气候变化研究进展 ›› 2021, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (4): 400-409.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.014
所属专题: 减污降碳协同增效专栏
中国水泥行业节能减排措施的协同控制效应评估研究
何峰1,2, 刘峥延3, 邢有凯1,4, 高玉冰1,5, 毛显强1( )
)
- 1 北京师范大学环境学院,北京 100875
2 北京易二零环境股份有限公司,北京 100195
3 中国宏观经济研究院国土开发与地区经济研究所,北京 100038
4 交通运输部规划研究院,交通排放控制监测技术实验室, 北京 100028
5 北京亚太展望环境发展咨询中心,北京 100191
-
收稿日期:2021-03-08修回日期:2021-04-20出版日期:2021-07-30发布日期:2021-08-11 -
通讯作者:毛显强 -
作者简介:何峰,男,环境保护工程师 -
基金资助:能源基金会工业项目“钢铁、水泥行业深度脱碳的协同控制效果评估与路径设计”(G-1809-28536)
Co-control effect evaluation of the energy saving and emission reduction measures in Chinese cement industry
HE Feng1,2, LIU Zheng-Yan3, XING You-Kai1,4, GAO Yu-Bing1,5, MAO Xian-Qiang1( )
)
- 1 School of Environment, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China
2 Beijing E20 Environment Co., Ltd, Beijing 100195, China
3 Institute of Spatial Planning and Regional Economy, China Academy of Macroeconomic Research, Beijing 100038, China
4 Transport Planning and Research Institute, Ministry of Transport, Laboratory of Transport Pollution Control and Monitoring Technology, Beijing 100028, China
5 Asia-Pacific Consulting Center for Environment and Development, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2021-03-08Revised:2021-04-20Online:2021-07-30Published:2021-08-11 -
Contact:MAO Xian-Qiang
摘要:
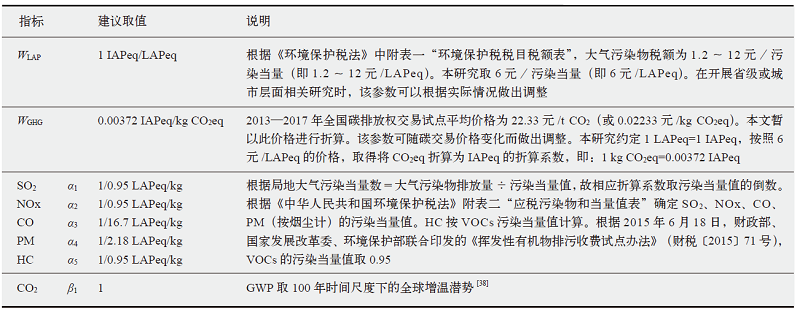
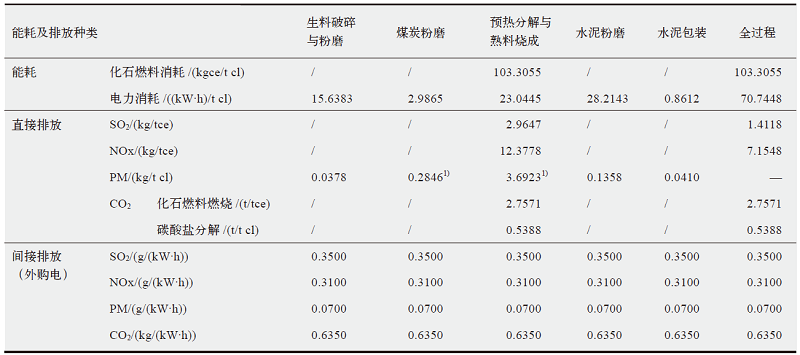
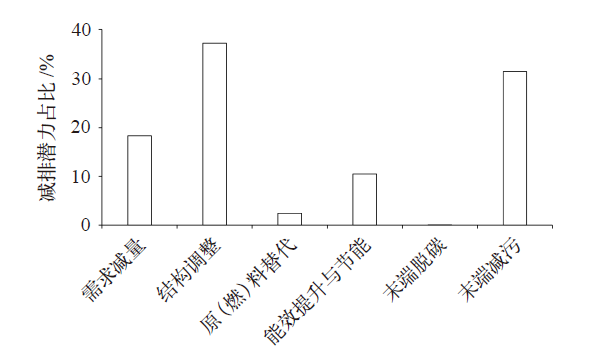
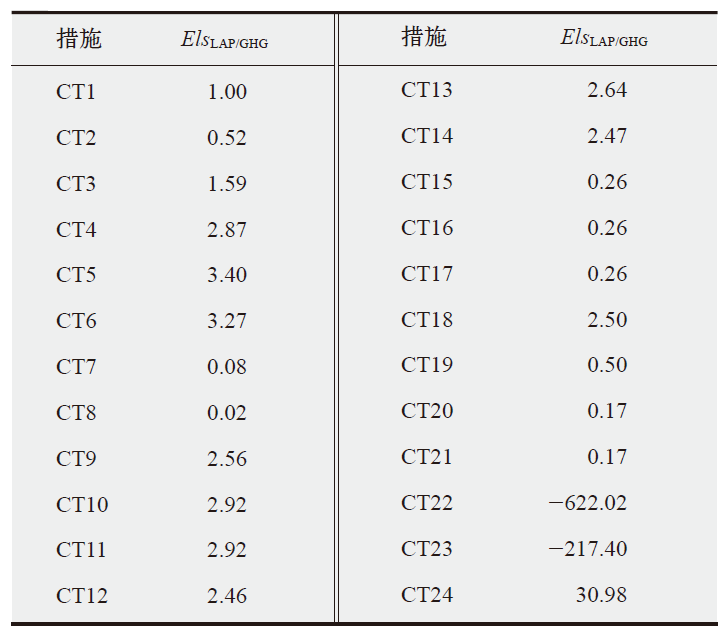
水泥行业是温室气体与局地污染物协同控制的重点行业。以往该行业的协同控制评估或针对个别企业,或采用自上而下和自下而上模拟模型结合情景分析评估行业协同减排效益,尚缺乏系统评估水泥行业全系列节能减排措施(或技术)协同控制效果的研究。文中首先测算水泥行业24项节能减排措施综合大气污染物协同减排量,再通过协同控制效应坐标系、交叉弹性、单位污染物减排成本等评估指标和方法,对这些措施开展协同控制效果评估。结果表明大多数节能减排措施可协同减排局地大气污染物;协同减排潜力最大的是结构调整措施;能效提升与节能措施的协同减排成本较低,但减排潜力有限。本文强化了水泥行业节能减排措施的协同控制效能特性分析,可为水泥行业开展协同控制路径规划提供参考。
引用本文
何峰, 刘峥延, 邢有凯, 高玉冰, 毛显强. 中国水泥行业节能减排措施的协同控制效应评估研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(4): 400-409.
HE Feng, LIU Zheng-Yan, XING You-Kai, GAO Yu-Bing, MAO Xian-Qiang. Co-control effect evaluation of the energy saving and emission reduction measures in Chinese cement industry[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(4): 400-409.
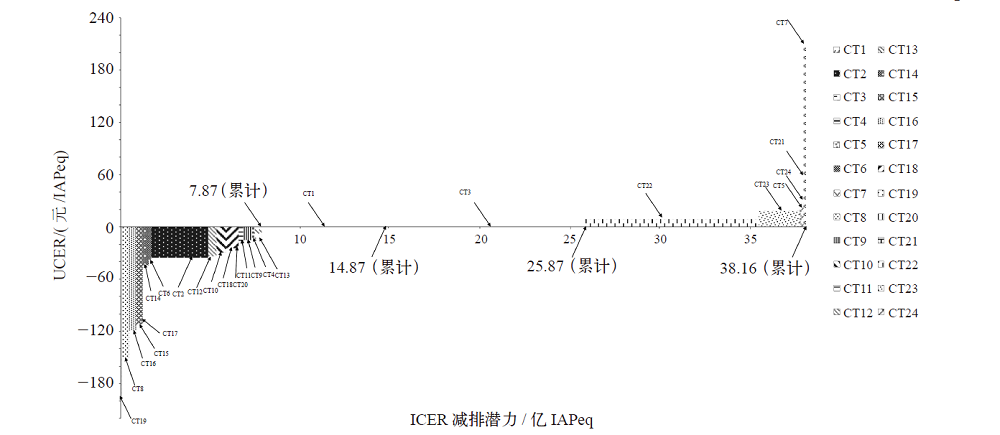
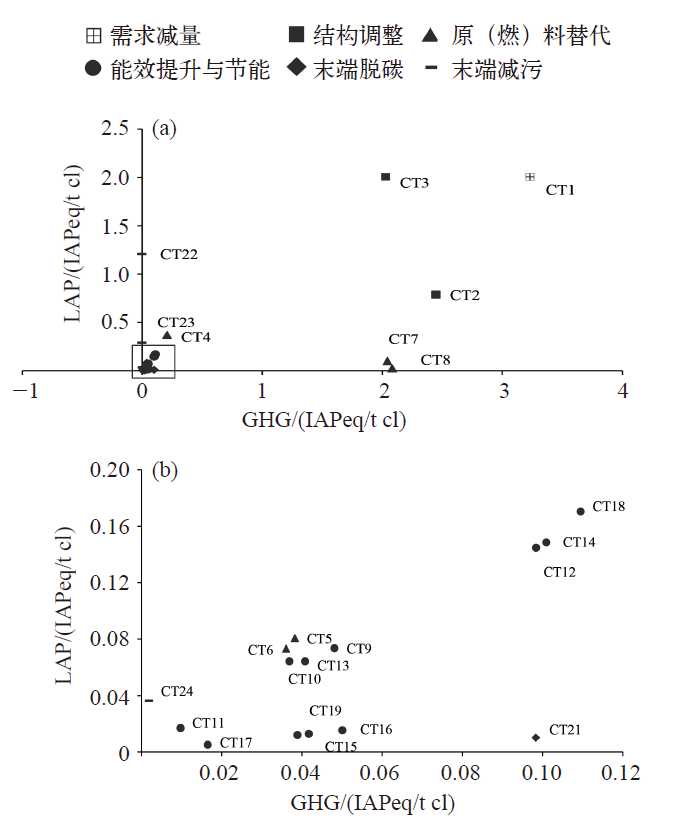
图3 中国水泥行业节能减排措施ICER单位(边际)减排成本曲线 注:图中每个矩形代表一项减排措施,矩形在横坐标上的长度代表该项措施对某种污染物的减排量或减排潜力(单位为亿IAPeq),矩形在纵坐标上的高度代表该项措施的单位污染物减排成本,矩形的面积代表该措施实现减排量(或减排潜力)时的减排成本。
Fig. 3 ICER unit (marginal) abatement cost curve for the energy saving and emission reduction measures in Chinese cement industry
| [1] | 高长明. 我国水泥工业低碳转型的技术途径: 兼评联合国新发布的《水泥工业低碳转型技术路线图》[J]. 水泥, 2019 (1):4-8. |
| Gao C M. The technical path of my country’s cement industry’s low-carbon transformation: comment on the “technical roadmap for low-carbon transformation of cement industry” newly released by the United Nations[J]. Cement, 2019 (1):4-8 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 中国煤炭消费总量控制方案和政策研究项目. 水泥行业“十三五”煤控中期评估及后期展望 [R/OL]. 2019 [2021-01-01]. http://coalcap.nrdc.cn/datum/info?id=92&type=1. |
