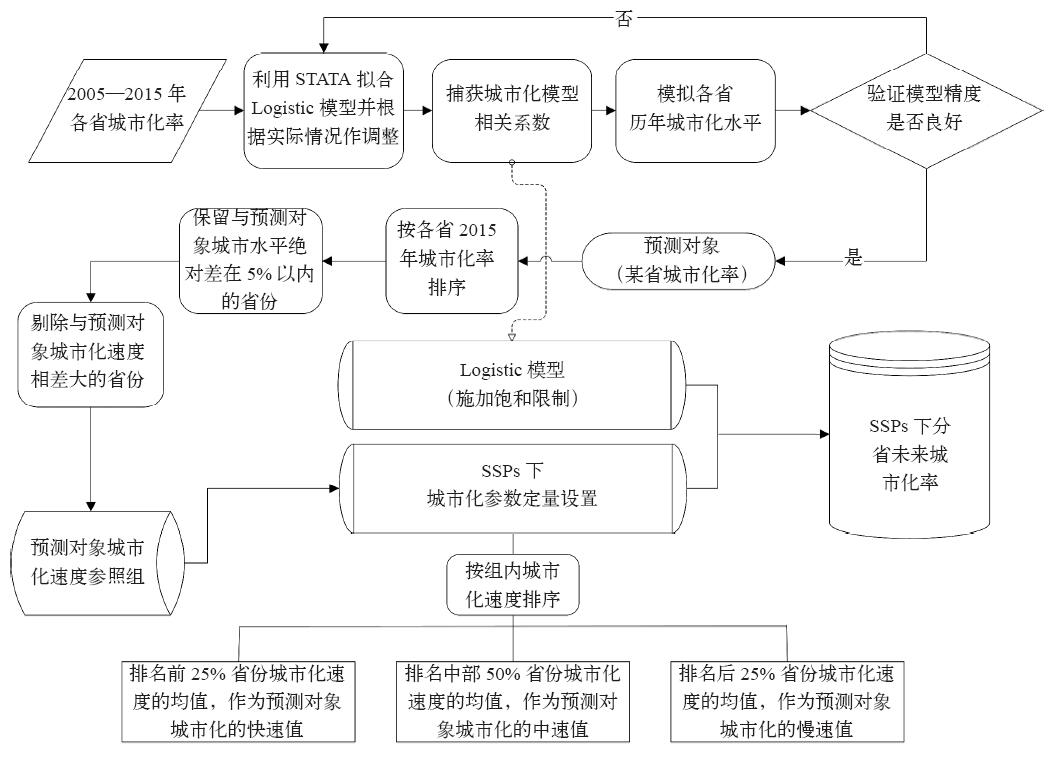
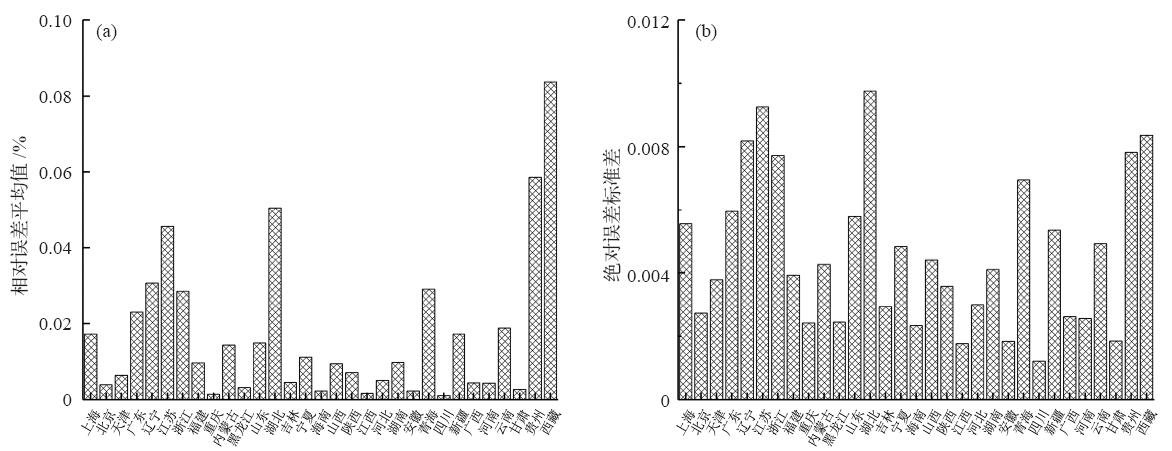
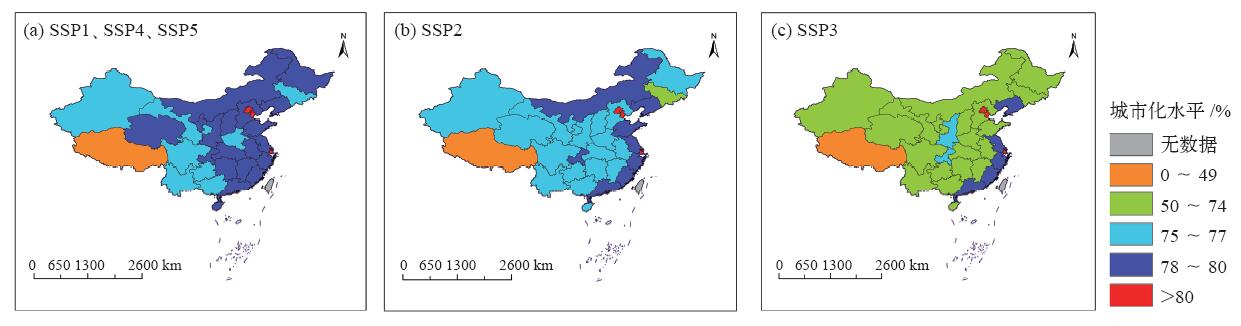
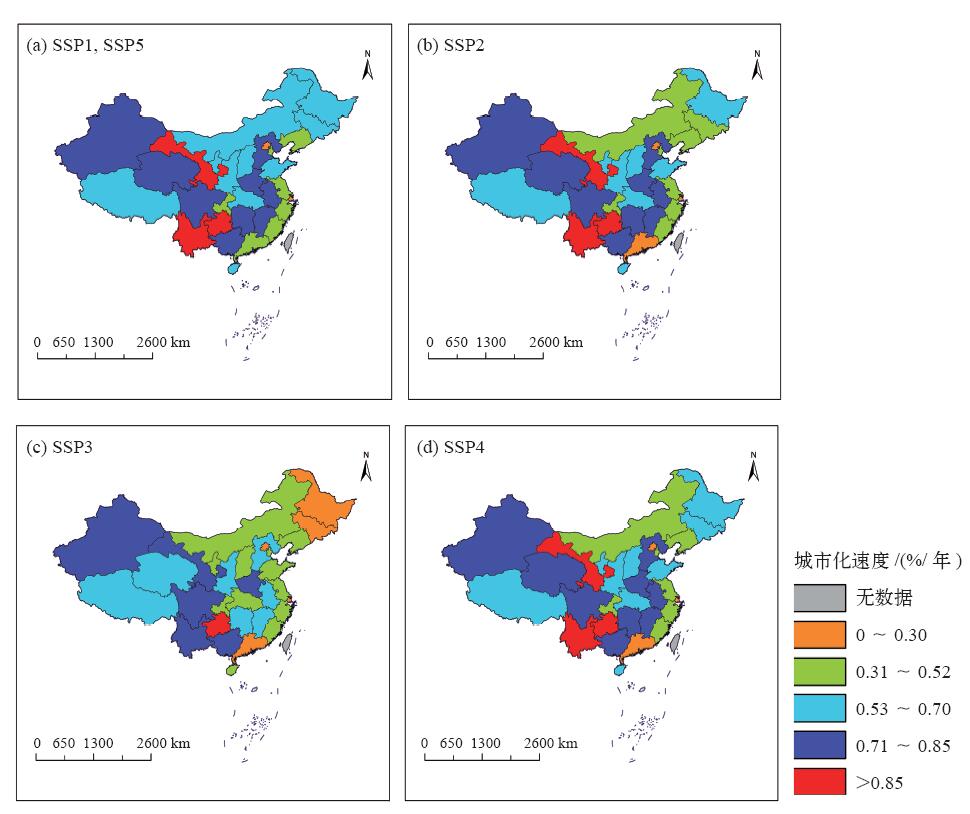
| [1] | Vuuren D P V, Riahi K, Moss R , et al . A proposal for a new scenario framework to support research and assessment in different climate research communities[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2012,22(1):21-35 | | [2] | Jiang L , O’Neill B C. Global urbanization projections for the shared socioeconomic pathways[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2017,42:193-199 | | [3] | O’neill B C, Kriegler E, Riahi K , et al. A new scenario framework for climate change research: the concept of shared socioeconomic pathways[J]. Climatic Change, 2014,122(3):387-400 | | [4] | Jiang L . Internal consistency of demographic assumptions in the shared socioeconomic pathways[J]. Population Environment, 2014,35(3):261-285 | | [5] | Moss R H, Edmonds J A, Hibbard K A , et al. The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment[J]. Nature, 2010,463(7282):747-756 | | [6] | 曹丽格, 方玉, 姜彤 , 等. IPCC影响评估中的社会经济新情景(SSPs)进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012,8(1):74-78 | | [7] | Kc S, Lutz W . The human core of the shared socioeconomic pathways: population scenarios by age, sex and level of education for all countries to 2100[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2017,42(1):181-192 | | [8] | Leimbach M, Kriegler E, Roming N , et al. Future