气候变化研究进展 ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (6): 720-730.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.037
适应与绿色复苏:应对新冠疫情和气候复合风险的协同
- 1 中国人民大学环境学院,北京 100872
2 中国人民大学农业与农村发展学院,北京 100872
-
收稿日期:2022-02-28修回日期:2022-04-19出版日期:2022-11-30发布日期:2022-08-22 -
通讯作者:陈敏鹏 -
作者简介:张熹,女,学士 -
基金资助:国家重点研发项目(2018YFA0606503);国家社会科学基金重点项目(21AZD063);国家社会科学基金重点项目(22AZD098)
Adaptation and green recovery: synergistic responses to the COVID-19 pandemic and climate compounding risks
- 1 School of Environment and Natural Resources, Renmin University of China, Beijing 100872, China
2 School of Agricultural Economics and Rural Development, Renmin University of China, Beijing 100872, China
-
Received:2022-02-28Revised:2022-04-19Online:2022-11-30Published:2022-08-22 -
Contact:CHEN Min-Peng
摘要:
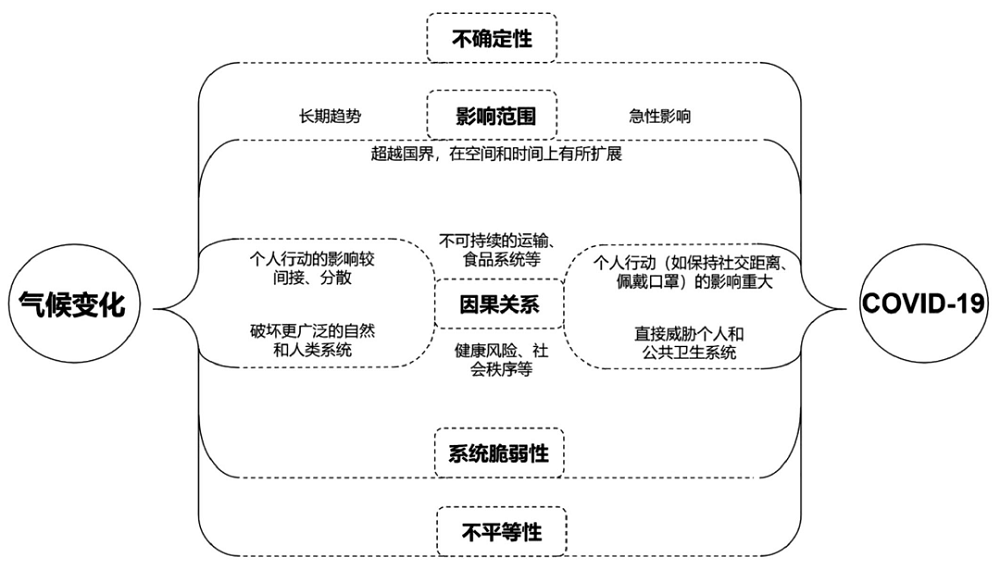
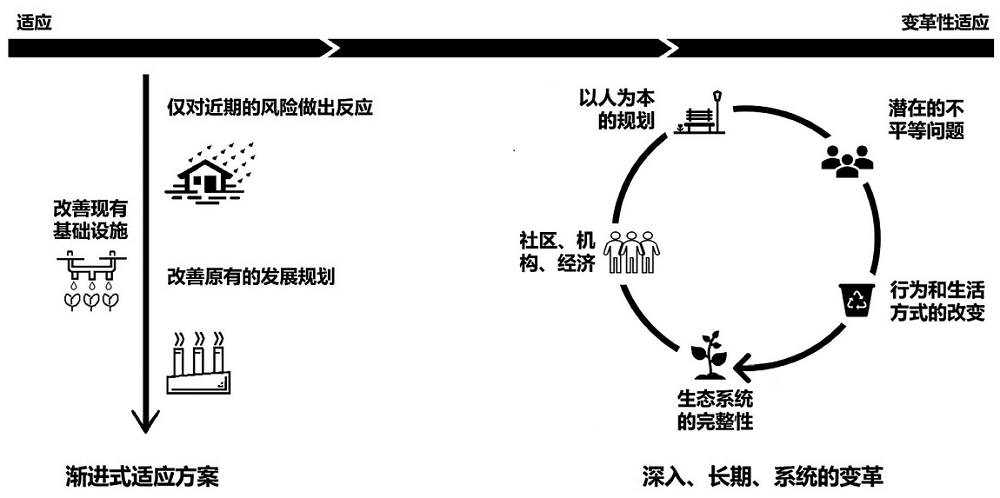
作为全球性危机,新冠疫情和气候危机在影响范围、效果、原因等方面的相似之处可能使两种危机的效果叠加,而二者的不同之处又可能导致应对政策的相互干扰,带来更加严峻的复合风险。文中全面分析了全球面临的新冠疫情和气候危机的复合风险,识别了新冠疫情对全球气候变化适应进程的影响,以及适应在各国疫后绿色复苏计划中的地位。研究表明,目前全球的绿色复苏中较少考虑适应,而绿色复苏为同时恢复经济和增强气候恢复力提供了机会,如果能在绿色复苏中考虑变革性适应,将显著提升社会经济系统对气候变化等冲击的抵御能力与恢复力,实现疫情后更持续和更有韧性的经济发展。
引用本文
张熹, 陈敏鹏. 适应与绿色复苏:应对新冠疫情和气候复合风险的协同[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(6): 720-730.