| China Coal Cap Project Cement Partner. China cement industry Thirteenth Five Year coal cap mid-term evaluation and later-term outlook [R/OL]. 2019 [2021-01-01]. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | Hu T, He J W, Vennomo H, et al. USEPA IES China country study phase IV report: China’s co-control policy study[R]. US: Policy Research Center of SEPA, Development Research Center of State Council, ECON Center for Economic Analysis, 2007 |
| [4] | IPCC. Climate change 2001: mitigation [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001 |
| [5] |
Schwanitz V J, Longden T, Knopf B, et al. The implications of initiating immediate climate change mitigation: a potential for co-benefits?[J]. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2015, 90:166-177
doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2014.01.003 URL |
| [6] |
Shih Y H, Tseng C H. Cost-benefit analysis of sustainable energy development using life-cycle co-benefits assessment and the system dynamics approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 119:57-66
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.12.031 URL |
| [7] |
Muller N Z. The design of optimal climate policy with air pollution co-benefits[J]. Resource and Energy Economics, 2012, 34(4):696-722
doi: 10.1016/j.reseneeco.2012.07.002 URL |
| [8] |
Wagner F, Amann M, Borken-Kleefeld J, et al. Sectoral marginal abatement cost curves: implications for mitigation pledges and air pollution co-benefits for annex I countries[J]. Sustainability Science, 2012, 7(2):169-184
doi: 10.1007/s11625-012-0167-3 URL |
| [9] |
Shrestha R M, Pradhan S. Co-benefits of CO2 emission reduction in a developing country[J]. Energy Policy, 2010, 38(5):2586-2597
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2010.01.003 URL |
| [10] |
Markandya A, Armstrong B J, Hales S, et al. Public health benefits of strategies to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions: overview and implications for policy makers[J]. The Lancet, 2009, 374(9706):2006-2015
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61715-3 URL |
| [11] |
Groosman B, Muller N Z, O’Neill-Toy E. The ancillary benefits from climate policy in the United States[J]. Environmental and Resource Economics, 2011, 50(4):585-603
doi: 10.1007/s10640-011-9483-9 URL |
| [12] |
Zeng A, Mao X Q, Hu T, et al. Regional co-control plan for local air pollutants and CO2 reduction: method and practice[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 140:1226-1235
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.037 URL |
| [13] | 邢有凯, 毛显强, 冯相昭, 等. 城市蓝天保卫战行动协同控制局地大气污染物和温室气体效果评估: 以唐山市为例[J]. 中国环境管理, 2020, 12(4):20-28. |