growth patterns of world regions: a GDP scenario approach[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2017,42:215-225 | | [9] | 姜彤, 赵晶, 景丞 , 等. IPCC共享社会经济路径下中国和分省人口变化预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017,13(2):128-137 | | [10] | 姜彤, 赵晶, 曹丽格 , 等. 共享社会经济路径下中国及分省经济变化预测[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018,14(1):50-58 | | [11] | 姜彤, 王艳君, 袁佳双 , 等. “一带一路”沿线国家2020—2060年人口经济发展情景预测[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018,14(2):155-164 | | [12] | Calvin K, Bond-Lamberty B, Clarke L , et al. The SSP4: a world of deepening inequality[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2016,42:284-296 | | [13] | 姚从容 . 城市化进程中人口变动对气候变化的影响机制: 理论框架与协整检验[J]. 城市发展研究, 2012,19(10):86-91 | | [14] | 国家统计局.国家数据 [DB/OL]. 2018 [ 2018- 01- 02]. | | [15] | 孙久文, 肖春梅, 施晓丽 . 我国城乡发展的成就、问题及未来选择[J]. 社会科学辑刊, 2009 ( 4):82-86 | | [16] | 佟新华, 孙猛 . 中国城市化进程中的低碳经济发展路径选择[J]. 人口学刊, 2010 ( 6):60-63 | | [17] | 陈明星 . 城市化领域的研究进展和科学问题[J]. 地理研究, 2015,34(4):614-630 | | [18] | Gossop C . Low carbon cities: an introduction to the special issue[J]. Cities, 2011,28(6):495-497 | | [19] | 杨续超, 陈葆德, 胡可嘉 . 城市化对极端高温事件影响研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 2015,34(10):1219-1228 | | [20] | Mcdonald R I, Gleick P H . Urban growth, climate change, and freshwater availability[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011,108(15):6312-6317 | | [21] | Mcgranahan G, Balk D, Anderson B . The rising tide: assessing the risks of climate change and human settlements in low elevation coastal zones[J]. Environment & Urbanization, 2016,19(1):17-37 | | [22] | 赵守栋, 王京凡, 何新 , 等. 