ZHANG Xi, CHEN Min-Peng. Adaptation and green recovery: synergistic responses to the COVID-19 pandemic and climate compounding risks[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(6): 720-730.
| [1] | World Health Organization (WHO). Statement of the thirtieth Polio IHR emergency committee[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-02-10]. https://www.who.int/news/item/23-11-2021-statement-of-the-thirtieth-polio-ihr-emergency-committee |
| [2] |
Padhan R, Prabheesh K P. The economics of COVID-19 pandemic: a survey[J]. Economic Analysis and Policy, 2021, 70 (1): 220-237
doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2021.02.012 URL |
| [3] |
Susskind D, Vines D. The economics of the COVID-19 pandemic: an assessment[J]. Oxford Review of Economic Policy, 2020, 36 (1): 1-13
doi: 10.1093/oxrep/grz035 URL |
| [4] | World Bank Database. GDP (constant 2015 US$)[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-05-25]. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD?view=chart |
| [5] | World Bank Database. GDP growth[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-05-25]. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD.ZG?view=chart&locations=1W-VE |
| [6] | IPCC. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis[M/OL]. 2021 [2022-02-10]. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/downloads/report/IPCC_AR6_WGI_SPM_final.pdf |
| [7] | United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). COP26 postponed[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-02-10]. https://unfccc.int/news/cop26-postponed |
| [8] | International Monetary Fund (IMF). Greening the recovery[M]. Washington, DC: International Monetary Fund, 2020 |
| [9] | Ebi K B L, Bowen K B J, Calkins J, et al. Interactions between two existential threats: COVID-19 and climate change[J]. Climate Risk Management, 2021, 34: 100363 |
| [10] | United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Global sustainable development report 2019: the future is now: science for achieving sustainable development[R/OL]. 2019 [2022-04-17]. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/24797GSDR_report_2019.pdf |
| [11] |
Berrang-Ford L, Siders A R, Lesnikowski A, et al. A systematic global stocktake of evidence on human adaptation to climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2021, 11: 989-1000
doi: 10.1038/s41558-021-01170-y URL |
| [12] | Eriksen S, Schipper E L F, Scoville-Simonds M, et al. Adaptation interventions and their effect on vulnerability in developing countries: help, hindrance or irrelevance?[J]. World Development, 2021, 141 (4): 105383 |
| [13] | Hepburn C, O’Callaghan B, Stern N, et al. Will COVID-19 fiscal recovery packages accelerate or retard progress on climate change?[J]. Oxford Review of Economic Policy, 2020, 36: 359-381 |
| [14] | Ringsmuth A K, Otto I M, van den Bart H, et al. Lessons from COVID-19 for managing transboundary climate risks and building resilience[J]. Climate Risk Management, 2022, 35: 100395 |
| [15] | Manzanedo R D, Manning P. COVID-19: lessons for the climate change emergency[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 742: 140563 |
| [16] | United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Adaptation gap report 2021: the gathering storm: adapting to climate change in a post-pandemic world[R/OL]. 2021 [2022-01-31]. https://www.unep.org/resources/adaptation-gap-report-2021 |
| [17] | Morgan S. Plotting a green COVID recovery: how the EU, US and China stack up[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-01-31]. https://chinadialogue.net/en/business/plotting-green-covid-recovery-how-eu-us-china-stack-up/ |
| [18] | Galvin R, Healy N. The Green New Deal in the United States: what it is and how to pay for it[J]. Energy Research & Social Science, 2020, 67: 101529 |
| [19] | Sanja B. COVID-19, climate change action and the road to green recovery[J]. Journal of Environmental Law, 2020 (3): 3 |
| [20] |