| Xing Y K, Mao X Q, Feng X Z, et al. Assessment of co-control effectiveness of implementing blue sky defense action plan at city level: a case study of Tangshan city[J]. China Environmental Management, 2020, 12(4):20-28 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 李丽平, 姜苹红, 李雨青, 等. 湘潭市“十一五”总量减排措施对温室气体减排协同效应评价研究[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2012, 37(1):36-40. |
| Li L P, Jiang P H, Li Y Q, et al. Study of co-benefits assessment of pollution reduction on greenhouse gas reduction in Xiangtan during 11th Five-Year Plan[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2012, 37(1):36-40 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 李丽平, 周国梅, 季浩宇. 污染减排的协同效应评价研究: 以攀枝花市为例[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2010, 20(5):91-95. |
| Li L P, Zhou G M, Ji H Y. Study of co-benefits assessment of pollution reduction: a case study in Panzhihua[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2010, 20(5):91-95 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 田春秀, 李丽平, 胡涛, 等. 气候变化与环保政策的协同效应[J]. 环境保护, 2009 (12):67-68. |
| Tian C X, Li L P, Hu T, et al. Co-effect between climate change and environmental protection policies[J]. Environmental Protection, 2009 (12):67-68 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] |
Mao X Q, Zeng A, Hu T, et al. Co-control of local air pollutants and CO2 from the Chinese coal-fired power industry[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2014, 67:220-227
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.12.017 URL |
| [18] |
Mao X Q, Zeng A, Hu T, et al. Co-control of local air pollutants and CO2 in the Chinese iron and steel industry[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(21):12002-12010
doi: 10.1021/es4021316 URL |
| [19] | 刘胜强, 毛显强, 胡涛, 等. 中国钢铁行业大气污染与温室气体协同控制路径研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2012, 35(7):168-174. |
| Liu S Q, Mao X Q, Hu T, et al. Roadmap of co-control of air pollutants and GHGs in iron and steel industry in China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 35(7):168-174 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 毛显强, 邢有凯, 胡涛, 等. 中国电力行业硫、氮、碳协同减排的环境经济路径分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2012, 32(4):748-756. |
| Mao X Q, Xing Y K, Hu T, et al. An environmental-economic analysis of carbon, sulfur and nitrogen co-reduction path for China’s power industry[J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32(4):748-756 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 高玉冰, 毛显强, Gabriel C, 等. 城市交通大气污染物与温室气体协同控制效应评价: 以乌鲁木齐市为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014 (11):2985-2992. |
| Gao Y B, Mao X Q, Gabriel C, et al. Assessment of co-control effects for air pollutants and greenhouse gases in urban transport: a case study in Urumqi[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014 (11):2985-2992 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] |
Xue B, Ma Z X, Geng Y, et al. A life cycle co-benefits assessment of wind power in China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 41:338-346
