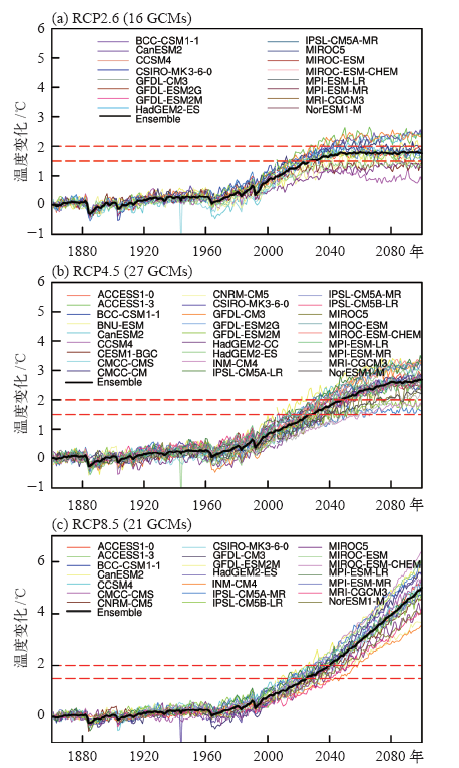
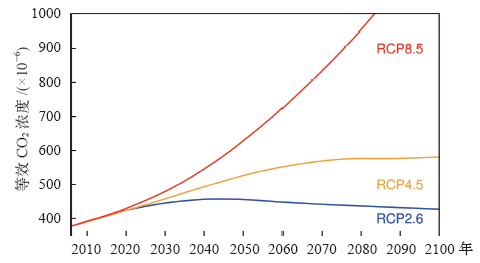
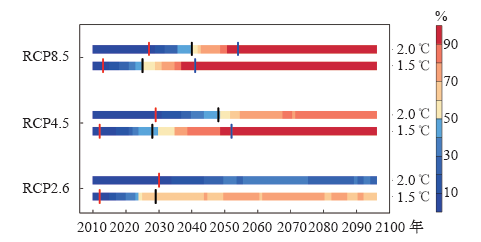
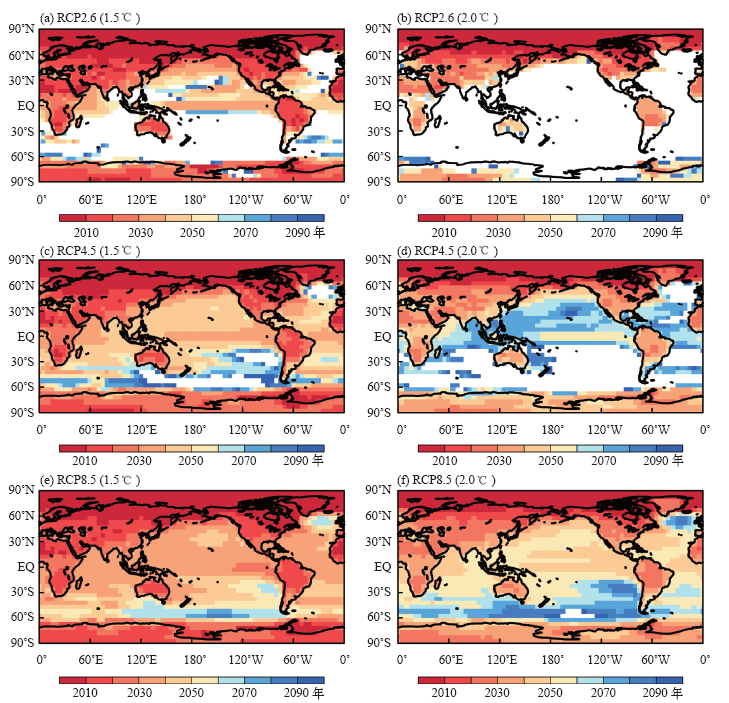
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 1535 | | [2] | Joshi M, Hawkins E, Sutton R , et al. Projections of when temperature change will exceed 2℃above pre-industrial levels[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2011,1(8):407-412 | | [3] | 姜大膀, 富元海 . 2℃全球变暖背景下中国未来气候变化预估[J]. 大气科学, 2012,36(2):234-246 | | [4] | Jiang D, Sui Y, Lang X . Timing and associated climate change of a 2℃ global warming[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2016,36(14):4512-4522 | | [5] | 张莉, 丁一汇, 吴统文 , 等. CMIP5模式对21世纪全球和中国年平均地表气温变化和 2℃升温阈值的预估[J]. 气象学报, 2013,71(6):1047-1060 | | [6] | Vautard R, Gobiet A, Sobolowski S , et al. The European climate under a 2℃ global warming[J]. Booklist, 2014,9(3):034006 | | [7] | 徐影, 周波涛, 吴婕 , 等. 1.5~4℃升温阈值下亚洲地区气候变化预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017,13(4):306-315 | | [8] | 孔莹, 王澄海 . 全球升温1.5℃时北半球多年冻土及雪水当量的响应及其变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017,13(4):316-326 | | [9] | Zhan M, Li M, Sun H , et al. Changes in extreme maximum temperature events and population exposure in China under global warming scenarios of 1.5 and 2.0℃: analysis using the regional climate model COSMO-CLM[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2018,32(1):99-112 | | [10] | Moss R, Edmonds J, Hibbard K , et al. The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment[J]. Nature, 2010,463(7282):747-756 | | [11] | 王绍武, 罗勇, 赵宗慈 , 等. 新一代温室气体排放情景[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012,8(4):305-307 | | [12] | 王安乾, 苏布达, 王艳君 , 等. 全球升温1.5℃与2.0℃情景下中国极端低温事件变化与耕地暴露度研究[J]. 气象学报, 2017,75(3):415-428 | | [13] | Chen J, Gao C, Zeng X . Assessing changes of river discharge under global warming of 1.5℃ and 2℃ in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River Basin: approach by using multiple-GCMs and hydrological models[J]. Quaternary International, 2017,453(25):63-73 | | [14] | Zhang Y . Projections of 2.0℃ warming over the globe and China under RCP4.5[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Letters, 2012,5(6):514-520 | | [15] | Morice C, Kennedy J, Rayner N , et al. Quantifying uncertainties in global and regional temperature change using an ensemble of observational estimates: the HadCRUT4 dataset[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2012,117(D8):D08101 | | [16] | Screen J , Simmonds. The central role of diminishing sea ice in recent Arctic temperature amplification[J]. Nature, 2010,464(7293):1334-1337 | | [17] | Kumar A, Perlwitz J, Eischeid J , et al. Contribution of sea ice loss to Arctic amplification[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010,37(21):389-400 | | [18] | Sui Y, Lang X, Jiang D . Time of emergence of cimate signals over China under the RCP4.5 scenario[J]. Climatic Change, 2014,125(2):265-276 | | [19] | Chen X, Zhou T . Uncertainty in crossing time of 2℃ warming threshold over China[J]. Science Bulletin, 2016,61(18):1451-1459 | | [20] | 姜大膀, 刘叶一 . 温室效应会使地球温度上升多高: 关于平衡气候敏感度[J]. 科学通报, 2016,61(7):691-694 |
|
 ),Xiao-Min LYU1,Li ZHOU1,Yu-He JI1
),Xiao-Min LYU1,Li ZHOU1,Yu-He JI1