Obergassel W, Hermwille L, Oberthür S. Harnessing international climate governance to drive a sustainable recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. Climate Policy, 2021, 21 (10): 1298-1306
doi: 10.1080/14693062.2020.1835603 URL |
| [21] |
Gusheva E, Gooyert V D. Can we have our cake and eat it? A review of the debate on green recovery from the COVID-19 crisis[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13 (2): 874
doi: 10.3390/su13020874 URL |
| [22] |
Mansuy N. Stimulating post-COVID-19 green recovery with ecological restoration[J]. Restoration Ecology, 2020, 28 (6): 1343-1347
doi: 10.1111/rec.13296 URL |
| [23] |
Rosenbloom D, Markard J. A COVID-19 recovery for climate[J]. Science, 2020, 368 (6490): 447
doi: 10.1126/science.abc4887 pmid: 32355005 |
| [24] | Botzen W, Duijndam S, Beukering P. Lessons for climate policy from behavioral biases towards COVID-19 and climate change risks[J]. World Development, 2021, 137: 105214 |
| [25] |
Ranger N, Mahul O, Monasterolo I. Managing the financial risks of climate change and pandemics: what we know (and don’t know)[J]. One Earth, 2021, 4 (10): 1375-1385
doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2021.09.017 URL |
| [26] | Young A Z. From federal transfers and local investments to a potential convergence of COVID-19 and climate change: the case study of São Paulo city[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2022, 76: 103450 |
| [27] |
Zang S M, Benjenk I, Breakey S, et al. The intersection of climate change with the era of COVID-19[J]. Public Health Nursing, 2021, 38 (2): 321-335
doi: 10.1111/phn.12866 pmid: 33521994 |
| [28] |
Phillips C A, Caldas A, Cleetus R, et al. Compound climate risks in the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2020, 10: 586-588
doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0804-2 URL |
| [29] |
Schwartz S A. Climate change, COVID-19, preparedness, and consciousness[J]. Explore, 2020, 16 (3): 141-144
doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2020.02.022 URL |
| [30] | IPCC. Climate change 2014: synthesis report[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014 |
| [31] | World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Tropical cyclone Harold challenges disaster and public health management[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-02-01]. https://public.wmo.int/en/media/news/tropical-cyclone-harold-challenges-disaster-and-public-health-management |
| [32] | World Meteorological Organization (WMO). More heavy rainfall hits East Africa amid locust invasion[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-02-01]. https://public.wmo.int/en/media/news/more-heavy-rainfall-hits-east-africa-amid-locust-invasion |
| [33] | World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Northern Hemisphere wildfire season flares up[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-02-01]. https://public.wmo.int/en/media/news/northern-hemisphere-wildfire-season-flares |
| [34] | Rasul G. Twin challenges of COVID-19 pandemic and climate change for agriculture and food security in South Asia[J]. Environmental Challenges, 2021, 2: 100027 |
| [35] |
Gabriel-Campos E, Werner-Masters K, Cordova-Buiza F, et al. Community eco-tourism in rural Peru: resilience and adaptive capacities to the COVID-19 pandemic and climate change[J]. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 2021, 48 (27): 416-427
doi: 10.1016/j.jhtm.2021.07.016 URL |
| [36] |
Steffen B, Egli F, Pahle M, et al. Navigating the clean energy transition in the COVID-19 crisis[J]. Joule, 2020, 4 (16): 1137-1141
doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2020.04.011 URL |
| [37] | O’Callaghan B, Murdock E. Are we building back better? Evidence from 2020 and pathways for inclusive green recovery spending[R/OL]. 2021 [2022-02-01]. https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/35281/AWBBB.pdf |
| [38] | Werikhe A. Towards a green and sustainable recovery from COVID-19[J]. Current Research in Environmental Sustainability, 2022, 4: 100124 |