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.08.056 URL |
| [23] |
Ma Z X, Xue B, Geng Y, et al. Co-benefits analysis on climate change and environmental effects of wind-power: a case study from Xinjiang, China[J]. Renewable Energy, 2013, 57:35-42
doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2013.01.018 URL |
| [24] | 毛显强, 曾桉, 刘胜强, 等. 钢铁行业技术减排措施硫、氮、碳协同控制效应评价研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012 (5):1253-1260. |
| Mao X Q, Zeng A, Liu S Q, et al. Assessment of SO2, NOx and CO2 co-control effects by technological reduction measures in iron & steel industry[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012 (5):1253-1260 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 顾阿伦, 滕飞, 冯相昭. 主要部门污染物控制政策的温室气体协同效果分析与评价[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2016, 26(2):10-17. |
| Gu A L, Teng F, Feng X Z. Assessment and analysis on co-benefits of pollution control and greenhouse gases emission reduction in key sectors[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2016, 26(2):10-17 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
Lei Y, Zhang Q, Nielsen C, et al. An inventory of primary air pollutants and CO2 emissions from cement production in China, 1990-2020[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(1):147-154
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.09.034 URL |
| [27] | 周颖, 张宏伟, 蔡博峰, 等. 水泥行业常规污染物和二氧化碳协同减排研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2013, 36(12):164-168. |
| Zhou Y, Zhang H W, Cai B F, et al. Synergetic reduction of local pollutants and CO2 from cement industry[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 36(12):164-168 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] |
Feng X Z, Oleg L, Qin H. Co-controlling CO2 and NOx emission in China’s cement industry: an optimal development pathway study[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2018, 9(1):34-42
doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2018.02.004 URL |
| [29] |
Pang J, Shi Y C, Feng X Z, et al. Analysis on impacts and co-abatement effects of implementing the low carbon cement standard[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2014, 5(1):41-50
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.041 URL |
| [30] |
Zhang S H, Ren H T, Zhou W J, et al. Assessing air pollution abatement co-benefits of energy efficiency improvement in cement industry: a city level analysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 185:761-771
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.293 URL |
| [31] | 王同桂, 吴莉萍, 张灿, 等. 碳减排项目协同效益评价体系构建研究: 以重庆市某水泥厂余热发电项目为例[J]. 环境影响评价, 2019, 41(6):86-90. |
| Wang T G, Wu L P, Zhang C, et al. Study on construction of cooperative benefit evaluation system for carbon emission reduction projects: taking the project of waste heat power generation in a cement plant in Chongqing as an example[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2019, 41(6):86-90 (in Chinese) | |
