X Y, Feng H Y. Research on the water footprint quantification of the hotel service industry based on the hybrid LCA model: a case of Zhangye[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38 (9): 3780-3786 (in Chinese) | |
| [46] | Swiss Centre for Life Cycle Inventories. The eco-invent database[EB/OL]. 2015 [2021-01-15]. http://www.ecoinvent. |
| [47] | Aldaya M M, Chapagain A K, Hoekstra A Y, et al. The water footprint assessment manual[J]. London: Eearthscan, 2011 |
| [48] | 马忠, 张继良. 张掖市虚拟水投入产出分析[J]. 统计研究, 2008 (5): 65-70. |
| Ma Z, Zhang J L. Analysis on virtual water in Zhangye city using regional input-output model[J]. Statistical Research, 2008 (5): 65-70 (in Chinese) | |
| [49] |
Wang S, Cao T, Chen B. Water-energy nexus in China’s electric power system[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 105: 3972-3977
doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.828 URL |
| [50] |
Wang S, Chen B. Energy-water nexus of urban agglomeration based on multiregional input-output tables and ecological network analysis: a case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 178: 773-783
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.06.112 URL |
| [51] | 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. “疆电外送”首次突破500亿千瓦时[EB/OL]. 2019 [2021-02-01]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-02/01/content_5363129.htm. |
| The Central People’s Government of The People’s Republic of China. ‘Xinjiang Power Transmission’ for the first time exceeded 50 billion kWh[EB/OL]. 2019 [2021-02-01]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-02/01/content_5363129.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [52] | 热孜娅∙阿曼, 方创琳, 赵瑞东. 新疆水资源承载力评价与时空演变特征分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2020, 29 (7): 1576-1585. |
| Re A, Fang C L, Zhao R D. Research on the water resources carrying capacity and spatial-temporal characteristics in Xinjiang[J]. Resources and Environment in The Yangtze Basin, 2020, 29 (7): 1576-1585 (in Chinese) | |
| [53] | 邓铭江, 李湘权, 龙爱华, 等. 支撑新疆经济社会跨越式发展的水资源供需结构调控分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2011, 34 (3): 379-390. |
| Deng M J, Li X Q, Long A H, et al. Regulation of supply and demand structure of the water resources and support economic and social leap-forward development of protection measures[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2011, 34 (3): 379-390 (in Chinese) | |
| [54] | Jiang K, He C, Xu X, et al. Transition scenarios of power generation in China under global 2℃ and 1.5℃ targets[J]. Global Energy Interconnection, 2018, 1 (4): 477-486 |
| [1] | 李丹阳, 陈文颖. 碳中和目标下全球交通能源转型路径[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 203-212. |
| [2] | 杨姗姗, 郭豪, 杨秀, 李政. 双碳目标下建立碳排放总量控制制度的思考与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 191-202. |
| [3] | 樊星, 李路, 秦圆圆, 高翔. 主要发达经济体从碳达峰到碳中和的路径及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 102-115. |
| [4] | 李品, 谢晓敏, 黄震. 德国能源转型进程及对中国的启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 116-126. |
| [5] | 郭偲悦, 耿涌. IPCC AR6报告解读:工业部门减排[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(5): 574-579. |
| [6] | 白泉, 胡姗, 谷立静. 对IPCC AR6报告建筑章节的介绍和解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(5): 557-566. |
| [7] | 曾桉, 谭显春, 王毅, 高瑾昕. 国际气候投融资监测、报告与核证制度及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 215-229. |
| [8] | 张浩楠, 申融容, 张兴平, 康俊杰, 袁家海. 中国碳中和目标内涵与实现路径综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 240-252. |
| [9] | 任佳雪, 高庆先, 陈海涛, 孟丹, 张阳, 马占云, 刘倩, 唐甲洁. 碳中和愿景下的污水处理厂温室气体排放情景模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(4): 410-419. |
| [10] | 刘远, 王芳, 张正涛, 黄承芳, 陈曦, 李宁. 中国七大地区“气候变化—作物产量—经济影响”综合评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(4): 455-465. |
| [11] | 姜克隽, 冯升波. 走向《巴黎协定》温升目标:已经在路上[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(1): 1-6. |
| [12] | 张雅欣, 罗荟霖, 王灿. 碳中和行动的国际趋势分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(1): 88-97. |
| [13] | 韩中,王刚. 基于多区域投入产出模型中美贸易隐含能源、碳排放的测算[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(4): 416-426. |
| [14] | 刘俊伶, 王克, 邹骥. 全球贸易隐含碳变化及其影响分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2015, 11(1): 54-60. |
| [15] | 范英;张晓兵;朱磊. 基于多目标规划的中国二氧化碳减排的宏观经济成本估计[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(02): 130-135. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||