| [39] | Quevedo A, Peters K, Cao Y. The impact of COVID-19 on climate change and disaster resilience funding trends and signals[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-01-31]. https://odi.org/en/publications/the-impact-of-covid-19-on-climate-change-and-disaster-resilience-funding-trends-and-signals/ |
| [40] | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). The impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) crisis on development finance[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-02-04]. http://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/the-impact-of-the-coronavirus-COVID-19-crisis-on-development-finance-9de00b3b/ |
| [41] | International Monetary Fund (IMF). Data mapper: general government gross debt[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-05-25]. http://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/GGXWDG_NGDP@WEO/OEMDC/ADVEC/WEOWORLD |
| [42] |
Dibley A, Wetzer T, Hepburn C. National COVID debts: climate change imperils countries’ ability to repay[J]. Nature, 2021, 592 (7853): 184-187
doi: 10.1038/d41586-021-00871-w URL |
| [43] | Filho W L, Wall T, Alves F, et al. The impacts of the early outset of the COVID-19 pandemic on climate change research: implications for policy-making[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2021, 124: 267-278 |
| [44] | Barouki R, Kogevinas M, Audouze K, et al. The COVID-19 pandemic and global environmental change: emerging research needs[J]. Environment International, 2021, 146: 106272 |
| [45] | Islam S, Sarkar T, Khan S H, et al. COVID-19-related infodemic and its impact on public health: a global social media analysis[J]. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 2020, 103 (4): 1-9 |
| [46] |
Zhao E, Wu Q, Crimmins E M, et al. Media trust and infection mitigating behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic in the USA[J]. British Medical Journal Global Health, 2020, 5 (10). DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003323
doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003323 |
| [47] | Latkin C, Dayton L, Coyle C, et al. The association between climate change attitudes and COVID-19 attitudes: the link is more than political ideology[J]. The Journal of Climate Change and Health, 2022, 5: 100099 |
| [48] |
Corfee-Morlot J, Depledge J, Winkler H. COVID-19 recovery and climate policy[J]. Climate Policy, 2021, 21 (10): 1249-1256
doi: 10.1080/14693062.2021.2001148 URL |
| [49] |
Engler D, Groh E D, Gutsche G, et al. Acceptance of climate-oriented policy measures under the COVID-19 crisis: an empirical analysis for Germany[J]. Climate Policy, 2021, 21: 10, 1281-1297
doi: 10.1080/14693062.2020.1864269 URL |
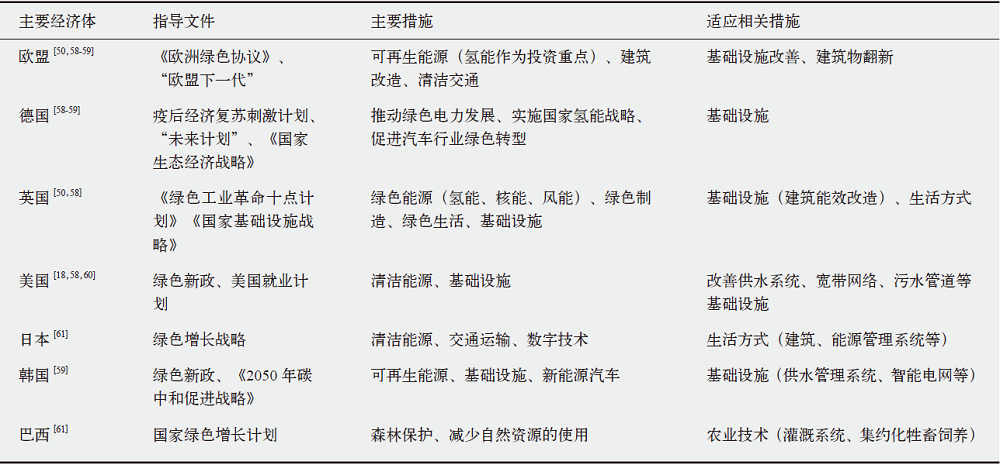
| [50] | 刘亚亚, 蔺洁, 王婷. 后疫情时代主要国家(组织)的“绿色复苏”政策实践[J]. 全球科技经济瞭望, 2021, 36 (8): 27-36. |
| Liu Y Y, Lin J, Wang T. Green recovery policy practices of major countries (organizations) in the post-epidemic era[J]. Global Science and Technology Economic Outlook, 2021, 36 (8): 27-36 (in Chinese) | |
| [51] | 耿国彪. 博鳌亚洲论坛唱响绿色奏鸣曲[J]. 绿色中国, 2010 (10): 42-45. |
| Geng G B. The Boao forum for Asia sings a green sonata[J]. Green China, 2010 (10): 42-45 (in Chinese) | |
| [52] | International Monetary Fund (IMF). The great lockdown: worst economic downturn since the Great Depression[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-02-01]. https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2020/03/23/pr2098-imf-managing-director-statement-following-a-g20-ministerial-call-on-the-coronavirus-emergency |
| [53] |
le Quéré C, Jackson R B, Jones M W, et al. Temporary reduction in daily global CO2 emissions during the COVID-19 forced confinement[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2020, 10: 647-653
doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-0797-x URL |
| [54] | 王遥, 潘冬阳. 绿色复苏中的金融角色[J]. 中国金融, 2021 (4): 43-44. |
| Wang Y, Pan D Y. The role of finance in green recovery[J]. China Finance, 2021 (4): 43-44 (in Chinese) | |
| [55] | United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Support grows for a ‘Better Recovery’ from COVID-19[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-04-13]. https://unfccc.int/news/support-grows-for-a-better-recovery-from-covid-19 |
