气候变化研究进展 ›› 2020, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (6): 657-666.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2019.226
• 气候系统变化 • 下一篇
一组RegCM4动力降尺度对中国群发性高温事件的模拟评估
- 1 成都信息工程大学大气科学学院,成都 610225
2 南京信息工程大学气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心/气象灾害教育部重点实验室/气候与环境变化国际合作联合实验室,南京 210044
3 南京信息工程大学大气科学学院,南京 210044
4 中国气象局国家气候中心,北京 100081
-
收稿日期:2019-09-25修回日期:2019-12-03出版日期:2020-11-30发布日期:2020-12-03 -
通讯作者:周波涛 -
作者简介:程阳,女,硕士研究生,chengyang199102@163.com -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2018YFA0606301);国家重点研发计划(2016YFA0600701);国家自然科学基金(41991280);南京信息工程大学人才启动经费(2018r060)
Evaluation of multi-RegCM4 dynamical downscaling simulations on cluster high temperature events in China
CHENG Yang1,3( ), ZHOU Bo-Tao2,3(
), ZHOU Bo-Tao2,3( ), HAN Zhen-Yu4, XU Ying4
), HAN Zhen-Yu4, XU Ying4
- 1 School of Atmospheric Sciences, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu 610225, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters/Key Laboratory of Meteorological Disaster, Ministry of Education/Joint International Research Laboratory of Climate and Environment Change, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
3 School of Atmospheric Sciences, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
4 National Climate Center, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
-
Received:2019-09-25Revised:2019-12-03Online:2020-11-30Published:2020-12-03 -
Contact:ZHOU Bo-Tao
摘要:
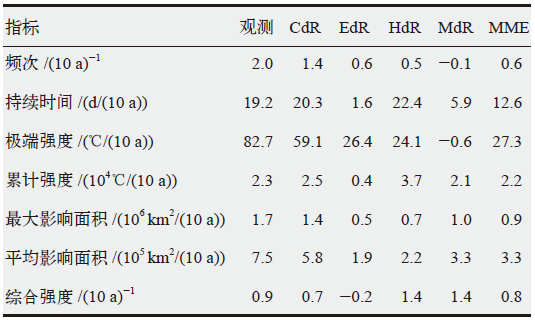
基于高分辨率格点数据集CN05.1和区域气候模式RegCM4对4个全球气候模式动力降尺度模拟(CdR、EdR、HdR、MdR),识别了观测和模拟的1981—2005年中国群发性高温事件(CHTE)。在此基础上,评估了模式对中国CHTE的模拟能力。结果表明:4个动力降尺度模拟以及多模式集合(MME)均能很好地模拟出中国CHTE频次、持续时间和累计强度的空间分布。不过,HdR模拟的CHTE发生次数在新疆地区略偏少,而其他3个模拟试验的CHTE次数在中国东南部略偏多。观测中CHTE持续时间、极端强度、累计强度、最大影响面积、平均影响面积、综合强度等的频率分布规律均能被合理再现。MME也能很好模拟观测揭示的CHTE综合强度以及频次、持续时间、强度、影响面积等单项指标的上升趋势。单模式成员亦可再现大多数指标的上升趋势,但也存在一定不足,如EdR模拟的CHTE综合强度呈减弱趋势,MdR模拟的CHTE频次和极端强度呈弱的下降趋势。
引用本文
程阳, 周波涛, 韩振宇, 徐影. 一组RegCM4动力降尺度对中国群发性高温事件的模拟评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(6): 657-666.
CHENG Yang, ZHOU Bo-Tao, HAN Zhen-Yu, XU Ying. Evaluation of multi-RegCM4 dynamical downscaling simulations on cluster high temperature events in China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(6): 657-666.