城市化对气候变化的影响及其反馈机制研究[J]. 北京师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014 ( 1):66-72 | | [23] | Grimm N B, Faeth S H, Golubiewski N E , et al. Global change and the ecology of cities[J]. Science, 2008,319(5864):756-760 | | [24] | Parrish D D, Zhu T . Clean air for megacities[J]. Science, 2009,326(5953):674-675 | | [25] | 林伯强, 刘希颖 . 中国城市化阶段的碳排放:影响因素和减排策略[J]. 经济研究, 2010 ( 8):66-78 | | [26] | 李恩平 . 城市化时间路径曲线的推导与应用: 误解阐释与研究拓展[J]. 人口研究, 2014,38(3):28-40 | | [27] | 陈彦光, 周一星 . 城市化Logistic过程的阶段划分及其空间解释: 对Northam曲线的修正与发展[J]. 经济地理, 2005,25(6):817-822 | | [28] | 王远飞, 张超 . Logistic模型参数估计与我国城市化水平预测[J]. 经济地理, 2015 ( 4):8-13 | | [29] | 陈彦光, 罗静 . 城市化水平与城市化速度的关系探讨: 中国城市化速度和城市化水平饱和值的初步推断[J]. 地理研究, 2006,25(6):1063-1072 | | [30] | 张妍, 黄志龙 . 中国城市化水平和速度的再考察[J]. 城市发展研究, 2010,17(11):7-12 | | [31] | 顾朝林, 管卫华, 刘合林 . 中国城镇化2050: SD模型与过程模拟[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017,47(7):818-832 | | [32] | 姚士谋, 陆大道, 王聪 , 等. 中国城镇化需要综合性的科学思维: 探索适应中国国情的城镇化方式[J]. 地理研究, 2011,30(11):1947-1955 | | [33] | 程必定 . 以城市为主导统筹区域经济协调发展[J]. 学习与实践, 2005 ( 1):46-49 | | [34] | 张杰, 曹丽格, 李修仓 , 等. IPCC AR5中社会经济新情景(SSPs)研究的最新进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013,9(3):225-228 | | [35] | Ewing R, Cervero R . Travel and the built environment[J]. Journal of the American Planning Association, 2010,76(3):265-294 | | [36] | Mohan R . The effect of population growth, the pattern of demand and of technology on the process of urbanization[J]. Journal of Urban Economics, 1984,15(2):125-156 | | [37] | Kelley A C, Williamson J G . Population growth industrial revolutions and the urban transition[J]. Population & Development Review, 1969,10(3):419 | | [38] | Skeldon R . Demographic and urban transitions in a global system and policy responses[M]. The New Global Frontier, 2008 | | [39] | Ledent J . Rural-urban migration, urbanization, and economic development[J]. Economic Development & Cultural Change, 1982,30(3):507-538 | | [40] | Abdel-Rahman A N, Safarzadeh M R, Bottomley M B . Economic growth and urbanization: a cross-section and time-series analysis of thirty-five developing countries[J]. Rivista Internazionale Di Scienze Economiche E Commerciali, 2006,53(3):334-348 | | [41] | Fay M, Opal C . urbanization without growth: a not-so-uncommon phenomenon[M]. World Bank, Washington DC, 2000 | | [42] | 习近平 . 决胜全面建成小康社会夺取新时代中国特色社会主义伟大胜利:在中国共产党第十九次全国代表大会上的报告 [R]. 北京: 人民出版社, 2017 | | [43] | 周一星 . 关于中国城镇化速度的思考[J]. 城市规划, 2006 ( S1):32-35, 40 | | [44] | 周干峙 . 如何正确地理解城市化 [N]. 企业家日报, 2013-03-02 (W01) | | [45] | 李善同, 吴三忙, 高春亮 . 中国城市化速度预测分析[J]. 发展研究, 2017 ( 11):19-22 | | [46] | 宁越敏 . 中国城市化特点、问题及治理[J]. 南京社会科学, 2012 ( 10):19-27 |
|
 ),毛锦凰1,宋晓谕2,3,黄春林4,5
),毛锦凰1,宋晓谕2,3,黄春林4,5
 ),Jin-Huang MAO1,Xiao-Yu SONG2,3,Chun-Lin HUANG4,5
),Jin-Huang MAO1,Xiao-Yu SONG2,3,Chun-Lin HUANG4,5