| [56] | Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Building back better: a sustainable, resilient recovery after COVID-19[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-02-19]. https://oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/building-back-better-a-sustainable-resilient-recovery-after-covid-19-52b869f5/ |
| [57] | United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Green recovery[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-04-13]. https://www.unep.org/resources/factsheet/green-recovery |
| [58] | 绿色和平组织. 绿色复苏全球进行时: 疫后复苏国际案例集[R/OL]. 2021 [2022-04-13]. https://www.greenpeace.org.cn/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/green-recovery-policy-brief-202106.pdf. |
| Greenpeace. Green recovery global now: an international casebook for post-epidemic recovery[R/OL]. 2021 [2022-04-13]. https://www.greenpeace.org.cn/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/green-recovery-policy-brief-202106.pdf (in Chinese) | |
| [59] | 汪万发, 张剑智. 疫情下国际绿色复苏政策动向与影响分析[J]. 环境保护, 2020, 48 (20): 64-67. |
| Wang W F, Zhang J Z. Analysis of international green recovery policy trends and impacts under the epidemic[J]. Environmental Protection, 2020, 48 (20): 64-67 (in Chinese) | |
| [60] | Arnon A, Dinerstein M, Huntley J, et al. President Biden’s $2.7 trillion American jobs plan: budgetary and macroeconomic effects[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-02-01]. https://budgetmodel.wharton.upenn.edu/issues/2021/4/7/president-biden-american-jobs-plan-effects |
| [61] | 葛春雷, 李宏. 国际科技创新战略何去何从[EB/OL]. 2022 [2022-03-17]. https://epaper.gmw.cn/gmrb/html/2022-03/17/nw.D110000gmrb_20220317_1-13.htm. |
| Ge C L, Li H. Where does the international science and technology innovation strategy go from here[EB/OL]. 2022 [2022-03-17]. https://epaper.gmw.cn/gmrb/html/2022-03/17/nw.D110000gmrb_20220317_1-13.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [62] | European Commission. Recovery plan for Europe[R/OL]. 2020 [2021-01-31]. https://www.euractiv.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2020/05/Green-Deal-Recovery-Package.pdf |
| [63] | Federal Ministry of Finance of Germany. Emerging from the crisis with full strength[R/OL]. 2020 [2021-01-31]. https://www.bundesfinanzministerium.de/Content/EN/Standardartikel/Topics/Public-Finances/Articles/2020-06-04-fiscal-package.html |
| [64] | Geels F W, Pereira G I, Pinkse J. Moving beyond opportunity narratives in COVID-19 green recoveries: a comparative analysis of public investment plans in France, Germany, and the United Kingdom[J]. Energy Research & Social Science, 2022, 84: 102368 |
| [65] | European Commission. EU adaptation strategy[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-02-01]. https://ec.europa.eu/clima/eu-action/adaptation-climate-change/eu-adaptation-strategy_en |
| [66] |
Schipper E L F. Maladaptation: when adaptation to climate change goes very wrong[J]. One Earth, 2020, 3 (4): 409-414
doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2020.09.014 URL |
| [67] |
Few R, Morchain D, Spear D, et al. Transformation, adaptation and development: relating concepts to practice[J]. Palgrave Communications, 2017, 3: 17092
doi: 10.1057/palcomms.2017.92 URL |
| [68] | Chu E, Brown A, Michael K, et al. Unlocking the potential for transformative climate adaptation in cities[R/OL]. 2019 [2022-02-18]. https://wrirosscities.org/sites/default/files/FINAL19_GCA_Cities_Background%20Paper.pdf |
| [69] | Resurrección B P, Bee B A, Dankelman I, et al. Gender-transformative climate change adaptation: advancing social equity[R/OL]. 2019 [2022-02-18]. https://www.sei.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/gender-transformative-climate-change-adaptation.pdf |
| [70] | Eriksen S H, Nightingale A J, Eakin H. Reframing adaptation: the political nature of climate change adaptation[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2015: 523-533 |
| [71] |