图1 1981—2005年中国群发性高温事件发生月份的频率分布
Fig. 1 Percentage of the frequency of cluster high temperature events in China in each month to the total events during 1981-2005

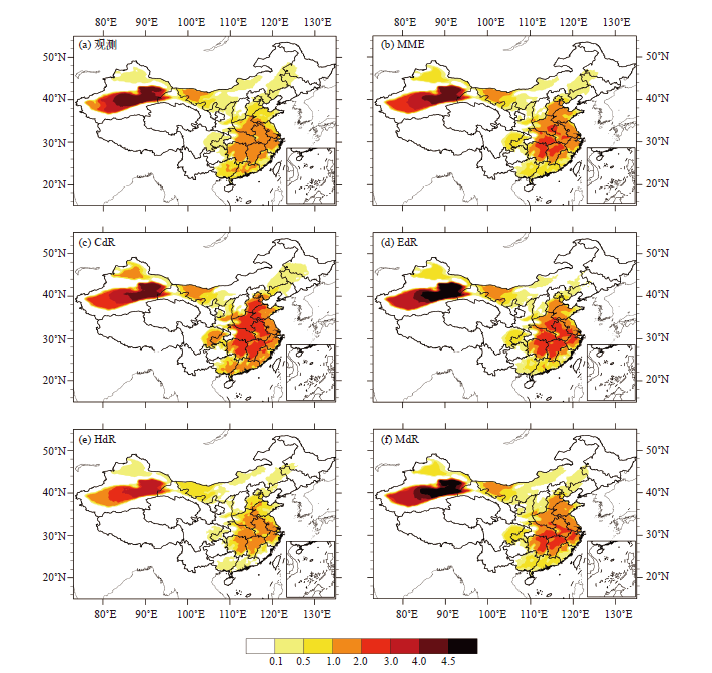
图3 1981—2005年平均的中国群发性高温事件的持续时间和累计强度空间分布
Fig. 3 Climatological distribution of the duration and cumulative intensity of cluster high temperature events during 1981-2005
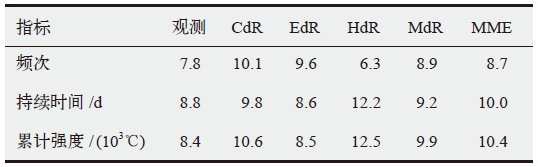 |
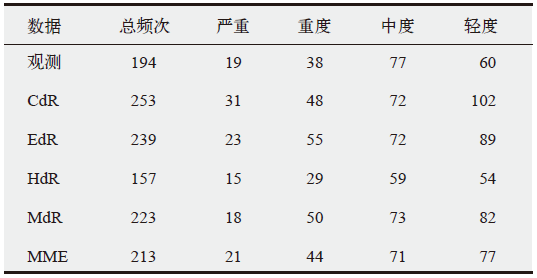
表2 1981—2005年观测和模拟的中国群发性高温事件指标的气候平均值
Table 2 Climate mean of each index for observed and simulated cluster high temperature events in China during 1981-2005
 |
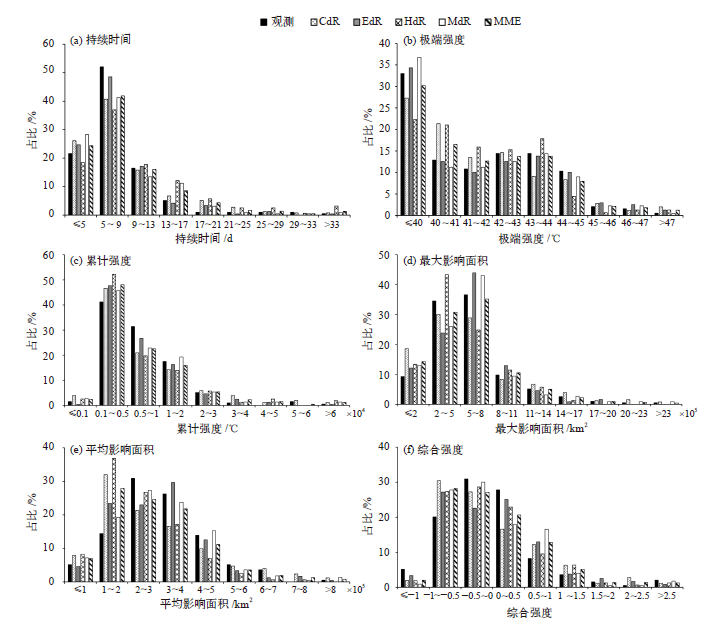
图4 1981—2005年模拟和观测的中国群发性高温事件各指标频率占比分布
Fig. 4 Frequency percentage distributions of the indices for all cluster high temperature events in China during 1981-2005
 |
表4 1981—2005年模拟的中国群发性高温事件各指标频率的均方根误差(E)和S评分
Table 4 Statistics of the root mean square error (E) and S score for the simulated indices of the cluster high temperature events in China during 1981-2005
 |
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 1535 |
| [2] | IPCC. Managing the risks of extreme events and disasters to advance climate change adaptation [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012: 582 |
| [3] | Zhai P M, Pan X H. Trends in temperature extremes during 1951-1999 in China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003,30:1913. DOI: 10.1029/2003GL018004 |
| [4] |
Zhai P M, Zhang X, Wan H, et al. Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2005,18:1096-1108
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-3318.1 URL |
| [5] |
Wang H J, Sun J Q, Chen H P, et al. Extreme climate in China: facts, simulation and projection[J]. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 2012,21:279-304
doi: 10.1127/0941-2948/2012/0330 URL |
| [6] |
Wang A H, Fu J J. Changes in daily climate extremes of observed temperature and precipitation in China[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2013,6:312-319
doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1674-2834.12.0106 URL |
| [7] |
Sun J Q, Ao J. Changes in precipitation and extreme precipitation in a warming environment in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013,58:1395-1401
doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5542-z URL |
| [8] |
Yin H, Donat M G, Alexander L V, et al. Multi-dataset comparison of gridded observed temperature and precipitation extremes over China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2015,35:2809-2827
doi: 10.1002/joc.2015.35.issue-10 URL |
| [9] |
Zhou B T, Xu Y, Wu J, et al. Changes in temperature and precipitation extreme indices over China: analysis of a high-resolution grid dataset[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2016,36:1051-1066
doi: 10.1002/joc.4400 URL |
| [10] | Wang Y J, Zhou B T, Qin D H, et al. Changes in mean and extreme temperature and precipitation over the arid region of northwestern China: observation and projection[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2017,34:287-305 |
| [11] |
Zhou B T, Wen H Q, Xu Y, et al. Projected changes in temperature and precipitation extremes in China by the CMIP5 multimodel ensembles[J]. Journal of Climate, 2014,27:6591-6611
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00761.1 URL |
| [12] |
Wu J, Zhou B T, Xu Y. Response of precipitation and its extremes over China to warming: CMIP5 simulation and projection[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015,58(5):461-473