| [32] |
Yang X, Teng F, Wang G H. Incorporating environmental co-benefits into climate policies: a regional study of the cement industry in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 112:1446-1453
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.03.040 URL |
| [33] | Hasanbeigi A, Lobscheid A, Lu H Y, et al. Quantifying the co-benefits of energy-efficiency policies: a case study of the cement industry in Shandong province, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2013, 458:624-636 |
| [34] | 毛显强, 曾桉, 胡涛, 等. 技术减排措施协同控制效应评价研究[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2011, 21(12):1-7. |
| Mao X Q, Zeng A, Hu T, et al. Study of coordinate control effect assessment of technological measures for emissions reduction[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2011, 21(12):1-7 (in Chinese) | |
| [35] |
Zeng A, Mao X Q, Hu T, et al. Regional co-control plan for local air pollutants and CO2 reduction: method and practice[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 140:1226-1235
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.037 URL |
| [36] | 全国人大常委会. 中华人民共和国环境保护税法(2018年修正)[Z]. 北京: 中国法制出版社, 2018. |
| Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress. Environmental protection tax law of the People’s Republic of China (Amended in 2018)[Z]. Beijing: China Legal Publishing House, 2018 (in Chinese) | |
| [37] | Ministry of Finance, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Environmental Protection. Pilot measures for volatile organic compound discharge fees (Caishui [2015] No. 71) [EB/OL]. 2015 [2021-02-01]. http://szs.mof.gov.cn/zhengcefabu/201506/t20150625_1261143.htm (in Chinese) |
| [38] | IPCC. Climate change 2014: synthesis report [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014 |
| [39] | 沈飞, 陈寿雨. 人力资本, 物质资本与经济增长关联研究: 基于长三角区域的实证[J]. 科技管理研究, 2014, 34(8):96-98. |
| Shen F, Chen S Y. Empirical study on correlation of human capital and economic growth in Yangze River Delta region based on the production function framework[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2014, 34(8):96-98 (in Chinese) | |
| [40] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 国家重点节能低碳技术推广目录(2015年本,节能部分)[R]. 北京, 2015. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. National key energy-saving and low-carbon technology promotion catalog (2015, Energy saving part)[R]. Beijing, 2015 (in Chinese) | |
| [41] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 国家重点节能低碳技术推广目录(2016年本,节能部分)[R]. 北京, 2017. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. National key energy-saving and low-carbon technology promotion catalog (2016, Energy saving part)[R]. Beijing, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 国家重点节能低碳技术推广目录(2017年本,节能部分)[R]. 北京, 2018. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. National key energy-saving and low-carbon technology promotion catalog (2017, Energy saving part)[R]. Beijing, 2018 (in Chinese) | |