Cole J, Dodds K. Unhealthy geopolitics: can the response to COVID-19 reform climate change policy?[J]. Bull World Health Organ. 2021, 99 (2): 148-154
doi: 10.2471/BLT.20.269068 URL |
| [72] | World Health Organization (WHO). COP26 special report on climate change and health: the health argument for climate action[R/OL]. 2021 [2022-03-12]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/cop26-special-report |
| [73] | 中国政府网. 中华人民共和国国民经济和社会发展第十四个五年规划和2035年远景目标纲要[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-02-18]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/13/content_5592681.htm. |
| The State Council of The People’s Republic of China. Outline of the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for national economic and social development of the People’s Republic of China and vision 2035[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-02-18]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/13/content_5592681.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [74] | 中国政府网. 国务院关于印发2030年前碳达峰行动方案的通知[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-02-18]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-10/26/content_5644984.htm. |
| The State Council of The People’s Republic of China. Notice of the State Council on the issuance of the action plan for carbon peaking by 2030[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-02-18]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2021-10/26/content_5644984.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [75] | 中国环保协会. 生态环境部: 将编制《国家适应气候变化战略2035》[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-03-13]. http://zhb.org.cn/zcfg/2020-10-28/9927.html. |
| China Environmental Protection Association. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: national adaptation strategy for climate change 2035 to be prepared[EB/OL]. 2020 [2022-03-13]. http://zhb.org.cn/zcfg/2020-10-28/9927.html (in Chinese) | |
| [76] | 刘慧心, 崔莹. 后疫情时代如何适应气候变化: UNEP《2021适应差距报告: 风暴前夕》解析[J]. 可持续发展经济导刊, 2021 (12): 15-18. |
| Liu H X, Cui Y. How to adapt to climate change in the post-epidemic era: an analysis of UNEP’s adaptation gap report 2021: on the eve of the storm[J]. Journal of Sustainable Development Economics, 2021 (12): 15-18 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 王玉洁, 林欣. 京津冀城市群气候变化及影响适应研究综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(6): 743-755. |
| [2] | 高美勋, 陈敏鹏, 滕飞. “一带一路”沿线国家适应气候变化的技术需求评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(6): 731-742. |
| [3] | 梅梅, 侯威, 周星妍. 新、旧气候态差异及对中国地区气候和极端事件评估业务的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(6): 653-669. |
| [4] | 张化, 李汶莉, 李雪敏, 董琳, 杨有田, 张国明, 许映军. 面向地震设防风险的未来中国城乡人口情景及暴露特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(6): 707-719. |
| [5] | 王卓妮, 袁佳双, 庞博, 黄磊. IPCC AR6 WGIII报告减缓主要结论、亮点和启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(5): 531-537. |
| [6] | 蒋含颖, 高翔, 王灿. 气候变化国际合作的进展与评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(5): 591-604. |
| [7] | 白泉, 胡姗, 谷立静. 对IPCC AR6报告建筑章节的介绍和解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(5): 557-566. |
| [8] | 马丽娟, 效存德, 康世昌. 全球主要山地气候变化特征和异同——IPCC AR6 WGI报告和SROCC综合解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(5): 605-621. |
| [9] | 刘俊国, 孟莹, 张学静. IPCC AR6报告解读:地下水[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 414-421. |
| [10] | 刘俊国, 陈鹤, 田展. IPCC AR6报告解读:气候变化与水安全[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 405-413. |
| [11] | 段居琦, 袁佳双, 徐新武, 居辉. 对IPCC AR6报告中有关农业系统结论的解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 422-432. |
| [12] | 张百超, 庞博, 秦云, 韩振宇, 陆波. IPCC AR6报告关于气候恢复力发展的解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 460-467. |
| [13] | 胡轶伦, 冀国旭, 李积宏, 干珠扎布, 胡国铮, 高清竹. IPCC AR6报告解读:陆地和淡水生态系统及其服务变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 395-404. |
| [14] | 王蕾, 张百超, 石英, 韩振宇, 陆波. IPCC AR6报告关于气候变化影响和风险主要结论的解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 389-394. |
| [15] | 秦云, 徐新武, 王蕾, 韩振宇, 陆波. IPCC AR6报告关于气候变化适应措施的解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 452-459. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||