doi: 10.1002/cjg2.2015.58.issue-5 URL |
| [13] |
Xu Y, Gao X J, Giorgi F, et al. Projected changes in temperature and precipitation extremes over China as measured by 50-year return values and periods based on CMIP5 ensemble[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2018,35:376-388
doi: 10.1007/s00376-017-6269-1 URL |
| [14] |
Guo J, Huang G, Wang X, et al. Dynamically-downscaled projections of changes in temperature extremes over China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018,50:1045-1066
doi: 10.1007/s00382-017-3660-7 URL |
| [15] |
董思言, 徐影, 周波涛, 等. 基于CMIP5模式的中国地区未来高温灾害风险预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014,10(5):365-369.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1719.2014.05.008 URL |
| Dong S Y, Xu Y, Zhou B T, et al. Projected risk of extreme heat in China based on CMIP5 models[J]. Climate Change Research, 2014,10(5):365-369 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 徐影, 张冰, 周波涛, 等. 基于CMIP5模式的中国地区未来洪涝灾害风险变化预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014,5(2):57-65. |
| Xu Y, Zhang B, Zhou B T, et al. Projected risk of flooding disaster in China based on CMIP5 models[J]. Climate Change Research, 2014,5(2):57-65 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | Klein Tank A M G, Zwiers F W, Zhang X B. Guidelines on analysis of extremes in a changing climate in support of informed decisions for adaptation[C]. Climate Data and Monitoring, WCDMP No.72, World Meteorological Organization No. 1500, Geneva, Switzerland, 2009: 1-56 |
| [18] |
Wang P Y, Tang J P, Wang S Y, et al. Regional heatwaves in China: a cluster analysis[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018,50:1901-1917
doi: 10.1007/s00382-017-3728-4 URL |
| [19] | 杨萍, 侯威, 封国林. 中国极端气候事件的群发性规律研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2010,15(4):365-370. |
| Yang P, Hou W, Feng G L. A study of the characteristics of the cluster extreme events in China[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2010,15(4):365-370 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 杨萍, 封国林, 刘伟东, 等. 空间点过程理论在极端气候事件中的应用研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 2010,21(3):352-359. |
| Yang P, Feng G L, Liu W D, et al. Cluster extreme events based on point process theory[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2010,21(3):352-359 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] |
Ren F M, Cui D L, Gong Z Q, et al. An objective identification technique for regional extreme events[J]. Journal of Climate, 2012,25:7015-7027
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00489.1 URL |
| [22] | 龚志强, 王晓娟, 崔冬林, 等. 区域性极端低温事件的识别及其变化特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 2012,23(2):195-204. |
| Gong Z Q, Wang X J, Cui D L, et al. The identification and changing characteristics of regional low temperature extreme events[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2012,23(2):195-204 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 王晓娟, 沈柏竹, 龚志强, 等. 中国冬季区域性极端低温事件分类及其与气候指数极端性的联系[J]. 物理学报, 2013,62(22):438-448. |
| Wang X J, Shen B Z, Gong Z Q, et al. The classification of winter regional extreme low temperature events in China and their corresponding relationship to climatic indices extreme anomaly[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013,62(22):438-448 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 王艳姣, 任福民, 闫峰. 中国区域持续性高温事件时空变化特征研究[J]. 地理科学, 2013,33(3):314-321. |