| [43] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 国家重点节能低碳技术推广目录(2017年本,低碳部分)[R]. 北京, 2017. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. National key energy-saving and low-carbon technology promotion catalog (2017, Low carbon part)[R]. Beijing, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [44] | 熊华文, 符冠云. 重塑能源:面向2050年能源消费和生产革命路线图∙中国∙工业卷[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2017. |
| Xiong H W, Fu G Y. Reshaping energy: a roadmap for the energy consumption and production revolution in 2050∙China∙industry volume [M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [45] | 中国水泥协会. 水泥行业煤炭消费总量控制方案及政策研究 [R]. 北京, 2015. |
| China Cement Association. Research on total coal consumption control plan and policy in cement industry[R]. Beijing, 2015 (in Chinese) | |
| [46] | 工业和信息化部. 建材工业十三五规划(2016—2020年)[Z]. 北京, 2016. |
| Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. 13th Five Year Plan for building materials industry (2016-2020)[Z]. Beijing, 2016 (in Chinese) | |
| [47] | 搜狐网. 全国最新电网销售电价汇总(9月1日执行)[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-01]. https://www.sohu.com/a/271827080_146940. |
| Sohu. Summary of the latest nationwide power grid sales price (implemented on September 1)[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-01]. https://www.sohu.com/a/271827080_146940. | |
| [48] | 王庆一. 2019能源数据 [R]. 北京: 绿色创新发展中心, 2019. |
| Wang Q Y. 2019 energy data[R]. Beijing: Innovative Green Development Program, 2019 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 张海军, 段茂盛. 中国试点ETS的碳减排效果评估——基于分省高耗能工业子行业数据的分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 579-589. |
| [2] | 邢有凯, 刘峥延, 毛显强, 高玉冰, 何峰, 余红. 中国交通行业实施环境经济政策的协同控制效应研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(4): 379-387. |
| [3] | 高玉冰, 邢有凯, 何峰, 蒯鹏, 毛显强. 中国钢铁行业节能减排措施的协同控制效应评估研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(4): 388-399. |
| [4] | 毛显强, 曾桉, 邢有凯, 高玉冰, 何峰. 从理念到行动:温室气体与局地污染物减排的协同效益与协同控制研究综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(3): 255-267. |
| [5] | 冯相昭, 赵梦雪, 王敏, 杜晓林, 田春秀, 高霁. 中国交通部门污染物与温室气体协同控制模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(3): 279-288. |
| [6] | 王敏, 冯相昭, 杜晓林, 吴莉萍, 赵梦雪, 王鹏, 安祺. 工业部门污染物治理协同控制温室气体效应评价——基于重庆市的实证分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(3): 296-304. |
| [7] | 陈怡, 田川, 曹颖, 刘强, 郑晓奇. 中国电力行业碳排放达峰及减排潜力分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(5): 632-640. |
| [8] | 刘侃,崔永丽,郑文茹. 中国三氟甲烷处置运行补贴政策效果评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(1): 99-104. |
| [9] | 崔铁宁, 鲁婷. 城市公共自行车自愿碳减排机制初探——以北京市为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(2): 112-117. |
| [10] | 王文军, 谢鹏程, 胡际莲, 王乐, 赵黛青. 碳税和碳交易机制的行业减排成本比较优势研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(1): 53-60. |
| [11] | 许金华 范英. 中国水泥行业节能潜力和CO2减排潜力分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9(5): 341-349. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||