| Wang Y J, Ren F M, Yan F. Study on temporal and spatial variations of regional continual high temperature event in China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2013,33(3):314-321 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] |
Wang Y J, Ren F M, Zhang X B. Spatial and temporal variations of regional high temperature events in China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2014,34:3054-3065
doi: 10.1002/joc.3893 URL |
| [26] |
Zou X K, Ren F M. Changes in regional heavy rainfall events in China during 1961-2012[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2015,32:704-714
doi: 10.1007/s00376-014-4127-y URL |
| [27] |
况雪源, 王遵娅, 张耀存, 等. 中国近50年来群发性高温事件的识别及统计特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014,57(6):1782-1791.
doi: 10.6038/cjg20140610 URL |
| Kuang X Y, Wang Z Y, Zhang Y C, et al. Identification and statistical characteristics of the cluster high temperature events during last Fifty years[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2014,57(6):1782-1791 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] |
Gao X J, Xu Y, Zhao Z C, et al. On the role of resolution and topography in the simulation of East Asia precipitation[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2006,86:173-185
doi: 10.1007/s00704-005-0214-4 URL |
| [29] |
Gao X J, Shi Y, Han Z Y, et al. Performance of RegCM4 over major river basins in China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2017,34:441-455
doi: 10.1007/s00376-016-6179-7 URL |
| [30] | Giorgi F, Jones C, Asrar G. Addressing climate information needs at the regional level: the CORDEX framework[J]. WMO Bulletin, 2009,58:175-183 |
| [31] |
Yu E T, Sun J Q, Chen H P, et al. Evaluation of a high-resolution historical simulation over China: climatology and extremes[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2015,45:2013-2031
doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2452-6 URL |
| [32] |
Yao J C, Zhou T J, Guo Z, et al. Improved performance of high-resolution atmospheric models in simulating the East-Asian summer monsoon rainbelt[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017,30(21):8825-8840
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0372.1 URL |
| [33] |
Giorgi F, Coppola E, Solmon F, et al. RegCM4: model description and preliminary tests over multiple CORDEX domains[J]. Climate Research, 2012,52:7-29
doi: 10.3354/cr01018 URL |
| [34] |
Gao X J, Shi Y, Giorgi F. Comparison of convective parameterizations in RegCM4 experiments over China with CLM as the land surface model[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2016,9:246-254
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2016.1172938 URL |
| [35] |
Gao X J, Wu J, Shi Y, et al. Future changes in thermal comfort conditions over China based on multi-RegCM4 simulations[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2018,11(4):291-299
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2018.1471578 URL |
| [36] |
Han Z Y, Zhou B T, Xu Y, et al. Projected changes in haze pollution potential in China: an ensemble of regional climate model simulations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2017,17:10109-10123
doi: 10.5194/acp-17-10109-2017 URL |
| [37] |
吴佳, 高学杰. 一套格点化的中国区域逐日观测资料及与其它资料的对比[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013,56(4):1102-1111.
doi: 10.6038/cjg20130406 URL |
| Wu J, Gao X J. A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 2013,56(4):1102-1111 (in Chinese) | |
| [38] |
Cannon A J, Sobie S R, Murdock T Q. Bias correction of GCM precipitation by quantile mapping: how well do methods preserve changes in quantiles and extremes?[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015,28:6938-6959
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00754.1 URL |
| [39] | 韩振宇, 童尧, 高学杰, 等. 分位数映射法在RegCM4中国气温模拟订正中的应用[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018,14:331-340. |
| Han Z Y, Tong Y, Gao X J, et al. Correction based on quantile mapping for temperature simulated by the RegCM4[J]. Climate Change Research, 2018,14:331-340 (in Chinese) | |
| [40] |
Perkins S E, Pitman A J, Holbrook N J, et al. Evaluation of the AR4 climate models' simulated daily maximum temperature, minimum temperature, and precipitation over Australia using probability density functions[J]. Journal of Climate, 2007,20:4356-4376
doi: 10.1175/JCLI4253.1 URL |
| [1] | 石英,韩振宇,徐影,周波涛,吴佳. 6.25 km高分辨率降尺度数据对雄安新区及整个京津冀地区未来极端气候事件的预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(2): 140-149. |
| [2] | 韩振宇,童尧,高学杰,徐影. 分位数映射法在RegCM4中国气温模拟订正中的应用[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(4): 331-340. |
| [3] | 徐经纬,徐 敏,蒋 熹,ArmelleReca C. Remedio,Dmitry V. Sein,Nikolay Koldunov,Daniela Jac. 区域气候模式REMO对中国气温和降水模拟能力的评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(4): 286-293. |
| [4] | 陶辉 黄金龙 翟建青 赖锡军. 长江流域气候变化高分辨率模拟与RCP4.5情景下的预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9(4): 246-251. |
| [5] | 左金清, 李维京, 任宏利. CMIP5模式对北极涛动的模拟评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9(3): 157-164. |
| [6] | 吴佳 高学杰 石英. 中国20年一遇气温和降水极值变化的高分辨率模拟[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012, 8(4): 243-249. |
| [7] | 石英;高学杰;Fillipo Giorgi;宋瑞艳;吴佳;董文杰. 全球变暖背景下中国区域不同强度降水事件变化的高分辨率数值模拟[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(03): 164-169. |
| [8] | 宋瑞艳 高学杰 石英 张冬峰 张喜娃. 未来我国南方低温雨雪冰冻灾害变化的数值模拟[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(006): 352-356. |
| [9] | 田红 许吟隆 林而达. 温室效应引起的江淮流域气候变化预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(006): 357-362. |
| [10] | 张冬峰;高学杰;赵宗慈;Jeremy S. PAL;Filippo GIORGI. RegCM3 区域气候模式对中国气候的模拟[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2005, 01(03): 119-121. |
| [11] | 许吟隆;黄晓莹;张勇;林万涛;林而达. 中国21世纪气候变化情景的统计分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2005, 01(02): 80-83. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||